
Tracey Goodman, WHO/HQ/IVB
AFRO Webinar
June 2, 2021
Update on WHO Interim
recommendations on COVID-19
vaccination of pregnant and
lactating women

2
2
Outline of Presentation
• Background on evidence
• WHO interim recommendations
Pregnancy
Lactation
• Global tracking of policies
• Safety Surveillance
• Tools and resources

3
3
Process for WHO Policy Recommendations on Immunization
Strategic Advisory Group of Experts on Immunization (SAGE)
International experts; independent review of evidence
SAGE video meetings monthly since January 2021
SAGE COVID-19 Working Group/sub-groups (2-3 times/week)
Reports to WHO Director General
www.who.int/groups/strategic-advisory-group-of-experts-on-immunization
Product specific documentation (6 EUL vaccines approved)
Generic guidance for policy-making on COVID-19 vaccines
Further resources – Vaccine Introduction Toolkit
WHO SAGE Roadmap For Prioritizing Uses of COVID-19
Vaccines in the Context of Limited Supply
Other COVID-19 related guidance (e.g. Gender; Influenza)
COVID-19 Technical Documents
materials-19-covidimmunization/-on-experts-of-group-advisory-strategicgroups/int/who.www.

4
4
Background evidence on COVID-19 vaccines and
pregnant/lactating women
• Pregnant and lactating women were not included in the
initial clinical trials of COVID-19 vaccines.
• Studies are underway* but long-term safety data are not yet
available
• Available COVID-19 vaccines are not live virus vaccines
• Data from animal studies and post-introduction surveillance
data have not shown harmful effects in pregnancy
• Vaccine effectiveness likely to be comparable to non-
pregnant women; initial immunogenicity data similar
* https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04754594
https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04765384
https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/safety/vsafepregnancyregistry.html

5
5
WHO Interim Recommendations
In the interim, WHO recommends vaccination in pregnant women
when the benefits of vaccination to the pregnant woman
outweigh the potential risks.
For example:
pregnant women at high risk of exposure to COVID-19
pregnant women with comorbidities that place them in a high-
risk group for severe COVID-19
https://www.who.int/groups/strategic-advisory-group-of-experts-on-immunization/covid-19-materials

6
6
Enabling Pregnant Women’s Choice:
Benefit/Risk Assessment
• Pregnant women should be provided with information about the:
risks of COVID-19 in pregnancy
likely benefits of vaccination in the local epidemiologic context
current limitations of the safety data in pregnant women
• Not necessary to conduct pregnancy testing prior to vaccination
• No need to delay or terminate pregnancy because of vaccination
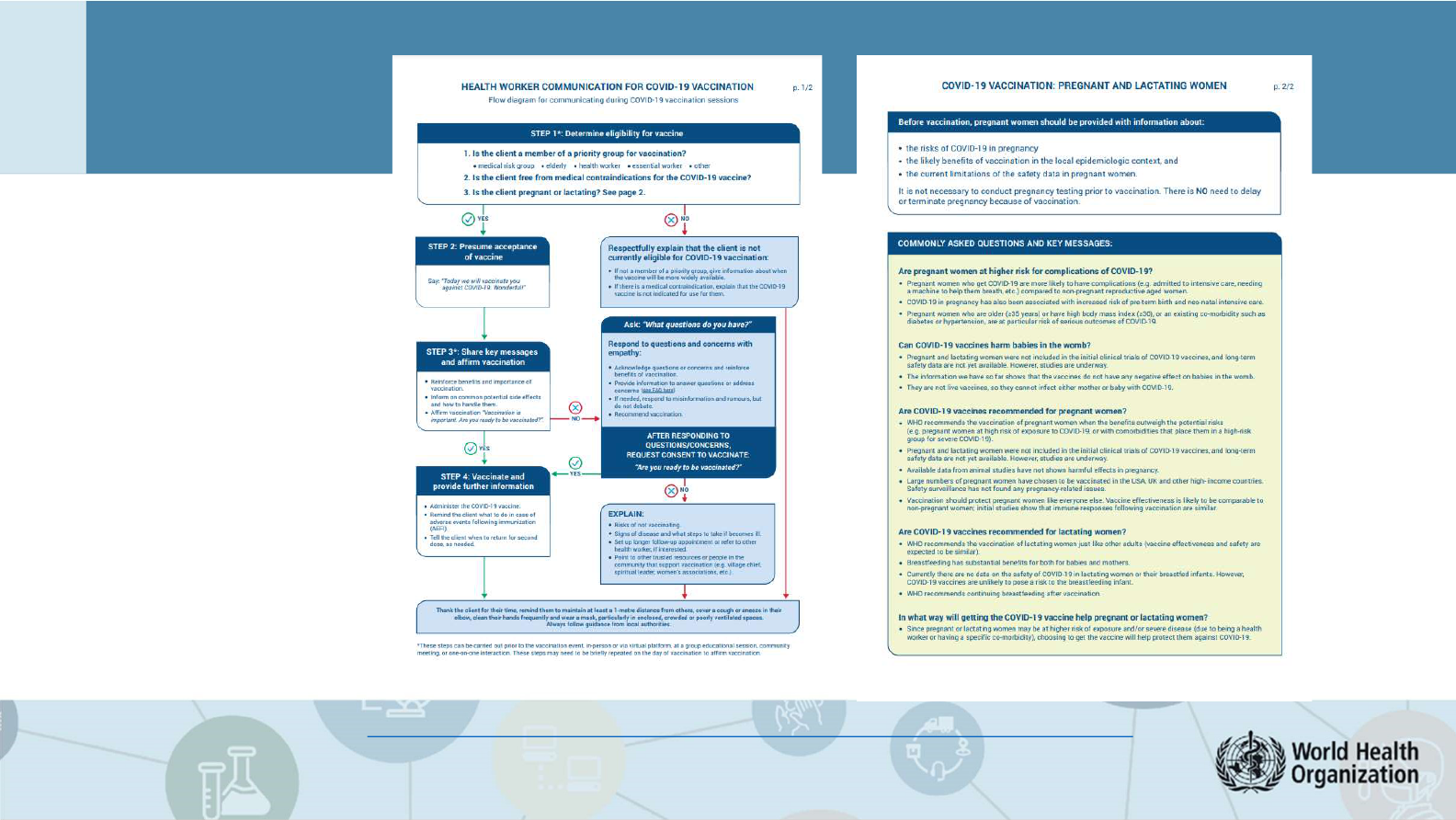
7
7
https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/health-worker-communication-for-covid-19-vaccination-flow-diagram
Health
worker
Job Aid

8
8
WHO Interim recommendations
Breastfeeding and COVID-19 vaccination
• Breastfeeding = substantial health benefits to mother & infant
• Vaccine effectiveness expected to be similar in lactating
women as in other adults
• Currently no data on the safety of COVID-19 vaccine in lactating
women or their breastfed infants
• However, unlikely to pose a risk to the breastfeeding child
• On the basis of these considerations, WHO recommends
vaccination in lactating women as in other adults
• WHO does not recommend to discontinue breastfeeding
because of vaccination
Hdoes ttps://www.who.int/docs/default-source/world-patient-safety-day/health-worker-safety-charter-wpsd-17-september-2020-3-1.pdf
https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240011588
https://www.who.int/teams/immunization-vaccines-and-biologicals/policies/who-recommendations-for-routine-immunization---summary-tables

9
9
Global tracking of national policies on COVID-19
vaccination of pregnant women - DRAFT June 1/21
https://www.comitglobal.org/

10
10
Safety surveillance for pregnant & breastfeeding women
• WHO COVID-19 vaccine safety surveillance
manual: NEW pregnancy module
• Immunization programmes to establish
surveillance of women who have been
vaccinated either intentionally or inadvertently
during pregnancy, and their infants
• Both active and passive surveillance approaches
recommended to assess adverse events following
immunization (AEFI), incl during pregnancy
https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/338400

11
11
Additional resources
• Living systematic reviews on
pregnancy and breastfeeding
https://www.who.int/news/item/01-09-2020-increasing-understanding-of-the-impact-
of-covid-19-for-pregnant-women-and-their-babies
https://nyaspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/nyas.14477
• Q&As: COVID-19 & pregnancy and
childbirth
https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/question-and-
answers-hub/q-a-detail/coronavirus-disease-covid-19-pregnancy-and-childbirth
• Q&As: COVID-19 & breastfeeding
https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/question-and-
answers-hub/q-a-detail/coronavirus-disease-covid-19-breastfeeding
• WHO COVID-19 vaccines
technical documents
https://www.who.int/groups/strategic-advisory-group-of-experts-on-
immunization/covid-19-materials
• WHO Unity Studies
https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-
2019/technical-guidance/early-investigations
• Measuring COVID-19 vaccines effectiveness
• A prospective cohort study investigating maternal,
pregnancy and neonatal outcomes for women and
neonates infected with SARS-CoV-2
• Infographics and videos
https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/question-and-
answers-hub/q-a-detail/coronavirus-disease-covid-19-breastfeeding
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OFGiy6t7k5E
• Scientific briefs
Breastfeeding and COVID-19
https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-2019-nCoV-
Sci_Brief-Breastfeeding-2020.1
Timing of mother-to-child transmission of SARS-CoV-2
https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-2019-nCoV-mother-to-
child-transmission-2021.1

Thank You!
