CAR T-Cell
HER2+ Breast Tumor
HER2
Anti HER2 CAR
transduction
marker
Single chain
variable
fragment
(scFv)
TCR
signaling
domain
Tarek Bacha
1,2
, Tamer Shabaneh
1
, Andrew Stevens
1
and Stanley Riddell
1
1
Fred Hutchinson Cancer Center, Clinical Research Division, Seattle, WA,
2
University of California, Davis, CA
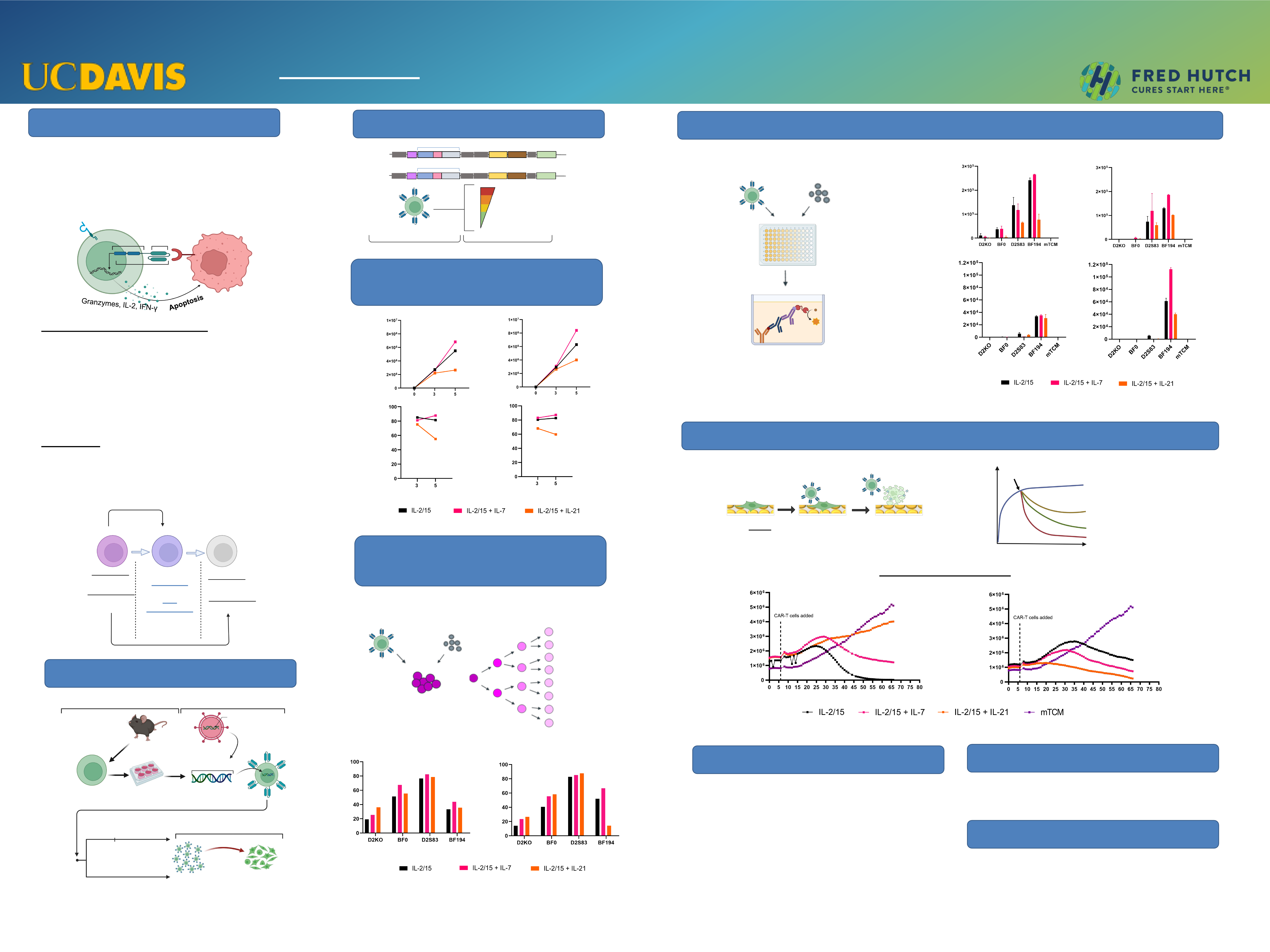
Background
• Expression of a Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR)
in T-lymphocytes is designed to mimic T cell
signaling.
• CAR T-cells can be redirected into patients and
specifically kill tumor cells.
• IL-2 and IL-15 are commonly used for CAR-T cell
expansion in vitro.
• However, strong proliferation and differentiation of CAR
T-cells in vitro can compromise their longevity in vivo.
• Culturing CAR T-cells with IL-7 and IL-21 has been
shown to improve T-cell maintenance and ameliorate
anti-tumor response.
Adding IL-7 or IL-21 in addition to IL-2/IL-15 will
improve CAR expansion, viability and effector function
against HER2 cell lines by promoting a stem-like
phenotype.
Targeting Strategy
Experimental Design
Figure 1: Addition of IL-7 enhances CAR T-
cell growth and viability compared to IL-21
Figure 2: CAR T-cells show lower
proliferation against tumor cells with high
HER2 antigen density
Figure 3: CAR-T cell expansion in the presence of IL-7 improves cytokine production
Acknowledgments
Future Directions
Figure 4: IL-7 and IL-21 improve killing capacity of CAR 359
• To explore how IL-2 and IL-21 interact together.
• To test different cytokine culturing conditions on
affinity tuned CAR T-cells.
Cytokines & T-Cell Differentiation:
Hypothesis:
A)
B)
Figure 3: Supernatant of 24 hours co-cultured CAR T-cells with tumor cells. Ratio of effector to target cells was 2:1. (A) ELISA schematic. After solution
turned yellow post-reaction, absorbance was measured, and cytokine production was then quantified. (B) IFN-γ and (C) IL-2 quantification using ELISA.
Stained with
CellTrace™ Violet
proliferation dye
Restimulation with
tumor cells for 2 days
Fluorescence
Effector : Target
Ratio
0:1 (negative control)
+ Effector Cells
1:3
1:1
3:1
Time (hours)
A)
B)
1) Capture antibody
2) Target antigen
3) Detection antibody
4) Biotinylated antibody
5) Streptavidin
Run ELISA:
IL-2/15 + IL-7 or IL-21
Advantage:
Long-lived
Disadvantage:
No cytotoxic
effect
?
Capacity to
self-renew
and become
less
differentiated
Naïve T-cell
T memory stem cell
Effector T-cell
Advantage:
High cytotoxicity
Disadvantage:
Short-lived
IL-2/15
T
N
T
SCM
T
E
A)
Figure 1: Effect of cytokine cultures on (A) CAR T-cell count and (B) viability.
Total Integrated Intensity
(GRI x um2/image)
Time (hours)
CAR 353
CAR 359
3:1 Effector to Target Ratio
Figure 4: eSight experiment to test CAR T-cell killing when co-cultured with tumor. (A) eSight killing assay schematic. (B) Change in fluorescence
over time for CAR T-cells cultured in different cytokine conditions.
Summary
• Addition of IL-7 enhances CAR T-cell growth, viability,
and cytokine production compared to IL-21.
• CAR T-cells show lower proliferation against tumor
cells with high HER2 antigen density.
• The roles of IL-7 and IL-21 on the killing capacity of
CAR T-cells is still unclear.
HER2 cell lines
Day 0: CD8+ T-cell activation Day 1: CAR Transduction
CAR gene
Insert CAR gene
CAR T-Cell
Acquire lymphocytes
from spleen and lymph
nodes
Amplification
Day 5: Test CAR effector function
Retroviral vector
CD8+
T-cell
Isolate CD8+
T-cells
Activate using plated
anti CD3/CD28 beads
IL-2
IL-15
2 days
3 days
IL-7 or IL-21
Immune Attack
Figure 2: CAR T-cells were collected after 48 hours of coculture. Ratio of effector
to target Cells is 2:1. (A) CTV staining procedure. After each cell division, the dye
intensity of each cell is halved. (B) Percentage of cells that underwent 2 or more
cell divisions.
Adherent D2S83 Cell
Effector cell binds
to target cell
Effector cell-mediated
lysis of target cell
Percentage (%)
Percentage (%)
2+ div
2+ div
B)
CAR 353
CAR T
-cell Count / well
CAR 359
CAR T
-cell Count / well
Viability (%)
Days Post Activation
Viability (%)
Days Post Activation
A) Cell Trace Violet (CTV) Staining Procedure:
B) CTV Analysis
0 div
1 div
2 div
3 div
Tumor Cell Lines
Tumor Cell Lines
CAR 353
CAR 359
High Affinity CAR-T cells
Target Cell Line
D2K0
BF0
D2S83
BF194
HER2 ++
HER2 +
HER2
LOW
HER2
KO
CAR T-cell after
day 5
CAR T-cell after day 5
CAR 353
CAR 359
IFN
-γ (pg/ml)
IFN
-γ (pg/ml)
Tumor Cell Lines
IL-2 (
pg/ml)
IL-2 (
pg/ml)
Tumor Cell Lines
CAR T-cell after
day 5
Restimulation with
tumor cells for 1 day
Collect Supernatant
Total Integrated Intensity
(GRI x um2/image)
Time (hours)
This work is funded by Lyell. The Summer
Undergraduate Research Program is supported in
parts by the Fred Hutch Internship Program and
individual research groups.
Investigating the role of IL-7 and IL-21 during in vitro CAR T-cell culture
pTS293 Thy1.1 (-Ctrl)
pTS191 rHER2.CAR (+Ctrl)
pTS297 1G3 VHVL
pTS398 1G3 VLVH
pTS299 1C9 VHVL
pTS300 1C9 VLVH
pTS345 1A4 VHVL
pTS346 1A4 VLVH
pTS347 1A5 VHVL
pTS348 1A5 VLVH
pTS349 1B1 VHVL
pTS350 1B1 VLVH
pTS351 1B12 VHVL
pTS352 1B12 VLVH
pTS353 1C6 VHVL
pTS354 1C6 VLVH
pTS355 1D2 VHVL
pTS356 1D2 VLVH
pTS357 1E6 VHVL
pTS358 1E6 VLVH
pTS359 1D9 VHVL
pTS360 1D9 VLVH
Thy1.1
myc
myc
mCD8-SP
MP71
V
1
218 V
2
CD28 mCD3ζ mCD19
t
hIgG4sh mCD28
tm
P2A
Thy1.1
*
*
*
*
*
1C6
1D9
pTS293 Thy1.1 (-Ctrl)
pTS191 rHER2.CAR (+Ctrl)
pTS297 1G3 VHVL
pTS398 1G3 VLVH
pTS299 1C9 VHVL
pTS300 1C9 VLVH
pTS345 1A4 VHVL
pTS346 1A4 VLVH
pTS347 1A5 VHVL
pTS348 1A5 VLVH
pTS349 1B1 VHVL
pTS350 1B1 VLVH
pTS351 1B12 VHVL
pTS352 1B12 VLVH
pTS353 1C6 VHVL
pTS354 1C6 VLVH
pTS355 1D2 VHVL
pTS356 1D2 VLVH
pTS357 1E6 VHVL
pTS358 1E6 VLVH
pTS359 1D9 VHVL
pTS360 1D9 VLVH
Thy1.1
myc
myc
mCD8-SP
MP71
V
1
218 V
2
CD28 mCD3ζ mCD19
t
hIgG4sh mCD28
tm
P2A
Thy1.1
*
*
*
*
*
