
Evaluation and Accountability
21 September 2015
INTERPOL HQ, Lyon

Presentation to INTERPOL Lyon 21 September 2015
Outline
1. Evaluation and accountability - overview
2. Evaluation and accountability in UNODC
3. Measuring
GA Resolution 69/237:
Building capacity for the
evaluation of development
activities at the country
level

Presentation to INTERPOL Lyon 21 September 2015
1. Evaluation and Accountability - Overview

Presentation to INTERPOL Lyon 21 September 2015
“In order to succeed, we need actions that can
turn commitments into results. And we need to
monitor, review, and evaluate those results
and make them accessible to policy-makers
and the public.”
“Evaluation is critical for promoting
accountability and for understanding what
we are doing right or wrong.”
UN Secretary-General, Mr. Ban Ki-moon

Presentation to INTERPOL Lyon 21 September 2015

Presentation to INTERPOL Lyon 21 September 2015

Presentation to INTERPOL Lyon 21 September 2015
“Accountability includes achieving objectives and high-quality
results in a timely and cost-effective manner, in fully
implementing and delivering on all mandates to the Secretariat
(…); truthful, objective, accurate and timely reporting on
performance results; (…) all aspects of performance, including a
clearly defined system of rewards and sanctions; and with due
recognition to the important role of the oversight bodies and in full
compliance with accepted recommendations.”
“An assessment, as systematic and impartial as possible (…). It
focuses on expected and achieved accomplishments, examining
the results chain, processes, contextual factors and causality, in
order to understand achievements or the lack thereof.”

Presentation to INTERPOL Lyon 21 September 2015
Accountability
• Accountability: Feedback mechanisms play key role in
International Organisations, Governments as well as
private sector.
Evaluation Quality Assurance
Audit Monitoring
Accountability

Presentation to INTERPOL Lyon 21 September 2015
Sustainable Development Goals

Presentation to INTERPOL Lyon 21 September 2015
SDGs and the cooperation UNODC-INTERPOL
• The agenda for SDGs 2030 includes e.g.:
– Goal 8: Promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic
growth, full and productive employment and decent work for all
• Take immediate and effective measures to eradicate forced labour, end
modern slavery and human trafficking
– Goal 16: Promote peaceful and inclusive societies for sustainable
development, provide access to justice for all and build effective,
accountable and inclusive institutions at all levels
• Significantly reduce illicit financial and arms flows and strengthen the
recover and return of stolen assets and combat organized crime;
• Strengthen national institutions, including through international
cooperation, for building capacity at all levels to prevent violence and
combat terrorism and crime

Presentation to INTERPOL Lyon 21 September 2015
SDGs, evaluation and accountability
• Evaluation and accountability mainstreamed in SDGs - the
follow-up and review process will be:
– Rigorous and based on evidence, informed by country-led evaluations;
– Requiring enhanced capacity-building support for developing countries,
including the strengthening of national data systems and evaluation programs
• Evaluation and accountability mainstreamed in Goals:
– Goal 16.6: Develop effective, accountable and transparent
institutions at all levels.
“We commit to engage in systematic follow-up and review of
implementation of this Agenda (…). Operating at the national, regional
and global level, it will promote accountability to our citizens, support
effective international cooperation (…) and foster exchanges of best
practices and mutual learning” (p. 27)

Presentation to INTERPOL Lyon 21 September 2015
Lessons learned from Millennium Development Goals
“In this regard, the Office of Internal Oversight Services makes one
recommendation for consideration, namely, that the Secretary-General
formulate an overarching strategy and action plan to support coherent,
coordinated and timely monitoring and evaluation, together with relevant
capacity development needed to support decision-making, (…).”
“Evaluation (…) has the potential to serve as a bridge between
monitoring and accountability at key levels and junctures of
deliberation and decision-making by stakeholders. This will
enhance decision makers’ ability to make necessary
improvements and mid-course corrections (…).
“one key lesson learned is that the post-2015 sustainable
development goals (…) would benefit from a clear,
overarching framework of monitoring and evaluation
objectives (…).”

Presentation to INTERPOL Lyon 21 September 2015
2. Evaluation and Accountability in UNODC

Presentation to INTERPOL Lyon 21 September 2015
“By increasing transparency, and enhancing
learning and critical thinking, evaluation can
empower people, and in this way support
positive change. (…) In short, evaluation can
help us to provide clarity in a complex, inter-
connected world.“
Director-General/Executive Director UNOV/UNODC,
Mr. Yury Fedotov

Presentation to INTERPOL Lyon 21 September 2015
The Independent Evaluation Unit – timeline
Before 2010
• Sporadic evaluations
• Internal reporting lines
2010
• Evaluation Unit dissolved
• Member States’ Resolutions for fully independent evaluation
• Institutionalization of the Evaluation Function
After 2010
• Independent Unit - reporting lines to MS and ED
• Full coverage of all projects and programmes
• Knowledge and strategic products
• Evaluation capacity building for external stakeholders

Presentation to INTERPOL Lyon 21 September 2015
The Independent Evaluation Unit – current status
• Evaluation Function:
– Team: 3 professional and 1 support staff
– Reporting to Member States and the Executive Director
• Premise: All UNODC interventions are evaluated
every four years and/or before completion
– Final evaluations: six months before the end of the
interventions; focus on accountability and performance
– Mid-term evaluations: For continuing interventions
every four years with a focus on learning and improving
Presentation to INTERPOL Lyon 21 September 2015
Evaluation in UNODC
Evaluation
in UNODC
Capacity
Building
Evaluation
results
Knowledge
products

Presentation to INTERPOL Lyon 21 September 2015
Evaluation portfolio in UNODC - examples
UNODC
Interventions
Around 70
Programmes
(geographic and
thematic)
Around 260 Projects
Policies, strategies,
etc.
Types of
evaluations
In depth evaluations
(four - eight annually)
Independent Project
Evaluations (20-25
annually)
Knowledge
Products
Portfolio management
Evaluation Meta
Analysis
Recommendations
database; etc.
Presentation to INTERPOL Lyon 21 September 2015
Evaluation in the project cycle
Strategy
Setting
Programme
development
Resource
Mobilisation
Implementation
& Monitoring
Evaluation
Project/
Programme
Cycle
Evaluation results
and lessons learned
used for strategy
setting
Plan, budget and
define scope of
evaluation(s) –
consultations with
IEU
2-3% of
overall
budget
reserved for
evaluation
Generation of
data for
future
evaluation
Implementation
of evaluation at
HQ and FO

Presentation to INTERPOL Lyon 21 September 2015
Percentage of completed projects evaluated
75%
22%
3%
Evaluation status of completed/operationally completed
projects 2014
Projects evaluated/planned to
evaluate in 2015
Projects not evaluated
Evaluations discontinued

Presentation to INTERPOL Lyon 21 September 2015
Fully evaluated completed projects 2011-2014
2011 2012 2013 2014
Series1
40.00% 51.00% 52.00% 75.00%
0.00%
10.00%
20.00%
30.00%
40.00%
50.00%
60.00%
70.00%
80.00%
Percentage of completed/operationally
completed projects evaluated

Presentation to INTERPOL Lyon 21 September 2015
Evaluation and Accountability – services
Evaluation and Accountability
Evaluation
Capacity
Training of
internal and
external
stakeholders
Development
evaluation
norms and
standards
Evaluation
Results
Project,
programmatic,
corporate and
thematic
evaluations
Ex-Ante
evaluations
Knowledge
Products
Meta
analytical,
strategic
reports
Portfolio
assessments
Accountability
frameworks

Presentation to INTERPOL Lyon 21 September 2015
Evaluation Knowledge Management in UNODC
• UNODC Evaluation Database (also online:
http://www.unodc.org/unodc/en/evaluation/index.html)
• Recommendations database (internal)
• Lessons Learned database (interal)
• Automated Evaluation Recommendation follow-up system

Presentation to INTERPOL Lyon 21 September 2015
Evaluation Application 1/2

Presentation to INTERPOL Lyon 21 September 2015
Evaluation Application 2/2

Presentation to INTERPOL Lyon 21 September 2015
Portfolio Analysis

Presentation to INTERPOL Lyon 21 September 2015
Meta Analysis
100
evaluations
105
evaluators
/ experts
1003
Recomm-
endations
445
Lessons
Learned
1 Meta
Analysis
https://www.unodc.org/unodc/en/
evaluation/evaluation.html
Presentation to INTERPOL Lyon 21 September 2015
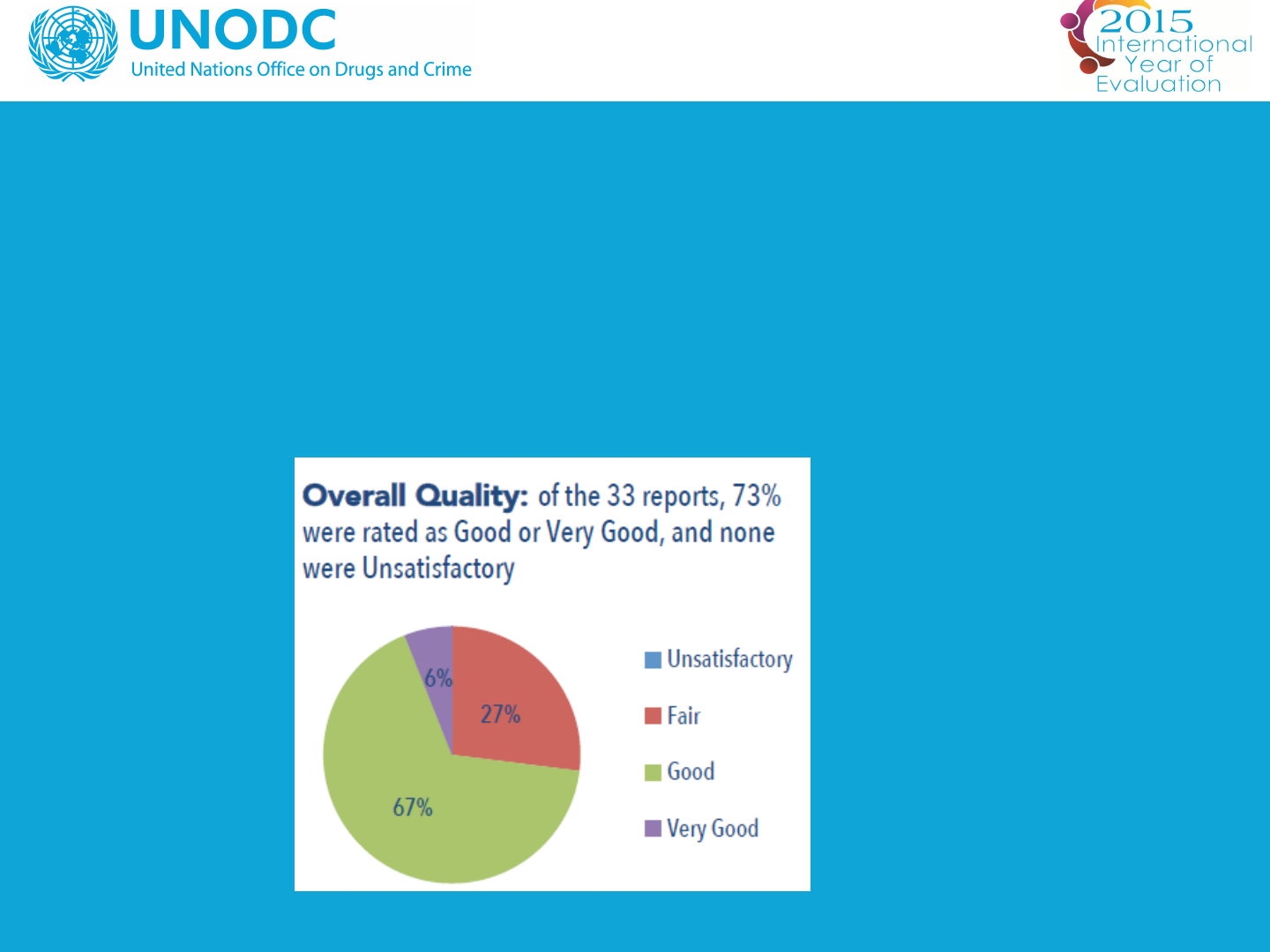
Quality of evaluation reports
• Independent quality assessment of all evaluation reports
January 2014 to June 2015
• In line with best practices in other UN Organisations (e.g.
UNWOMEN; UNDP; UNFPA; etc.)

Presentation to INTERPOL Lyon 21 September 2015
Feedback survey to Member States and Project Managers
1
2
3

Presentation to INTERPOL Lyon 21 September 2015
Services – evaluation capacity building (external)
• Capacity Building for external stakeholders:
– Member States (in line with GA Resolution on evaluation capacity
building)
– Partner Organisations
– NGOs/CSOs
• Tailored trainings on evaluation and accountability
• Trainings in relation to substantive topics
• Innovative approaches: cost-sharing evaluation positions
for mutual learning
GA Resolution 69/237: "Capacity building for the evaluation of
development activities at the country level”

Presentation to INTERPOL Lyon 21 September 2015
3. Measuring
“You cannot manage what you cannot measure”

Presentation to INTERPOL Lyon 21 September 2015
Elements of accountability in implementation
1. Planning
Specific Results
Framework
Plan for sustainability
Operational
implementation plan
Risk Assessment
Clear and specific
indicators
Stakeholder
engagement and
communication
strategy
2. Performance
Results-based data
collection plan
Performance
measurement
Evaluation capacity
building
Ex ante evaluations
Mid-term evaluations
after 2 and every 4
years
3. Reporting
Financial and
Performance Reporting
Final Outcome (Impact)
evaluation

Presentation to INTERPOL Lyon 21 September 2015
Planning-phase
Stakeholder
engagement
and
communicati
on strategy
Clear and
specific
indicators
Risk
Assessment
Operational
implementati
on plan
Plan for
sustainability
Specific
Results
Framework

Presentation to INTERPOL Lyon 21 September 2015
Indicators – a core facet of accountability
• Qualitative or quantitative variables to measure
achievements
• Consultative process
• Baseline development
• Monitor progress at all levels of results-based systems -
with respect to inputs, outputs, outcomes and goals
• Specific, measurable, attainable, realistic and time-bound
Indicators
• Key question: Are we moving toward achieving our desired
outcomes?

Presentation to INTERPOL Lyon 21 September 2015
Illustrations of Indicators
• Objective: “Through international cooperation, Norway will help to
make countries and organisations better equipped to prevent,
respond to and combat global security challenges”
– Percentage of trained Law Enforcement personnel uses knowledge provided
by UNODC/INTERPOL for border control in region X by 2017.
– Number of terrorism-related arrests in region X as a result of improved
cooperation of Member States through UNODC/INTERPOL intervention XY.
• Partnership indicators:
– Number of new projects developed through UNODC/INTERPOL partnership by
2020.
– Clear roles and responsibilities of all partners identified in the Joint Action Plan.
Presentation to INTERPOL Lyon 21 September 2015
Performance/Implementation-phase
Mid-term
evaluations
after 2 and
every 4 years
Ex ante
evaluations
Evaluation
capacity
building
Performance
measurement
Results-based
data collection
plan
Presentation to INTERPOL Lyon 21 September 2015
Reporting
Final Outcome (Impact) evaluation
Financial and Performance
Reporting based on evidence

Presentation to INTERPOL Lyon 21 September 2015
Example: results of evaluations (crime portfolio)
Intelligence
and data
sharing
Collaboration
with partners
Engagement
at highest
level
Communi-
cation
Measuring
impact
Human
rights and
Gender
Collaboration
with IOs and
CSOs positive
impact
30 Evaluations
40 independent
evaluators

Presentation to INTERPOL Lyon 21 September 2015
What we can offer in building this partnership
1. Accountability
to stakeholders
2. Management
vis-á-vis results
3. Assessment of
provisions for
sustainable
partnership
Development of joint
products, e.g.
evaluations; knowledge
products; etc.
Development or transfer
and application of
norms, standards,
instruments, etc.
Ex-ante evaluations of
the partnership and
informing strategic
development

Presentation to INTERPOL Lyon 21 September 2015
“Evaluation is not easy. Nor is it
popular. But it is essential.”
UN Secretary-General, Ban Ki-moon, 9 March 2015

