
_______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use Depo-
Provera Contraceptive Injection (Depo-Provera CI) safely and effectively.
See full prescribing information for Depo-Provera Contraceptive
Injection.
DEPO-PROVERA CI (medroxyprogesterone acetate) injectable
suspension, for intramuscular use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1959
WARNING: LOSS OF BONE MINERAL DENSITY
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
• Women who use Depo-Provera Contraceptive Injection may lose
significant bone mineral density. Bone loss is greater with
increasing duration of use and may not be completely reversible.
(5.1)
• It is unknown if use of Depo-Provera Contraceptive Injection during
adolescence or early adulthood, a critical period of bone accretion,
will reduce peak bone mass and increase the risk for osteoporotic
fracture in later life. (5.1)
• Depo-Provera Contraceptive Injection should not be used as a long-
term birth control method (i.e., longer than 2 years) unless other
birth control methods are considered inadequate. (5.1)
----------------------------RECENT MAJOR CHANGES--------------------------
Warnings and Precautions; Loss of Bone Mineral Density (5.1) 10/2010
------------------------INDICATIONS AND USAGE------------------------
Depo-Provera CI is a progestin injectable contraceptive indicated only for
the prevention of pregnancy. (1)
-----------------------DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION----------------
The recommended dose is 150 mg of Depo-Provera CI every 3 months (13
weeks) administered by deep, IM injection in the gluteal or deltoid muscle.
(2.1)
----------------------------DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS---------------
Vials containing sterile aqueous suspension: 150 mg per mL (3)
Prefilled syringes: prefilled syringes are available packaged with 22-gauge
x 1 1/2 inch BD SafetyGlide Needles (3)
------------------------------------CONTRAINDICATIONS-------------------------
• Known or suspected pregnancy or as a diagnostic test for pregnancy. (4)
• Active thrombophlebitis, or current or past history of thromboembolic
disorders, or cerebral vascular disease. (4)
• Known or suspected malignancy of breast. (4)
• Known hypersensitivity to Depo-Provera CI (medroxyprogesterone
acetate or any of its other ingredients). (4)
• Significant liver disease. (4)
• Undiagnosed vaginal bleeding. (4)
------------------------------WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS-----------------
Thromboembolic Disorders: Discontinue Depo-Provera CI in patients
who develop thrombosis (5.2)
Cancer Risks: Monitor women with breast nodules or a strong family
history of breast cancer carefully. (5.3)
Ectopic Pregnancy: Consider ectopic pregnancy if a woman using
Depo-Provera CI becomes pregnant or complains of severe abdominal
pain. (5.4)
Anaphylaxis and Anaphylactoid Reactions: Provide emergency medical
treatment. (5.5)
Liver Function: Discontinue Depo-Provera CI if jaundice or
disturbances of liver function develop. (5.6)
Carbohydrate Metabolism: Monitor diabetic patients carefully. (5.11)
----------------------------------ADVERSE REACTIONS---------------------------
Most common adverse reactions (incidence >5%) are: menstrual irregularities
(bleeding or spotting) 57% at 12 months, 32% at 24 months, abdominal
pain/discomfort 11%, weight gain > 10 lbs at 24 months 38%, dizziness 6%,
headache 17%, nervousness 11%, decreased libido 6%. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Pfizer Inc. at
1-800-438-1985 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
-----------------------------------DRUG INTERACTIONS--------------------------
Drugs or herbal products that induce certain enzymes, including CYP3A4,
may decrease the effectiveness of contraceptive drug products. Counsel
patients to use a back-up method or alternative method of contraception when
enzyme inducers are used with Depo-Provera CI. (7.1)
-------------------------------USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS----------------
Nursing Mothers: Detectable amounts of drug have been identified in the
milk of mothers receiving Depo-Provera CI. (8.2)
Pediatric: Depo-Provera CI is not indicated before menarche. (8.3)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-
approved patient labeling.
Revised: 10/2010
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
WARNING
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Prevention of Pregnancy
2.2 Switching from other Methods of Contraception
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Loss of Bone Mineral Density
5.2 Thromboembolic Disorders
5.3 Cancer Risks
5.4 Ectopic Pregnancy
5.5 Anaphylaxis and Anaphylactoid Reaction
5.6 Liver Function
5.7 Convulsions
5.8 Depression
5.9 Bleeding Irregularities
5.10 Weight Gain
5.11 Carbohydrate Metabolism
5.12 Lactation
5.13 Fluid Retention
5.14 Return of Fertility
5.15 Protection Against Sexually Transmitted Diseases
5.16 Pregnancy
5.17 Monitoring
5.18 Interference with Laboratory Tests
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Post-marketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Changes in Contraceptive Effectiveness Associated with Co-
Administration of Other Products
7.2 Aminoglutethimide
7.3 Laboratory Test Interactions
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Nursing Mothers
8.3 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Contraception
14.2 BMD Changes in Adult Women
14.3 BMD Changes in Adolescent Females (12-18 years of age)
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
*Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information
are not listed.
1
This label may not be the latest approved by FDA.
For current labeling information, please visit https://www.fda.gov/drugsatfda

Full Prescribing Information
WARNING: LOSS OF BONE MINERAL DENSITY
Women who use Depo-Provera Contraceptive Injection may lose significant bone mineral density.
Bone loss is greater with increasing duration of use and may not be completely reversible.
It is unknown if use of Depo-Provera Contraceptive Injection during adolescence or early adulthood, a
critical period of bone accretion, will reduce peak bone mass and increase the risk for osteoporotic
fracture in later life.
Depo-Provera Contraceptive Injection should not be used as a long-term birth control method
(i.e., longer than 2 years) unless other birth control methods are considered inadequate. (See Warnings
and Precautions (5.1)).
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Depo-Provera CI is indicated only for the prevention of pregnancy. The loss of bone mineral density
(BMD) in women of all ages and the impact on peak bone mass in adolescents should be considered,
along with the decrease in BMD that occurs during pregnancy and/or lactation, in the risk/benefit
assessment for women who use Depo-Provera CI long-term [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Prevention of Pregnancy
Both the 1 mL vial and the 1 mL prefilled syringe of Depo-Provera CI should be vigorously shaken just
before use to ensure that the dose being administered represents a uniform suspension.
The recommended dose is 150 mg of Depo-Provera CI every 3 months (13 weeks) administered by deep IM
injection in the gluteal or deltoid muscle. Depo-Provera CI should not be used as a long-term birth control
method (i.e. longer than 2 years) unless other birth control methods are considered inadequate. Dosage does
not need to be adjusted for body weight [See Clinical Studies (14.1)].
To ensure the patient is not pregnant at the time of the first injection, the first injection should be given
ONLY during the first 5 days of a normal menstrual period; ONLY within the first 5-days postpartum if not
breast-feeding; and if exclusively breast-feeding, ONLY at the sixth postpartum week. If the time interval
between injections is greater than 13 weeks, the physician should determine that the patient is not pregnant
before administering the drug. The efficacy of Depo-Provera CI depends on adherence to the dosage
schedule of administration.
2.2 Switching from other Methods of Contraception
When switching from other contraceptive methods, Depo-Provera CI should be given in a manner that
ensures continuous contraceptive coverage based upon the mechanism of action of both methods,
(e.g., patients switching from oral contraceptives should have their first injection of Depo-Provera CI on the
day after the last active tablet or at the latest, on the day following the final inactive tablet).
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Sterile Aqueous suspension: 150mg/ml
Prefilled syringes are available packaged with 22-gauge x 1 1/2 inch BD SafetyGlide
TM
Needles.
2
This label may not be the latest approved by FDA.
For current labeling information, please visit https://www.fda.gov/drugsatfda

4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
The use of Depo-Provera CI is contraindicated in the following conditions:
• Known or suspected pregnancy or as a diagnostic test for pregnancy.
• Active thrombophlebitis, or current or past history of thromboembolic disorders, or cerebral vascular
disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
• Known or suspected malignancy of breast [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
• Known hypersensitivity to Depo-Provera CI (medroxyprogesterone acetate) or any of its other
ingredients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
• Significant liver disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
• Undiagnosed vaginal bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Loss of Bone Mineral Density
Use of Depo-Provera CI reduces serum estrogen levels and is associated with significant loss of bone
mineral density (BMD). This loss of BMD is of particular concern during adolescence and early
adulthood, a critical period of bone accretion. It is unknown if use of Depo-Provera CI by younger
women will reduce peak bone mass and increase the risk for osteoporotic fracture in later life.
After discontinuing Depo-Provera CI in adolescents, mean BMD loss at total hip and femoral neck did not
fully recover by 60 months (240 weeks) post-treatment [see Clinical Studies (14.3)]. Similarly, in adults,
there was only partial recovery of mean BMD at total hip, femoral neck and lumbar spine towards
baseline by 24 months post-treatment. [See Clinical Studies (14.2).]
Depo-Provera CI should not be used as a long-term birth control method (i.e., longer than 2 years) unless
other birth control methods are considered inadequate. BMD should be evaluated when a woman needs to
continue to use Depo-Provera CI long-term. In adolescents, interpretation of BMD results should take
into account patient age and skeletal maturity.
Other birth control methods should be considered in the risk/benefit analysis for the use of Depo-Provera CI
in women with osteoporosis risk factors. Depo-Provera CI can pose an additional risk in patients with risk
factors for osteoporosis (e.g., metabolic bone disease, chronic alcohol and/or tobacco use, anorexia nervosa,
strong family history of osteoporosis or chronic use of drugs that can reduce bone mass such as
anticonvulsants or corticosteroids). Although there are no studies addressing whether calcium and Vitamin
D may lessen BMD loss in women using Depo-Provera CI, all patients should have adequate calcium and
Vitamin D intake.
5.2 Thromboembolic Disorders
There have been reports of serious thrombotic events in women using Depo-Provera CI (150 mg). However,
Depo-Provera CI has not been causally associated with the induction of thrombotic or thromboembolic
disorders. Any patient who develops thrombosis while undergoing therapy with Depo-Provera CI should
discontinue treatment unless she has no other acceptable options for birth control.
Do not readminister Depo-Provera CI pending examination if there is a sudden partial or complete loss of
vision or if there is a sudden onset of proptosis, diplopia, or migraine. Do not readminister if examination
reveals papilledema or retinal vascular lesions.
5.3 Cancer Risks
Breast Cancer
Women who currently have or have had breast cancer should not use hormone contraceptives, including
3
This label may not be the latest approved by FDA.
For current labeling information, please visit https://www.fda.gov/drugsatfda
Depo-Provera CI, because breast cancer may be hormonally sensitive. Women with a strong family history
of breast cancer or who have breast nodules should be monitored with particular care.
A pooled analysis from two case-control studies, the World Health Organization Study and the New
Zealand Study, reported the relative risk (RR) of breast cancer for women who had ever used Depo-
Provera CI as 1.1 (95% confidence interval [CI] 0.97 to 1.4). Overall, there was no increase in risk with
increasing duration of use of Depo-Provera CI. The RR of breast cancer for women of all ages who had
initiated use of Depo-Provera CI within the previous 5 years was estimated to be 2.0 (95% CI 1.5 to 2.8).
The World Health Organization Study, a component of the pooled analysis described above, showed an
increased RR of 2.19 (95% CI 1.23 to 3.89) of breast cancer associated with use of Depo-Provera CI in
women whose first exposure to drug was within the previous 4 years and who were under 35 years of age.
However, the overall RR for ever-users of Depo-Provera CI was 1.2 (95% CI 0.96 to 1.52).
The National Cancer Institute reports an average annual incidence rate for breast cancer for US women,
all races, age 15 to 34 years of 8.7 per 100,000. A RR of 2.19, thus, increases the possible risk from 8.7 to
19.0 cases per 100,000 women.
Cervical Cancer
A statistically nonsignificant increase in RR estimates of invasive squamous-cell cervical cancer has been
associated with the use of Depo-Provera CI in women who were first exposed before the age of 35 years
(RR 1.22 to 1.28 and 95% CI 0.93 to 1.70). The overall, nonsignificant relative rate of invasive
squamous-cell cervical cancer in women who ever used DEPO-PROVERA CI was estimated to be 1.11
(95% CI 0.96 to 1.29). No trends in risk with duration of use or times since initial or most recent exposure
were observed.
Other Cancers
Long-term case-controlled surveillance of users of Depo-Provera CI found no overall increased risk of
ovarian or liver cancer.
5.4 Ectopic Pregnancy
Be alert to the possibility of an ectopic pregnancy among women using Depo-Provera CI who become
pregnant or complain of severe abdominal pain.
5.5 Anaphylaxis and Anaphylactoid Reaction
Anaphylaxis and anaphylactoid reaction have been reported with the use of Depo-Provera CI. Institute
emergency medical treatment if an anaphylactic reaction occurs.
5.6 Liver Function
Discontinue Depo-Provera CI use if jaundice or acute or chronic disturbances of liver function develop. Do
not resume use until markers of liver function return to normal and Depo-Provera CI causation has been
excluded.
5.7 Convulsions
There have been a few reported cases of convulsions in patients who were treated with Depo-Provera CI.
Association with drug use or pre-existing conditions is not clear.
4
This label may not be the latest approved by FDA.
For current labeling information, please visit https://www.fda.gov/drugsatfda
5.8 Depression
Monitor patients who have a history of depression and do not readminister Depo-Provera CI if depression
recurs.
5.9 Bleeding Irregularities
Most women using Depo-Provera CI experience disruption of menstrual bleeding patterns. Altered
menstrual bleeding patterns include amenorrhea, irregular or unpredictable bleeding or spotting,
prolonged spotting or bleeding, and heavy bleeding. Rule out the possibility of organic pathology if
abnormal bleeding persists or is severe, and institute appropriate treatment.
As women continue using Depo-Provera CI, fewer experience irregular bleeding and more experience
amenorrhea. In clinical studies of Depo-Provera CI, by month 12 amenorrhea was reported by 55% of
women, and by month 24, amenorrhea was reported by 68% of women using Depo-Provera CI
.
5.10 Weight Gain
Women tend to gain weight while on therapy with Depo-Provera CI. From an initial average body weight of
136 lb, women who completed 1 year of therapy with Depo-Provera CI gained an average of 5.4 lb. Women
who completed 2 years of therapy gained an average of 8.1 lb. Women who completed 4 years gained an
average of 13.8 lb. Women who completed 6 years gained an average of 16.5 lb. Two percent of women
withdrew from a large-scale clinical trial because of excessive weight gain.
5.11 Carbohydrate Metabolism
A decrease in glucose tolerance has been observed in some patients on Depo-Provera CI treatment. Monitor
diabetic patients carefully while receiving Depo-Provera CI.
5.12 Lactation
Detectable amounts of drug have been identified in the milk of mothers receiving Depo-Provera CI. In
nursing mothers treated with Depo-Provera CI, milk composition, quality, and amount are not adversely
affected. Neonates and infants exposed to medroxyprogesterone from breast milk have been studied for
developmental and behavioral effects through puberty. No adverse effects have been noted.
5.13 Fluid Retention
Because progestational drugs including Depo-Provera CI may cause some degree of fluid retention, monitor
patients with conditions that might be influenced by this condition, such as epilepsy, migraine, asthma, and
cardiac or renal dysfunction.
5.14 Return of Fertility
Return to ovulation and fertility is likely to be delayed after stopping Depo-Provera CI. In a large US study
of women who discontinued use of Depo-Provera CI to become pregnant, data are available for 61% of
them. Of the 188 women who discontinued the study to become pregnant, 114 became pregnant. Based on
Life-Table analysis of these data, it is expected that 68% of women who do become pregnant may conceive
within 12 months, 83% may conceive within 15 months, and 93% may conceive within 18 months from the
last injection. The median time to conception for those who do conceive is 10 months following the last
injection with a range of 4 to 31 months, and is unrelated to the duration of use. No data are available for
39% of the patients who discontinued Depo-Provera CI to become pregnant and who were lost to follow-up
or changed their mind.
5.15 Sexually Transmitted Diseases
Patients should be counseled that Depo-Provera CI does not protect against HIV infection (AIDS) and other
sexually transmitted diseases.
5
This label may not be the latest approved by FDA.
For current labeling information, please visit https://www.fda.gov/drugsatfda
5.16 Pregnancy
Although Depo-Provera CI should not be used during pregnancy, there appears to be little or no increased
risk of birth defects in women who have inadvertently been exposed to medroxyprogesterone acetate
injections in early pregnancy. Neonates exposed to medroxyprogesterone acetate in-utero and followed to
adolescence showed no evidence of any adverse effects on their health including their physical, intellectual,
sexual or social development.
5.17 Monitoring
A woman who is taking hormonal contraceptive should have a yearly visit with her healthcare provider for a
blood pressure check and for other indicated healthcare.
5.18 Interference with Laboratory Tests
The use of Depo-Provera CI may change the results of some laboratory tests, such as coagulation factors,
lipids, glucose tolerance, and binding proteins. [See Drug Interactions (7.3)].
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following important adverse reactions observed with the use of Depo-Provera CI are discussed in greater
detail in the Warnings and Precautions section (5):
• Loss of Bone Mineral Density [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
•
Thromboembolic disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
•
Breast Cancer [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
•
Anaphylaxis and Anaphylactoid Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
• Bleeding Irregularities[see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
• Weight Gain [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the
clinical studies of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may
not reflect the rates observed in practice.
In the two pivotal clinical trials with Depo-Provera CI, over 3,900 women, who were treated for up to
7 years, reported the following adverse reactions, which may or may not be related to the use of Depo-
Provera CI. The population studied ranges in age from 15 to 51 years, of which 46% were White, 50% Non-
White, and 4.9% Unknown race. The patients received 150 mg Depo-Provera CI every 3-months (90 days).
The median study duration was 13 months with a range of 1-84 months. Fifty eight percent of patients
remained in the study after 13 months and 34% after 24 months.
6
This label may not be the latest approved by FDA.
For current labeling information, please visit https://www.fda.gov/drugsatfda

Table 1 Adverse Reactions that Were Reported by More than 5% of Subjects
Body System* Adverse Reactions (Incidence (%))
Body as a Whole
Headache (16.5%)
Abdominal pain/discomfort (11.2%)
Metabolic/Nutritional
Increased weight> 10 lbs at 24 months (37.7%)
Nervous
Nervousness (10.8%)
Dizziness (5.6%)
Libido decreased (5.5%)
Urogenital
Menstrual irregularities:
bleeding (57.3% at 12 months, 32.1% at 24 months)
amenorrhea (55% at 12 months, 68% at 24 months)
* Body System represented from COSTART medical dictionary.
Table 2 Adverse Reactions that Were Reported by between 1 and 5% of Subjects
Body System* Adverse Reactions (Incidence (%))
Body as a Whole
Asthenia/fatigue (4.2%)
Backache (2.2%)
Dysmenorrhea (1.7%)
Hot flashes (1.0%)
Digestive
Nausea (3.3%)
Bloating (2.3%)
Metabolic/Nutritional
Edema (2.2%)
Musculoskeletal
Leg cramps (3.7%)
Arthralgia (1.0%)
Nervous
Depression (1.5%)
Insomnia (1.0%)
Skin and Appendages
Acne (1.2%),
No hair growth/alopecia (1.1%)
Rash (1.1%)
Urogenital
Leukorrhea (2.9%)
Breast pain (2.8%)
Vaginitis (1.2%)
Body System represented from COSTART medical dictionary.
Adverse reactions leading to study discontinuation in ≥ 2% of subjects: bleeding (8.2%), amenorrhea
(2.1%), weight gain (2.0%)
Post-marketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of Depo-Provera CI.
Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always
possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
There have been cases of osteoporosis including osteoporotic fractures reported post-marketing in patients
taking Depo-Provera CI.
7
6.2
This label may not be the latest approved by FDA.
For current labeling information, please visit https://www.fda.gov/drugsatfda
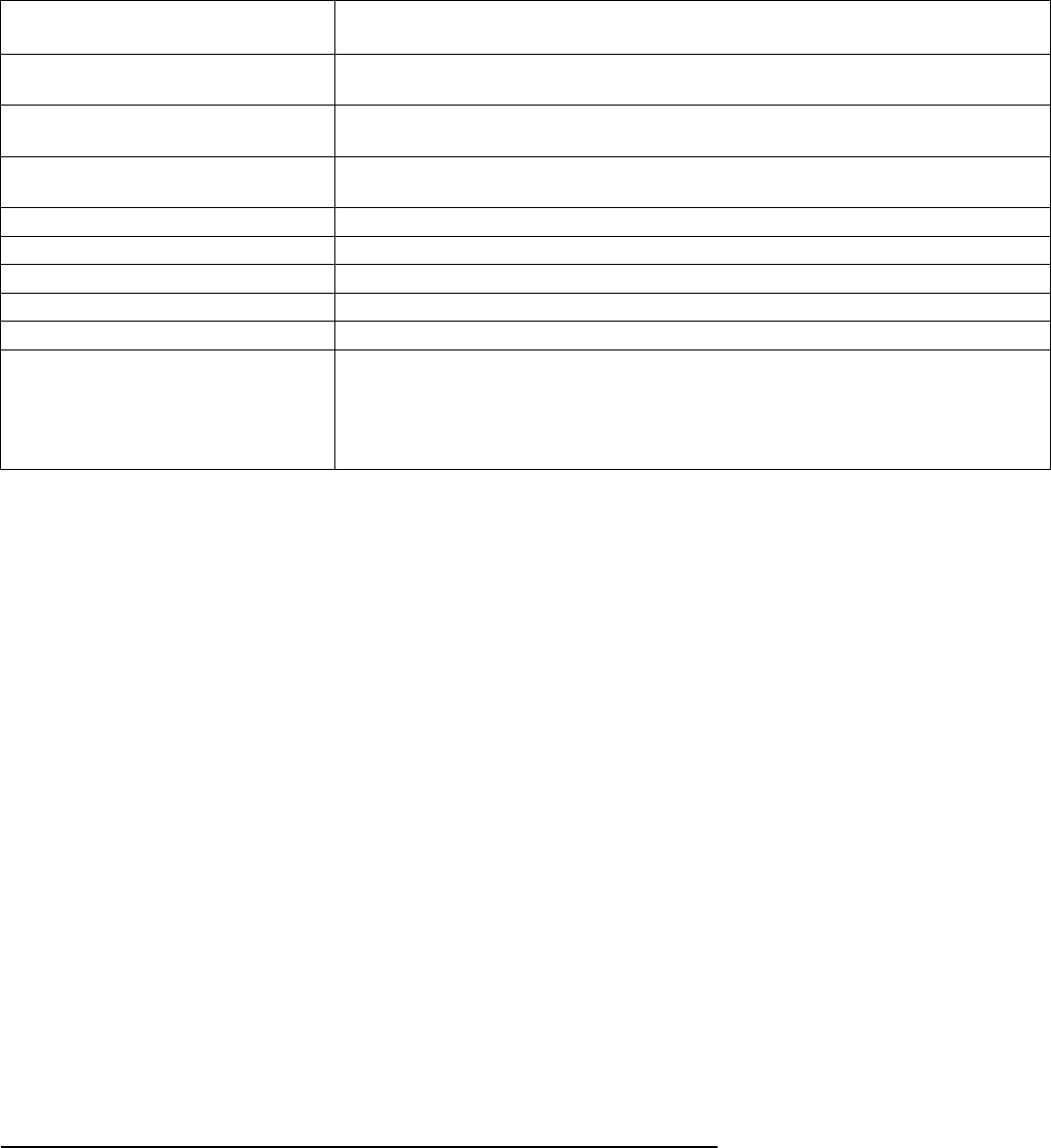
Table 3 Adverse Reactions Reported during Post-Marketing Experience
Body System Adverse Reactions
Body as a Whole Chest pain, Allergic reactions, Fever, Pain at injection site, Chills, Axillary
swelling
Cardiovascular Syncope, Tachycardia, Thrombophlebitis, Deep vein thrombosis,
Pulmonary embolus, Varicose veins
Digestive Changes in appetite, Gastrointestinal disturbances, Jaundice, Excessive
thirst, Rectal bleeding
Hematologic and Lymphatic
Anemia, Blood dyscrasia
Musculoskeletal
Osteoporosis
Nervous
Paralysis, Facial palsy, Paresthesia, Drowsiness
Respiratory
Dyspnea and asthma, Hoarseness
Skin and Appendages
Hirsutism, Excessive sweating and body odor, Dry skin, Scleroderma
Urogenital
Cervical cancer, Breast cancer, Lack of return to fertility, Unexpected
pregnancy, Prevention of lactation, Changes in breast size, Breast lumps
or nipple bleeding, Galactorrhea, Melasma, Chloasma, Increased libido,
Uterine hyperplasia, Genitourinary infections, Vaginal cysts, Dyspareunia
* Body System represented from COSTART medical dictionary.
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Changes in Contraceptive Effectiveness Associated with Co-Administration of
Other Products
If a woman on hormonal contraceptives takes a drug or herbal product that induces enzymes, including
CYP3A4, that metabolize contraceptive hormones, counsel her to use additional contraception or a different
method of contraception. Drugs or herbal products that induce such enzymes may decrease the plasma
concentrations of contraceptive hormones, and may decrease the effectiveness of hormonal contraceptives.
Some drugs or herbal products that may decrease the effectiveness of hormonal contraceptives include:
• barbiturates
• bosentan
• carbamazepine
• felbamate
• griseofulvin
• oxcarbazepine
• phenytoin
• rifampin
• St. John’s wort
• topiramate
HIV protease inhibitors and non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors: Significant changes (increase or
decrease) in the plasma levels of progestin have been noted in some cases of co-administration of HIV
protease inhibitors. Significant changes (increase or decrease) in the plasma levels of the progestin have
been noted in some cases of co-administration with non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors.
8
This label may not be the latest approved by FDA.
For current labeling information, please visit https://www.fda.gov/drugsatfda

Antibiotics: There have been reports of pregnancy while taking hormonal contraceptives and antibiotics, but
clinical pharmacokinetic studies have not shown consistent effects of antibiotics on plasma concentrations
of synthetic steroids.
Consult the labeling of all concurrently-used drugs to obtain further information about interactions with
hormonal contraceptives or the potential for enzyme alterations.
7.2 Aminoglutethimide
Aminoglutethimide administered concomitantly with the Depo-Provera CI may significantly depress the
serum concentrations of medroxyprogesterone acetate. Users of Depo-Provera CI should be warned of the
possibility of decreased efficacy with the use of this or any related drugs.
7.3 Laboratory Test Interactions
The pathologist should be advised of progestin therapy when relevant specimens are submitted.
The following laboratory tests may be affected by progestins including Depo-Provera CI:
(a) Plasma and urinary steroid levels are decreased (e.g., progesterone, estradiol, pregnanediol,
testosterone, cortisol).
(b) Gonadotropin levels are decreased.
(c) Sex-hormone-binding-globulin concentrations are decreased.
(d) Protein-bound iodine and butanol extractable protein-bound iodine may increase.
T
3
-uptake values may decrease.
(e) Coagulation test values for prothrombin (Factor II), and
Factors VII, VIII, IX, and X may increase.
(f) Sulfobromophthalein and other liver function test values may be increased.
(g) The effects of medroxyprogesterone acetate on lipid metabolism are inconsistent. Both
increases and decreases in total cholesterol, triglycerides, low-density lipoprotein (LDL)
cholesterol, and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol have been observed in studies.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Depo-Provera CI should not be administered during pregnancy. See Warnings and Precautions (5.16).
8.3 Nursing Mothers
Detectable amounts of drug have been identified in the milk of mothers receiving Depo-Provera CI. [See
Warnings and Precautions (5.12).]
8.4 Pediatric Use
Depo-Provera CI is not indicated before menarche. Use of Depo-Provera CI is associated with significant
loss of BMD. This loss of BMD is of particular concern during adolescence and early adulthood, a critical
period of bone accretion. In adolescents, interpretation of BMD results should take into account patient
age and skeletal maturity. It is unknown if use of Depo-Provera CI by younger women will reduce peak
bone mass and increase the risk of osteoporotic fractures in later life. Other than concerns about loss of
BMD, the safety and effectiveness are expected to be the same for postmenarchal adolescents and adult
women.
9
This label may not be the latest approved by FDA.
For current labeling information, please visit https://www.fda.gov/drugsatfda

8.5 Geriatric Use
This product has not been studied in post-menopausal women and is not indicated in this population.
8.6 Renal Impairment
The effect of renal impairment on Depo-Provera CI pharmacokinetics has not been studied.
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
The effect of hepatic impairment on Depo-Provera CI pharmacokinetics has not been studied. Depo-
Provera CI should not be used by women with significant liver disease and should be discontinued if
jaundice or disturbances of liver function occur. [See Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions
(5.6).]
11 DESCRIPTION
Depo-Provera CI contains medroxyprogesterone acetate, a derivative of progesterone, as its active
ingredient. Medroxyprogesterone acetate is active by the parenteral and oral routes of administration. It is a
white to off-white; odorless crystalline powder that is stable in air and that melts between 200°C and 210°C.
It is freely soluble in chloroform, soluble in acetone and dioxane, sparingly soluble in alcohol and methanol,
slightly soluble in ether, and insoluble in water.
The chemical name for medroxyprogesterone acetate is pregn-4-ene-3,20-dione, 17-(acetyloxy)-6-methyl-,
(6α-).
The structural formula is as follows:
O
CH
3
CH
3
H
3
C
O
CH
3
CH
3
O
O
Depo-Provera CI for intramuscular (IM) injection is available in vials and prefilled syringes, each
containing 1 mL of medroxyprogesterone acetate sterile aqueous suspension 150 mg/mL.
Each mL contains:
Medroxyprogesterone acetate
Polyethylene glycol 3350
Polysorbate 80
Sodium chloride
Methylparaben
Propylparaben
Water for injection
150 mg
28.9 mg
2.41 mg
8.68 mg
1.37 mg
0.150 mg
quantity sufficient
When necessary, pH is adjusted with sodium hydroxide or hydrochloric acid, or both.
10
This label may not be the latest approved by FDA.
For current labeling information, please visit https://www.fda.gov/drugsatfda
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Depo-Provera CI (medroxyprogesterone acetate [MPA]), when administered at the recommended dose to
women every 3 months, inhibits the secretion of gonadotropins which, in turn, prevents follicular
maturation and ovulation and results in endometrial thinning. These actions produce its contraceptive
effect.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
No specific pharmacodynamic studies were conducted with Depo-Provera CI.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Following a single 150 mg IM dose of Depo-Provera CI in eight women between the ages of 28 and 36
years old, medroxyprogesterone acetate concentrations, measured by an extracted radioimmunoassay
procedure, increase for approximately 3 weeks to reach peak plasma concentrations of 1 to 7 ng/mL.
Distribution
Plasma protein binding of MPA averages 86%. MPA binding occurs primarily to serum albumin. No
binding of MPA occurs with sex-hormone-binding globulin (SHBG).
Metabolism
MPA is extensively metabolized in the liver by P450 enzymes. Its metabolism primarily involves ring A
and/or side-chain reduction, loss of the acetyl group, hydroxylation in the 2-, 6-, and 21-positions or a
combination of these positions, resulting in more than 10 metabolites.
Excretion
The concentrations of medroxyprogesterone acetate decrease exponentially until they become
undetectable (<100 pg/mL) between 120 to 200 days following injection. Using an unextracted
radioimmunoassay procedure for the assay of medroxyprogesterone acetate in serum, the apparent half-life
for medroxyprogesterone acetate following IM administration of Depo-Provera CI is approximately 50
days. Most medroxyprogesterone acetate metabolites are excreted in the urine as glucuronide conjugates
with only minor amounts excreted as sulfates.
Specific Populations
The effect of hepatic and/or renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of Depo-Provera CI is unknown.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
See Warnings and Precautions, (5.3, 5.14, and 5.16).
11
This label may not be the latest approved by FDA.
For current labeling information, please visit https://www.fda.gov/drugsatfda

14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Contraception
In five clinical studies using Depo-Provera CI, the 12-month failure rate for the group of women treated
with Depo-Provera CI was zero (no pregnancies reported) to 0.7 by Life-Table method. The effectiveness of
Depo-Provera CI is dependent on the patient returning every 3 months (13 weeks) for reinjection.
14.2 Bone Mineral Density (BMD) Changes in Adult Women
In a controlled, clinical study, adult women using Depo-Provera CI for up to 5 years showed spine and hip
BMD mean decreases of 5–6%, compared to no significant change in BMD in the control group. The
decline in BMD was more pronounced during the first two years of use, with smaller declines in
subsequent years. Mean changes in lumbar spine BMD of -2.86%, -4.11%, -4.89%, -4.93% and -5.38%
after 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 years, respectively, were observed. Mean decreases in BMD of the total hip and
femoral neck were similar.
After stopping use of Depo-Provera CI (150 mg), there was partial recovery of BMD toward baseline
values during the 2-year post-therapy period. Longer duration of treatment was associated with less
complete recovery during this 2-year period following the last injection. Table 4 shows the change in
BMD in women after 5 years of treatment with Depo-Provera CI and in women in a control group, as well
as the extent of recovery of BMD for the subset of the women for whom 2-year post treatment data were
available.
Table 4. Mean Percent Change from Baseline in BMD in Adults by Skeletal Site and
Cohort (5 Years of Treatment and 2 Years of Follow-Up)
Time in
Study
Spine Total Hip Femoral Neck
Depo-Provera* Control** Depo-Provera* Control** Depo-Provera* Control**
5 years -5.38%
n=33
0.43%
n=105
-5.16%
n=21
0.19%
n=65
-6.12%
n=34
-0.27%
n=106
7 years -3.13%
n=12
0.53%
n=60
-1.34%
n=7
0.94%
n=39
-5.38%
n=13
-0.11%
n=63
*The treatment group consisted of women who received Depo-Provera CI for 5 years and were then followed
for 2 years post-use (total time in study of 7 years).
**The control group consisted of women who did not use hormonal contraception and were followed for 7 years.
14.3 Bone Mineral Density Changes in Adolescent Females (12-18 years of age)
The impact of Depo-Provera CI (150 mg) use for up to 240 weeks (4.6 years) was evaluated in an open-
label non-randomized clinical study in 389 adolescent females (12-18 years). Use of Depo-Provera CI was
associated with a significant decline from baseline in BMD.
Partway through the trial, drug administration was stopped (at 120 weeks). The mean number of injections
per Depo-Provera CI user was 9.3. The decline in BMD at total hip and femoral neck was greater with
longer duration of use (see Table 5). The mean decrease in BMD at 240 weeks was more pronounced at
total hip (-6.4%) and femoral neck (-5.4%) compared to lumbar spine (-2.1%).
12
This label may not be the latest approved by FDA.
For current labeling information, please visit https://www.fda.gov/drugsatfda

In general, adolescents increase bone density during the period of growth following menarche, as seen in
the untreated cohort. However, the two cohorts were not matched at baseline for age, gynecologic age,
race, BMD and other factors that influence the rate of acquisition of bone mineral density.
Table 5. Mean Percent Change from Baseline in BMD in Adolescents Receiving
≥4 Injections per 60-week Period, by Skeletal Site and Cohort
Duration of
Treatment
Depo-Provera CI
(150 mg IM)
Unmatched, Untreated
Cohort
N Mean % Change N Mean % Change
Total Hip BMD
Week 60 (1.2 years)
Week 120 (2.3 years)
Week 240 (4.6 years)
113
73
28
-2.75
-5.40
-6.40
166
109
84
1.22
2.19
1.71
Femoral Neck BMD
Week 60
Week 120
Week 240
113
73
28
-2.96
-5.30
-5.40
166
108
84
1.75
2.83
1.94
Lumbar Spine BMD
Week 60
Week 120
Week 240
114
73
27
-2.47
-2.74
-2.11
167
109
84
3.39
5.28
6.40
BMD recovery post-treatment in adolescent women
Longer duration of treatment and smoking were associated with less recovery of BMD following the last
injection of Depo-Provera CI. Table 6 shows the extent of recovery of BMD up to 60 months post-treatment
for adolescent women who received Depo-Provera CI for two years or less compared to more than two
years. Post-treatment follow-up showed that, in women treated for more than two years, only lumbar spine
BMD recovered to baseline levels after treatment was discontinued. Subjects treated with Depo-Provera
for more than two years did not recover to their baseline BMD level at femoral neck and total hip even up to
60 months post-treatment. Adolescent women in the untreated cohort gained BMD throughout the trial
period (data not shown).
13
This label may not be the latest approved by FDA.
For current labeling information, please visit https://www.fda.gov/drugsatfda

Table 6: Extent of BMD Recovery (Months Post-Treatment) in Adolescents by Years of
Depo Provera CI Use (2 Years or Less vs. More than 2 Years)
Duration of
Treatment
2 years or less More than 2 years
N Mean % Change from
baseline
N Mean % Change from
baseline
Total Hip BMD
End of Treatment
49 -1.5% 49 -6.2%
12 M post-treatment 33 -1.4% 24 -4.6%
24 M post-treatment 18 0.3% 17 -3.6%
36 M post-treatment 12 2.1% 11 -4.6%
48 M post-treatment 10 1.3% 9 -2.5%
60 M post-treatment 3 0.2% 2 -1.0%
Femoral Neck BMD
End of Treatment
49 -1.6% 49 -5.8%
12 M post-treatment 33 -1.4% 24 -4.3%
24 M post-treatment 18 0.5% 17 -3.8%
36 M post-treatment 12 1.2% 11 -3.8%
48 M post-treatment 10 2.0% 9 -1.7%
60 M post-treatment 3 1.0% 2 -1.9%
Lumbar Spine BMD
End of Treatment
49 -0.9% 49 -3.5%
12 M post-treatment 33 0.4% 23 -1.1%
24 M post-treatment 18 2.6% 17 1.9%
36 M post-treatment 12 2.4% 11 0.6%
48 M post-treatment 10 6.5% 9 3.5%
60 M post-treatment 3 6.2% 2 5.7%
14
This label may not be the latest approved by FDA.
For current labeling information, please visit https://www.fda.gov/drugsatfda

16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Depo-Provera CI is supplied in the following strengths and package configurations:
Package
Configuration Strength NDC
Depo-Provera CI (medroxyprogesterone acetate sterile aqueous
suspension 150 mg/mL)
1 mL vial 150 mg/mL NDC 0009-0746-30
25 x 1 mL vials 150 mg/mL NDC 0009-0746-35
1 mL prefilled
syringe 150 mg/mL NDC 0009-7376-01
6 x 1 mL prefilled
syringes 150 mg/mL NDC 0009-7376-02
24 x 1 mL prefilled
syringes 150 mg/mL NDC 0009-7376-03
Depo-Provera CI prefilled syringes packaged with 22 gauge x 1 1/2
inch BD SafetyGlide
TM
Needles
1 mL prefilled
syringe
150 mg/mL NDC 0009-7376-04
6 x 1 mL prefilled
syringes 150 mg/mL NDC 0009-7376-05
24 x 1 mL prefilled
syringes 150 mg/mL NDC 0009-7376-06
Vials MUST be stored upright at controlled room temperature 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP].
Store at controlled room temperature 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP].
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA Approved Patient Labeling.
• Advise patients at the beginning of treatment that their menstrual cycle may be disrupted and that irregular
and unpredictable bleeding or spotting results, and that this usually decreases to the point of amenorrhea
as treatment with Depo-Provera CI continues, without other therapy being required.
• Counsel patients that this product does not protect against HIV infection (AIDS) and other sexually
transmitted diseases.
• Counsel patients on Warnings and Precautions associated with use of Depo-Provera CI.
LAB-0149-6.3
15
This label may not be the latest approved by FDA.
For current labeling information, please visit https://www.fda.gov/drugsatfda

FDA Approved Patient Labeling
Depo-Provera
®
(DEP-po pro-VAIR-ah) Contraceptive Injection (Depo-Provera
CI) (medroxyprogesterone acetate injectable suspension)
Patient Labeling
Use of Depo-Provera CI may cause you to lose calcium stored in your bone and
decrease your bone mass. The longer you are on Depo-Provera CI, the greater
the loss may be. The loss of calcium and bone mass may not recover
completely once you stop using Depo-Provera CI.
You should not use Depo-Provera CI for more than two years unless other
methods of birth control are not right for you. If you use Depo-Provera CI
continuously for a long time (for more than 2 years), it may increase the risk of
weak, porous bones (osteoporosis) that could increase the risk that your bones
might break, especially after menopause.
It is not known if your risk of developing osteoporosis is greater if you are a
teenager or young adult when you start to use Depo-Provera CI. (See “What
are the possible side effects of Depo-Provera CI?”)
This product is intended to prevent pregnancy. Depo-Provera CI does not
protect against HIV infection (AIDS) and other sexually transmitted diseases
(STDs).
Read this Patient Information carefully before you decide if Depo-Provera CI is right for
you. This information does not take the place of talking with your gynecologist or other
healthcare provider who specializes in women’s health. If you have any questions about
Depo-Provera CI, ask your healthcare provider. You should also learn about other birth
control methods to choose the one that is best for you.
What is Depo-Provera CI?
Depo-Provera CI is a progestin hormone birth control method that is given by injection
(a shot) to prevent pregnancy.
How well does Depo-Provera CI work ?
The effectiveness of Depo-Provera CI depends on you returning every 3 months for your
next injection. In clinical studies, fewer than 1 out of 100 women got pregnant during
the first year that they used Depo-Provera CI.
The following chart shows the chance of getting pregnant for women who use different
methods of birth control. Each box on the chart contains a list of birth control methods
that are similar in effectiveness. The most effective methods are at the top of the chart.
The box on the bottom of the chart shows the chance of getting pregnant for women
16
This label may not be the latest approved by FDA.
For current labeling information, please visit https://www.fda.gov/drugsatfda
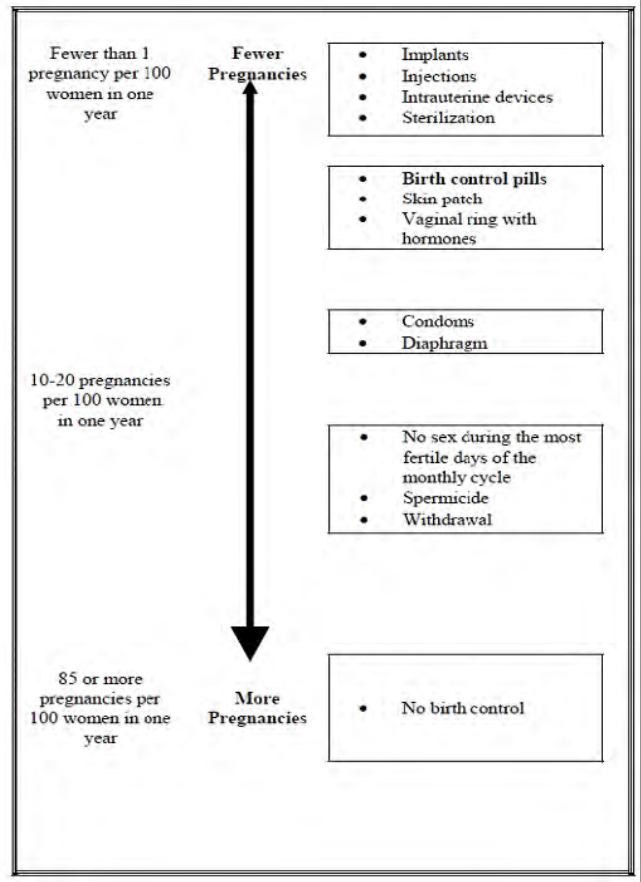
who do not use birth control and are trying to get pregnant.
How should I take Depo-Provera CI?
• Depo-Provera CI is given as a shot into a muscle (intramuscular injection) in your
buttock or upper arm once every 3 months. At the end of the 3 months, you will
need to return to your healthcare provider for your next injection in order to
continue your protection against pregnancy.
• To make sure that you are not pregnant before you take Depo-Provera CI,
the first injection should be given:
o Only during the first 5 days of a normal menstrual period, or
o Only within the first 5 days after giving birth, if you are not breastfeeding, or
o Only at the 6th week after giving birth, if you only breastfeed your baby
17
This label may not be the latest approved by FDA.
For current labeling information, please visit https://www.fda.gov/drugsatfda
• During treatment with Depo-Provera CI, you should see your healthcare provider
every year for a blood pressure check and other healthcare needs.
Who Should Not Use Depo-Provera CI?
Do not use Depo-Provera CI if you
• are pregnant or think you might be pregnant
• have bleeding from the vagina that has not been explained
• have breast cancer now or in the past, or think you have breast cancer
• have had a stroke
• ever had blood clots in your arms, legs or lungs
• have problems with your liver or liver disease
• are allergic to medroxyprogesterone acetate or any of the other ingredients in
Depo-Provera CI. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in
Depo-Provera CI.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking Depo-Provera CI?
Before taking Depo-Provera CI, tell your healthcare provider if you have:
• risk factors for weak bones (osteoporosis) such as bone disease, use alcohol or
smoke regularly, anorexia nervosa, or a strong family history of osteoporosis
• irregular or lighter than usual menstrual periods
• breast cancer now or in the past, or think you have breast cancer
• a family history of breast cancer
• an abnormal mammogram (breast X-ray), fibrocystic breast disease, breast
nodules or lumps, or bleeding from your nipples
• kidney problems
• high blood pressure
• had a stroke
• had blood clots in your arms, legs or lungs
• migraine headaches
• asthma
• epilepsy (convulsions or seizures)
• diabetes
• depression or a history of depression
• any other medical conditions
If you are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed, Depo-Provera CI can pass into your
breast milk. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby if
you take Depo-Provera CI.
Tell your healthcare provider about all of the medicines you take, including prescription
and nonprescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Depo-Provera CI and certain other medicines may affect each other, causing serious side
effects.
Sometimes the doses of other medicines may need to be changed while you are taking
Depo-Provera CI.
18
This label may not be the latest approved by FDA.
For current labeling information, please visit https://www.fda.gov/drugsatfda
Some medicines may make Depo-Provera CI less effective at preventing pregnancy.
Especially tell your healthcare provider if you take:
• a medicine that makes you sleepy (sedation)
• bosentan
• medicine for seizures
• griseofulvin
• an antibiotic
• medicine for HIV (AIDS)
• aminoglutethimide
• St. John’s wort
Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for a list of these medicines, if you are not
sure if your medicine is listed above.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of your medicines with you to show your
healthcare provider or pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions about using a back-up method of
birth control if you are taking medicines that may make Depo-Provera CI less
effective.
What are the possible side effects of Depo-Provera CI?
Depo-Provera CI can cause serious side effects, including:
• Effect on the bones: See the Boxed Warning.
Teenage years are the most important years to gain bone strength. The decrease
in calcium in your bones is of most concern if you are a teenager or have the
following risk factors:
- bone disease
- anorexia nervosa (an eating disorder)
- a strong family history of osteoporosis
- drug use that can lower the amount of calcium in bones (drugs for epilepsy
or steroids), or
- drinking a lot of alcohol (more than 2 drinks/day) or smoking
If you need a birth control method for more than 2 years, your healthcare provider
may ask you to switch to another birth control method or ask you to have a test of
your bones before continuing Depo-Provera CI, especially if you have other risks
for weak bones. When Depo-Provera CI is stopped, your bones may start to
recover. However, in a study of teenage girls who used Depo-Provera CI for more
than 2 years, this recovery was not complete for hip bones even 5 years after they
stopped using Depo-Provera CI. Taking calcium and Vitamin D and exercising daily
may lessen the loss of calcium from your bones.
19
This label may not be the latest approved by FDA.
For current labeling information, please visit https://www.fda.gov/drugsatfda
• Increased risk of breast cancer: Studies of women who have used different forms
of contraception found that women under 35 years of age who first used Depo-
Provera CI within the previous 4 to 5 years may have a slightly increased risk of
developing breast cancer.
• blood clots in your arms, legs, lungs, and eyes
• stroke
• a pregnancy outside of the uterus (ectopic pregnancy). Ectopic pregnancy is a
medical emergency that often requires surgery. Ectopic pregnancy can cause
internal bleeding, infertility, and even death.
• Allergic Reactions: Severe allergic reactions have been reported in some women
using Depo-Provera CI.
• Loss of vision or other eye problems
• migraine headaches
• depression
• convulsions or seizures
• liver problems
Call your healthcare provider right away if you have:
• Sharp chest pain, coughing up blood, or sudden shortness of breath (indicating a
possible clot in the lung)
• Sudden severe headache or vomiting, dizziness or fainting, problems with your
eyesight or speech, weakness, or numbness in an arm or leg (indicating a possible
stroke)
• Severe pain or swelling in the calf (indicating a possible clot in the leg)
• Unusually heavy vaginal bleeding
• Severe pain or tenderness in the lower abdominal area
• Persistent pain, pus, or bleeding at the injection site
• Yellowing of the eyes or skin
• Hives or difficulty breathing
The most common side effects of Depo-Provera CI include:
• Irregular vaginal bleeding, such as lighter or heavier menstrual bleeding, or
bleeding that does not stop
• Weight gain: You may experience weight gain while you are using Depo-Provera
CI. About two-thirds of the women who used Depo-Provera CI in the clinical trials
reported a weight gain of about 5 pounds during the first year of use. You may
continue to gain weight after the first year. Women who used Depo-Provera CI for
2 years gained an average of 8 pounds over those 2 years.
• abdominal pain
• headache
• weakness
• tiredness
20
This label may not be the latest approved by FDA.
For current labeling information, please visit https://www.fda.gov/drugsatfda
• nervousness
• dizziness
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or does not go
away.
These are not all the possible side effects of Depo-Provera CI. For more information, ask
your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Call your healthcare provider for medical advice about side effects. You may report side
effects to FDA at 1- 800-FDA-1088.
What other information should I consider before choosing Depo-Provera CI?
• STDs: Depo-Provera CI does not protect against transmission of HIV (AIDS) and
other sexually transmitted diseases such as chlamydia, genital herpes, genital
warts, gonorrhea, hepatitis B, and syphilis.
• Pregnancy: When you take Depo-Provera CI every 3 months, your chance of
getting pregnant is very low. You could miss a period or have a light period and
not be pregnant. If you miss 1 or 2 periods and think you might be pregnant, see
your healthcare provider as soon as possible. You should not use Depo-Provera CI
if you are pregnant. However, Depo-Provera CI taken by accident during
pregnancy does not seem to cause birth defects.
• Nursing Mothers: Although Depo-Provera CI can be passed to the nursing baby in
the breast milk, no harmful effects on babies have been found. Depo-Provera CI
does not stop the breasts from producing milk, so it can be used by nursing
mothers. However, to minimize the amount of Depo-Provera CI that is passed to
the baby in the first weeks after birth, you should wait until your baby is 6 weeks
old before you start using Depo-Provera CI for birth control.
How will Depo-Provera CI change my periods?
The side effect reported most frequently by women who use Depo-Provera CI for birth
controls is a change in their normal menstrual cycle. During the first year of using Depo-
Provera CI, you might have one or more of the following changes:
• irregular or unpredictable bleeding or spotting,
• an increase or decrease in menstrual bleeding
• no bleeding at all
Missed period: During the time you are using Depo-Provera CI for birth controls, you
may skip a period, or your periods may stop completely. If you have been receiving your
shot of Depo-Provera CI regularly every 3 months, then you are probably not pregnant.
However, if you think that you may be pregnant, see your healthcare provider.
Unusually heavy or continuous bleeding is not a usual effect of Depo-Provera CI and if
this happens you should see your healthcare provider right away.
21
This label may not be the latest approved by FDA.
For current labeling information, please visit https://www.fda.gov/drugsatfda

With continued use of Depo-Provera CI, bleeding usually decreases and many women
stop having periods completely. When you stop using Depo-Provera CI your menstrual
period will usually, in time, return to its normal cycle.
What if I want to become pregnant?
Because Depo-Provera CI is a long-acting birth control method, it takes some time after
your last shot for its effect to wear off. Most women who try to get pregnant after using
Depo-Provera CI get pregnant within 18 months after their last shot. The length of time
you use Depo-Provera CI has no effect on how long it takes you to become pregnant
after you stop using it.
General Information about Depo-Provera CI
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for conditions that are not mentioned in patient
information leaflets. This leaflet summarizes the most important information about
Depo-Provera CI. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider.
You can ask your healthcare provider for information about Depo-Provera CI that is
written for healthcare providers.
What are the ingredients in Depo-Provera CI?
Active ingredient: medroxyprogesterone acetate
Inactive ingredients: polyethylene glycol 3350, polysorbate 80, sodium chloride,
methylparaben, propylparaben, and water for injection. When necessary, pH is adjusted
with sodium hydroxide or hydrochloric acid, or both.
LAB-0148-5.1
22
This label may not be the latest approved by FDA.
For current labeling information, please visit https://www.fda.gov/drugsatfda
