
PLDO
Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator
Training
Instructor Guide
Prepared by the Interagency Aerial Ignition Group
Revised April 24, 2015

Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 2 -
PLDO
Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator
Revision History
Version
Description
Date
1.00
Original Materials
Date
1.10
Incorporate all PSD Manufacturer’s training curriculum
into one instructor guide.
1.29.2015

Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 3 -
PLDO
Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator
Course Overview
What is the purpose of the course?
The purpose of this course is to provide you with a working knowledge of the various
PSD machines approved for use by the Interagency Aerial Ignition Guide.
Who are the intended participants?
Interagency personnel who utilize the Plastic Sphere Dispenser for aerial ignition
missions.
Course Prerequisites:
Prior to requesting enrollment in PLDO, prospective students must complete the
following pre-requisites:
Specific required training and qualifications can be found in the current Federal
Wildland Qualifications Supplement to the NWCG PMS 310-1.
http://www.nwcg.gov/pms/docs/supplement-2015.pdf
REQUIRED TRAINING:
National Incident Management System, An Introduction (IS-700)
Introduction to ICS (ICS-100)
Annual Fireline Safety Refresher (RT-130)
Aviation Transport of Hazardous Material (A-110); triennial requirement
Plastic Sphere Dispenser (N-9016)
Annual Plastic Sphere Dispenser Refresher (RT-9016), required annually after
initial training
REQUIRED EXPERIENCE:
Satisfactory performance as Project Helicopter Crewmember (minimum)
AND
Interagency PLDO Training: A minimum of one successful assignment to include
a minimum1-hour in-flight machine operation and completion of the position Task
book
PHYSICAL FITNESS LEVEL:
None
How is the course conducted?
Instructor-led delivery in classroom with hands-on demonstration of the skills identified
in the position tasksheet for PLDO.

Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 4 -
What are the minimum instructor qualifications for the course?
This will vary based on agency specific requirements.
What are the course objectives?
At the conclusion of this course, participants will be able to:
1. Identify the approved Plastic Sphere Dispenser (PSD) machines approved for
use as identified in the Interagency Aerial Ignition Guide.
2. Identify the organization required for a safe operation.
3. Identify the requirements for safely working with the hazardous materials
involved with PSD operations.
4. Demonstrate knowledge of the operational functions before, during and after
the project.
5. Demonstrate knowledge of the firing commands and actions of a PSD
operator.
6. Demonstrate knowledge of emergency procedures.
7. List three advantages of using the PSD machine versus the helitorch aerial
ignition device.
8. Identify the parts and basic functions of each PSD machine.
9. Demonstrate knowledge to perform routine maintenance on the PSD
machine.
10. Demonstrate knowledge and perform a bench-test of the PSD machine.
11. Demonstrate knowledge and perform the operational functions of the Plastic
Sphere Dispenser Operator (PLDO) duties as identified in the position Task
book.
What is required to pass the course?
Include any specific requirements to pass the course, i.e. exam minimum score,
proficiency demonstrations, etc.
Logistical Information:
Recommended Class Size: 2 Min. 20 Max.
Length of Course: Approximately 4 - 6 hrs.
Supplies:
Computer/laptop
Projector
Screen
Speakers
Course electronic presentation slides
Course Participant Guide
Student Roster

Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 5 -
OAS-111 Student Course Evaluations
Course Exam
Hardcopy or electronic version of the Interagency Aerial Ignition Guide for each
student
Position Task book for each student
Plastic Sphere Dispenser Machine with tool kit
Personal Protective Equipment for bench testing equipment.
Appropriate equipment as identified in the Interagency Aerial Ignition Guide for
bench testing equipment (metal bucket, glycol, potassium permanganate
spheres, 40 rated B:C fire extinguisher, 5-gallons of water, etc…).
Internet Connection (not mandatory, but useful) for video and resource files to
demonstrate effective PSD Operations.
Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 6 -
PLDO
Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator
Course Map
Module 2: Operations
Module 3: Fuels and
Fire Behavior
Welcome and
Course Introduction
Module 5: Resources
and References
Module 1: Organization
and Safety
Module 4: Function and
Maintenance
Summary
Appendices
(Includes your
Resources or
References)

Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 7 -
Est. Instruction
Time: varied.
Welcome and Course Introduction
PPT – Title Slide
to be inputted by
instructor related
to equipment on
site.
PPT – Introduction
Welcome the students to the course.
Introduce yourself.
Have participants introduce themselves. You could have them
share some of the following information (as time allows):
Name
Where do you work?
Have you ever been involved in aerial ignition operations
or used a Plastic Sphere Dispenser before?
PPT - Participant
Workbook
Participant Workbook
Ensure each student has a Participant Workbook. Explain that
this is designed to be a guided note-taking tool as well as a
source of valuable information for review. Participants will be
asked to refer to it throughout the course.
Instructor Note: The icon in the lower right corner on some of
the presentation slides indicates the page reference that the
student should be viewing in the Participant Workbook.
PPT – Course
Purpose
PPT – Course
Objectives
Course Purpose
This course is designed to provide you with a working
knowledge of the various PSD machines approved for use by
the Interagency Aerial Ignition Guide.
This instructor guide is designed to be used for all the PSD
presentations, regardless of what is on site for inspection
or field use. The slide presentation will vary based on which
machine is being used and local modifications.
The instructor guide will cover the aspects of PSD
operations common to all machines.
The final unit PSD Function and Maintenance provides the
information for all three of the machines however the instructor
should focus their delivery for the machine(s) that is on-site for
Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 8 -
use and bench testing with the remaining information as
optional.
Course Objectives
Introduce the Course Objectives.
At the conclusion of this course, participants will be able to:
1. Identify the approved Plastic Sphere Dispenser (PSD)
machines approved for use as identified in the
Interagency Aerial Ignition Guide.
2. Identify the organization required for a safe operation.
3. Identify the requirements for safely working with the
hazardous materials involved with PSD operations.
4. Demonstrate knowledge of the operational functions
before, during and after the project.
5. Demonstrate knowledge of the firing commands and
actions of a PSD operator.
6. Demonstrate knowledge of emergency procedures.
7. List three advantages of using the PSD machine
versus the helitorch aerial ignition device.
8. Identify the parts and basic functions of each PSD
machine.
9. Demonstrate knowledge to perform routine
maintenance on the PSD machine.
10. Demonstrate knowledge and perform a bench-test of
the PSD machine.
11. Demonstrate knowledge and perform the operational
functions of the Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator
(PLDO) duties as identified in the position Task book.
Explain that as you cover each module, the specific objectives
for that module will be addressed.
Segue to next module: Organization and Safety
Let’s take a look at what is required for a safe PSD operation.

Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 9 -
Est. Instruction
Time: XX min.
Module 1: Organization and Safety
PPT – Module 1
Introduce the module/topic:
The Plastic Sphere Dispenser, otherwise known as PSD
machine, was developed to provide a method of igniting
continuous surface fuels in a short time, on large acreage
without causing undue damage to the over story. It is cost
effective, environmentally acceptable, simple to use and readily
available.
In general PSD operations are essentially a self-contained
operation with the PLDO and possibly one assistant are the
only personnel required.
The PSD ignition method may be used in any stand that can be
burned by conventional methods. The plastic sphere ignition
system is an excellent tool for hazard fuel reductions in pine
plantations. This system is safe, efficient, and economical for
users to burn with less risk to the plantation than by using the
helitorch ignition system.
PPT – Objectives
Objective(s):
After completing this module, participants should be able to:
1. Identify the approved Plastic Sphere Dispenser
(PSD) machines approved for use as identified in the
Interagency Aerial Ignition Guide.
2. Identify the organization required for a safe
operation.
3. Identify the requirements for safely working with
the hazardous materials involved with PSD operations.
Key teaching points to accomplish module objectives:
Discuss the machines approved for use for PSD
operations
Discuss the minimum safety organization needed for
PSD operations
Identify the safety requirements for working with PSD
equipment.

Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 10 -
PPT – Title of
Slide
PPT – Title of
Slide
Est. Time for
Activity: XX min.
PW Page: XX
Overview
PSD operations require the helicopter to maintain flight below
500 feet above ground level (AGL) and at a speed of less than
50 mph. The recommended operational flight altitude is 300 feet
AGL.
Hovering out of ground effect (HOGE) is the typical flight profile.
The Pilot must keep altitude, airspeed, wind direction and
aircraft capabilities and limitations in mind during all phases of
flight operations.
The Interagency Aerial Ignition Guide identifies 3 PSD
machines that have been approved for use for the Department
of the Interior and US Forest Service agencies. They are:
1. Premo Mark III Aerial Ignition Device
http://www.sei-ind.com/products/premo-fire-ignition-products
2. SEI Red Dragon
http://www.sei-ind.com/products/premo-fire-ignition-products
3. Aerostat PSDS Mark V
http://www.aerostatinc.com/MarkVUserTools.asp
The basic function of the PSD machine is the same for each
manufacturer: to inject undiluted ethylene glycol into a plastic
sphere containing potassium permanganate and to expel the
primed sphere from the aircraft after which an exothermic
reaction takes place.
The ethylene glycol commonly used is standard vehicle
antifreeze. Other types of antifreeze may not contain enough
ethylene glycol to create proper reaction with the potassium
permanganate. These other types of antifreeze include
biodegradable, RV, and antifreeze with high concentrations of
additives. Propylene glycol is not to be used.
The rate of chemical reaction is dependent on particle size
and concentration of the chemicals involved. Water-glycol
solutions ranging from 90 to 100% concentration of ethylene
glycol (common antifreeze) is advocated and will provide a
reliable ignition with a time delay of at least 20 seconds.
All shipping cases are labeled with the recommended
percentage of glycol solution needed to obtain the desired time

Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 11 -
delay for the sphere type in the case.
Let’s take a look at the organization and safety practices
necessary for a safe operation.
Instructor Note: Review the current copy of the Interagency
Aerial Ignition Guide for changes in approved equipment
since the completion of the instructor guide.
Interaction/Activity: REVIEW QUESTION
Question: What are the three approved PSD machines
identified in the aerial ignition guide?
Answer: Premo Mark III, Red Dragon, and Aerostat PSDS
Mark V.
PPT – Title of
Slide
PPT – Title of
Slide
Est. Time for
Activity: XX min.
PW Page: XX
Organization, Personnel Qualifications and
Responsibilities
As with any special use mission, the pilot and aircraft must be
carded for aerial ignition operations, and a project aviation
safety plan (PASP) completed and approved prior to
commencing prescribed fire operations.
1. Burn Boss (Qualified as Prescribed Fire Burn Boss 1 or 2
(RXB1 / RXB2)
o Has complete authority for firing operation.
o Directs firing operation.
o Develops the firing plan.
o Performs the initial briefing.
o Details assignments of each boss/supervisor and the
pilot.
o May be located in the aircraft with the PSD Operator.
2. Firing Boss (Qualified as a Firing Boss (FIRB)
o Reports to Burn Boss.
o Instructs the pilot as to the plan, firing sequences and
keeps the pilot informed throughout the entire operation.
o Directs the PSD operator.
o May be functioning as collateral duty/Burn Boss.
o May also be called Ignition Specialist
3. PSD Operator (Qualified as Plastic Sphere Dispenser
Operator (PLDO)

Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 12 -
o Works for the Firing Boss/Ignition Specialist.
o Briefs the pilot, identifies safety requirements at the
operations briefing and monitors overall operation.
o Provides information on aerial safety procedures to be
used by the Firing Boss/Ignition Specialist.
o Prepares, operates and maintains the PSD machine.
o Observes spacing of ignition of spheres and makes
recommendations to Firing Boss/Ignition Specialist for
adjustments to meet project objectives.
o Monitors operation of PSD machine and takes
appropriate action should a malfunction occur.
o Determines whether a fire contained within the machine
can be safely extinguished or if the unit must be
jettisoned in coordination with the pilot.
o Communicates with the pilot and Firing Boss/Ignition
Specialist on all procedures associated with the
operation and/or emergencies occurring during the
operation.
4. Pilot
(Carded for Aerial Ignition Operations – Current, confirm
prior to commencing operations.)
o Responsible for all matters related to aircraft operations
and safety.
o Follows the ignition plan under the direction of the firing
boss.
o Oversees the PSD installation to the aircraft.
o Completes the helicopter performance planning using
the load calculation form.
5. Helicopter Manager (may have collateral duties as PSD
Operator – PLDO)
o Qualified as Helicopter Manager (HMGB) and manages
the helicopter in compliance with agency policy.
6. Helibase Support (Helibase Manager (HEB2) required if 2
or more helicopters are on-site)
a. Helibase Fire Protection: At a minimum, one
40-B:C rated fire extinguisher and five gallons of
water will be positioned at the helibase.
i. Provide crash rescue and evacuation
equipment at the helibase.
b. Radio Operator: Will be positioned at the
helibase.
i. Will initiate radio communications with
Burn Boss and dispatch.

Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 13 -
Communications: Internal and External
1. Internal Communications
o All personnel inside the ship must have the ability to
communicate via intercom.
o Consider a noise cancelling mic for the PSD Operator to
reduce wind noise.
2. External Communication
o Use a dedicated air to ground frequency to communicate
to holding forces.
o Some burns may use only one frequency
o All flight following requirements will be followed by the
pilot.
Hazardous Material Handling
(Completing A-110 Aviation Transport of Hazardous Materials is
a prerequisite to this training. http://www.iat.gov/)
All hazardous materials handling will be in compliance with the
following Renewed Hazmat Special Permit: DOT-SP-9198
(Sixteenth Revision)
http://oas.doi.gov/dts/library/TechBull/TB_2015-02.pdf
1. Potassium permanganate and ethylene glycol are classified
as hazardous materials by DOT regulations. Use in aerial
ignition devices by the USDA Forest Service and US Dept. of
the Interior is exempt from these regulations under the above
mentioned permit as long as handling is in compliance of the
permit.
o Under NO circumstances will extra ethylene glycol
be carried on board the aircraft.
o The glycol tank MUST be filled and capped at least 25
feet away from the aircraft.
o When transporting to the project site, spheres and glycol
MUST be in separate compartments.
o Absolutely NO batteries will be carried on board the
aircraft to operate the PSD machine.
2. Storage of spheres containing potassium permanganate
o Keep boxes dry and rotate stock regularly.
o Store away from ethylene glycol and petroleum products.

Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 14 -
o Sweep away residue and spills promptly.
o Unused spheres should be stored in a clean plastic bag
and place in the original box.
CAUTION: An inadequate quantity of ethylene glycol injected
into the sphere can induce a violent reaction causing the sphere
to spin or roll and spray a hot mixture of potassium
permanganate and ethylene glycol a considerable distance.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
1. Approved ALSE rated Flight Helmet (ex: SPH-5)
2. Fire resistant/Nomex® long sleeved shirt and pants or
Nomex® flightsuit. (PSD operator should be prepared for
very cold temperatures in flight and consider wearing
natural fiber undergarments and/or a Nomex® or Natural
fiber jacket.)
3. Leather or leather/Nomex® flight gloves
4. Leather boots minimum above the ankles, pants should
cover the tops or the boots when the PSD operator is sitting
down.
5. Approved harness, tether and tether attachment.
6. Approved seat belt cutter for cutting strap in case of the
need to jettison the PSD.
7. Fire Shelter for EACH occupant of the helicopter.
Interaction/Activity: REVIEW QUESTIONS:
Question: What Personal Protective Equipment is required for
the PSD Operator?
Answer: Approved ALSE rated Flight Helmet, Fire
resistant/Nomex® long sleeved shirt and pants or Nomex®
flightsuit, leather or leather/Nomex® flight gloves, leather boots
minimum above the ankles, pants should cover the tops or the
boots when the PSD operator is sitting down, approved
harness, tether and tether attachment, approved seat belt cutter
for cutting strap in case of the need to jettison the PSD, and a
fire shelter.
Question: Can the spheres and glycol be transported in the
same compartment if they are both in factory sealed
containers?
Answer: No!!

Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 15 -
Segue to next module: Operations
Let’s take a look at the steps to conduct safe PSD Operations.

Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 16 -
Est. Instruction
Time: XX min.
Module 2: Operations
PPT – Module 2
Introduce the module/topic:
PPT – Objectives
Objective(s):
After completing this module, participants should be able to:
4. Demonstrate knowledge of the operational
functions before, during and after the project.
5. Demonstrate knowledge of the firing commands
and actions of a PSD operator.
6. Demonstrate knowledge of emergency
procedures.
Key teaching points to accomplish module objectives:
Discuss the elements of the mission briefing.
Discuss safety procedures to follow while bench testing
equipment.
Discuss general bench testing procedures.
Discuss elements of the helibase briefing.
Discuss the steps in preparation of PSD operations.
PPT – Title of
Slide
PPT – Title of
Slide
Est. Time for
Activity: XX min.
PW Page: XX
Prior to Operations
Mission Briefing
Prior to any special use mission a mission or operational
briefing must take place. The Project Aviation Safety Plan is
great tool to brief to the mission. During the mission briefing the
following items should be addressed:
1. Objectives
2. Organization and Personnel
3. Assignments
4. Air Operations Summary (if applicable)
5. Weather
6. Fire Behavior
7. Communication Plan
8. Medical Plan
9. Crash Rescue Plan
(1) Roles and Responsibilities

Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 17 -
(2) Engines, hand crews, dozers and aircraft
10. Contingency Plan (for escape)
Once the mission has been briefed, it’s time to bench test the
equipment to make sure everything is functioning properly.
PSD Bench Test
The purpose of the bench test is to confirm proper operation of
the PSD and proper sphere ignition.
This phase of the training requires the activation of ignited
spheres that has the potential to create several safety hazards
to personnel and adjoining property if not properly conducted.
The following safety procedures will be followed during bench
testing:
1. The training site must be outdoors and clear of buildings,
vehicles, aircraft, and flammable materials.
2. Adequate fire extinguishers and water sources must be
available.
3. During this testing, spheres shall not be dropped in the
water. If moisture is allowed to come in contact with an
injected live sphere, the sphere may be propelled
erratically long distances endangering personnel and
property.
4. The wind direction must be considered so that the
operator and trainees will stay clear of the smoke.
5. During bench testing operations, designated individuals
will remove activated spheres from the test area.
6. The students shall wear eye and hand protection, and
flight gloves.
7. The test platform needs to be a minimum of 30 inches
high and stable to allow for the proper installation of the
PSD (i.e., PSD box, heavy duty picnic table, or bench).
Testing Procedures:
Review manufacturers manual and procedures for bench
testing.
1. Bench testing should occur in an appropriate safe area.
2. To calibrate the machine, use empty plastic spheres to
determine proper calibration. Calibration instructions
are contained in manufacturer’s manual.

Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 18 -
CAUTION: Place DRY metal bucket under chute. NO WATER
in bucket.
3. Temperature and humidity may affect ignition delay,
causing delays to be greater than 20 seconds. Colder
temperatures will cause longer ignitions, often as long as
40 to 60 seconds. This is an appropriate ignition
timeframe if all spheres are igniting.
4. During machine start-up, it is normal for two of the first
four spheres that pass through the machine to not be
injected with sufficient glycol to promote ignition due to
the cam sequence and slipper block location. It is
recommended to promote priming of the glycol pump by
running for 30 seconds prior to adding balls into the
slipper blocks for testing purposes.
This test need only be conducted once at the start of the day.
Cleaning should follow the bench test in accordance with
manufacturer’s specifications.
Specific details of bench testing individual machines will be
covered in the PSD Function and Maintenance Unit.
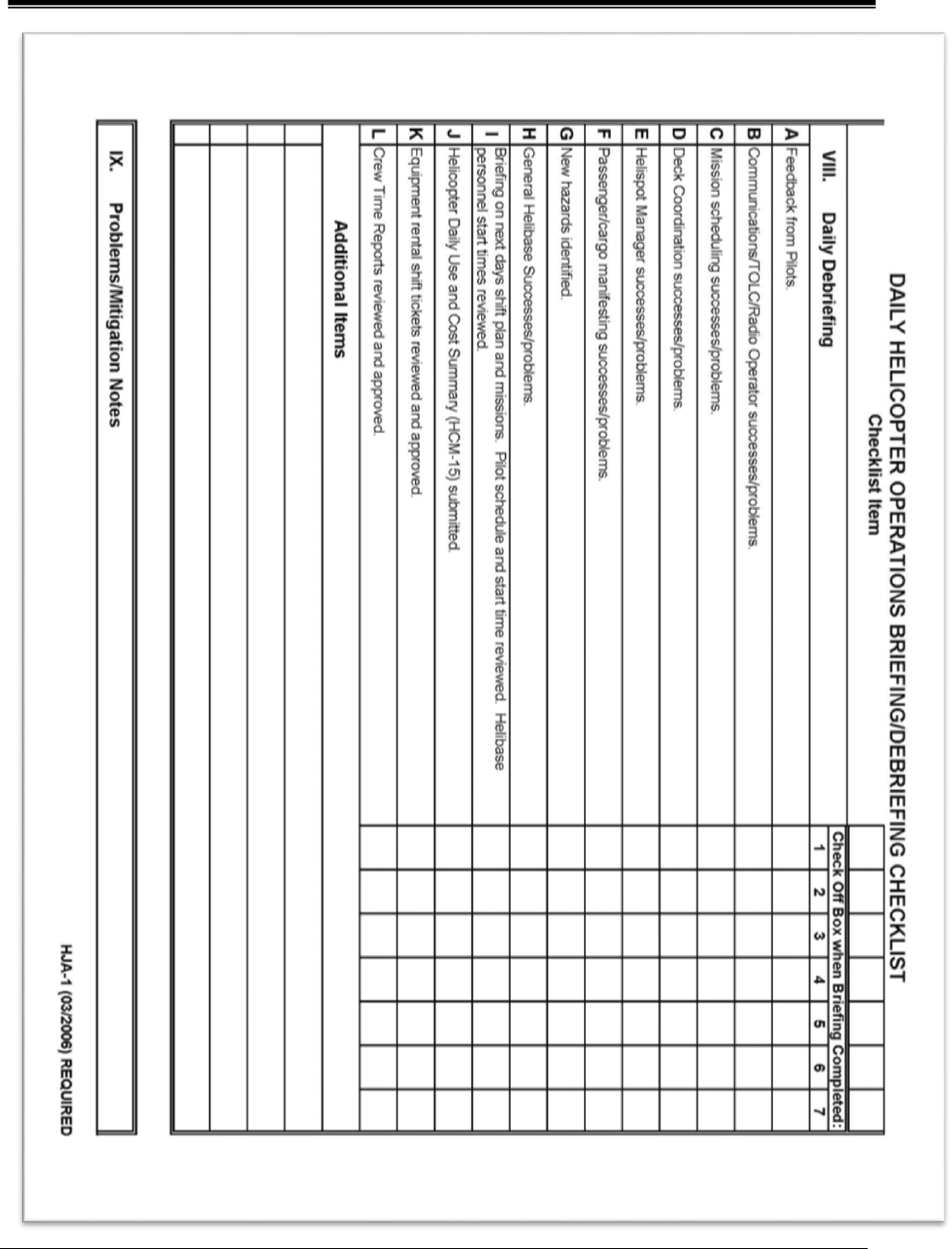
Helibase Briefing
1. Organization and personnel
2. Communications
3. Landing Areas
4. Safety / Hazards
5. Operations
6. Administration
The Interagency Helicopter Operations Guide (IHOG) has
the Helibase Briefing Checklist (HJA-1) which is a helpful
tool for this briefing and can be found in Appendix A.
Preparation for Aerial Ignition
1. The PLDO and the Pilot must discuss flight
profiles for aerial ignition operations which shall
be jointly determined before each mission by the
pilot and crew based on the environment and
mission. The pilot and burn crew shall minimize
their time inside the Height/Velocity “avoid” areas
as much as possible. Any flight profile that results

Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 19 -
in transference of risk to ground operations must
be mitigated to the extent possible.
2. In addition, crew resource management
discussions must occur between the pilot,
Prescribed Fire Burn Boss, Helicopter Manager,
and PLDO’s prior to all ignition operations. The
discussion shall focus on a heightened awareness
of the risks involved in low level flights the
limitations section of the flight manual and be
familiar with the limitation of flight with the door(s)
removed.
3. Helicopters shall be equipped with a power source
for PSD.
4. A bulkhead mounted MS 3112E- 12 3S, 3-pin
connector shall be provided. Pin B shall be
airframe ground. Pin A shall be +28 V.C. for a 28-
volt aircraft system. Pin C shall be +14 for a 14-
volt aircraft system. The circuit shall be protected
by a 5-amp circuit breaker. The mating connector
for the Government-furnished PSD shall be an MS
3116E-12-3P wired with the same pin
assignments. Reference a wiring diagram in the
aircraft procurement document.
5. Remove appropriate door/doors.
6. Remove all loose cushions and other loose
materials.
7. Locate and assure proper electrical connections.
8. Utilize approved aircraft hard point anchor or
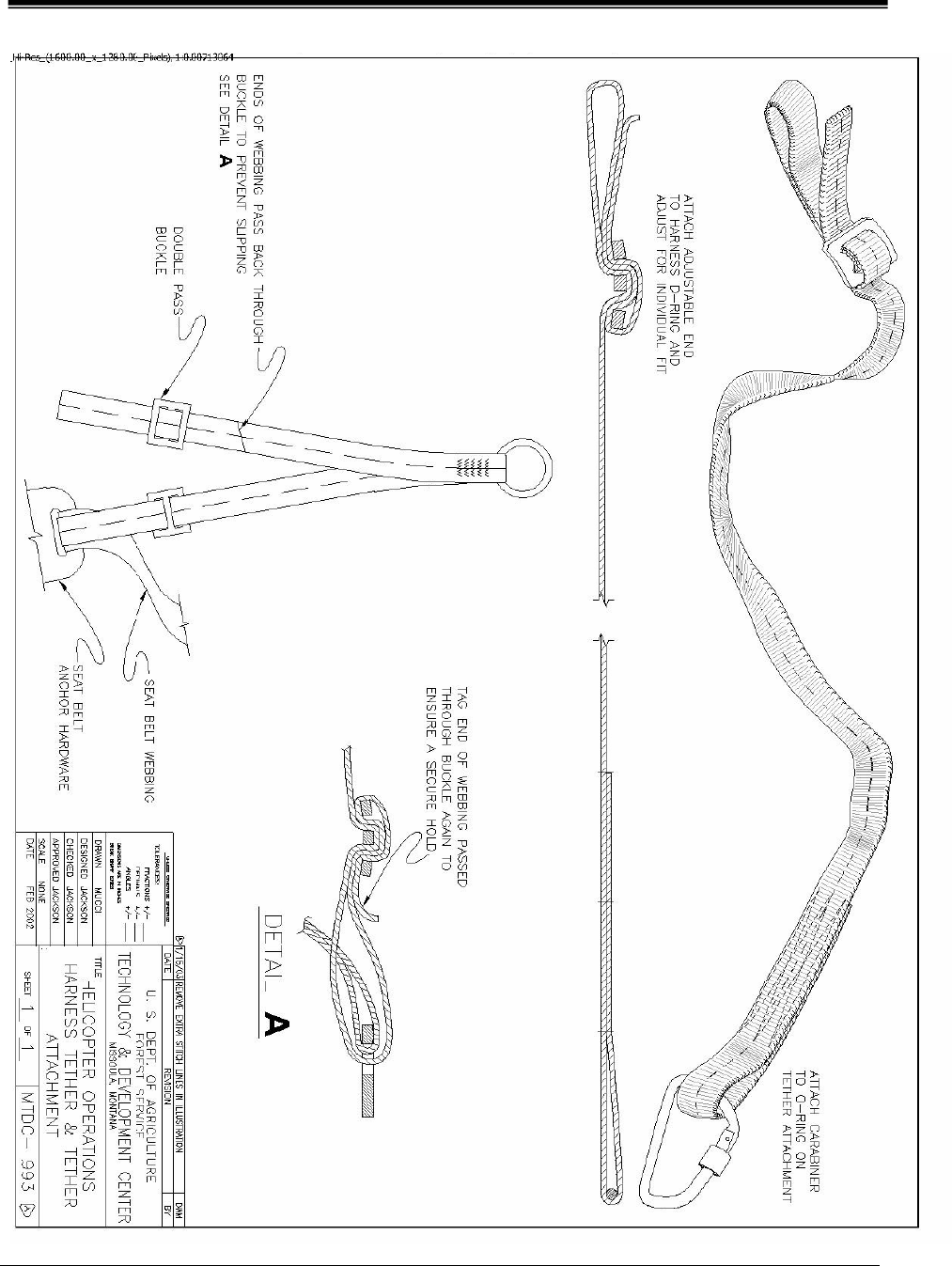
install tether attachments to hard points per
instructions on MTDC drawing # 993 (See
Appendix B.)
9. Install secondary restraint using approved
carabiner and adjust tether length. A properly
adjusted tether shall insure that the operator is
restrained inside the aircraft and will not reach
beyond the sill of the aircraft if the seat belt should
become unbuckled during flight.
10. Fill glycol tank at least 25 feet from aircraft.
11. Fill water storage tank.
12. Ensure adequate supply of plastic spheres is
available to complete project.
13. Ensure one-gallon container of water and seatbelt
cutter is on board, secured, and are readily
accessible.
14. Fire shelters for all occupants must be on board
and accessible, and one or more hand tools are
recommended.

Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 20 -
Preflight Briefing
1. The pilot, ignition specialist, and PSD operator must be
present at the pre-mission aircraft briefing. This is the
standard pilot preflight aircraft safety briefing that in addition
should address:
a. Safety / Aerial Hazards
b. Weight and Balance
c. In-flight Commands
d. Emergency Procedures
e. Frequency Management
f. Available Flight Time
g. Aircrew Responsibilities
h. PSD Go / No Go checklist.
2. The pilot and/or mechanic must inspect and approve
of the PSD machine installation.
3. Preflight Test of the PSD Machine
Sphere ignition delay time need not be checked in the
Preflight Test if the Bench Test has been performed.
CAUTION: Do not conduct this test near refueling area
or in flashy ground fuels.
Test procedures are as follows:
a) Place metal container under the exit chute.
b) Connect power leads
c) Power on – A/C.
d) Start up the PSD
e) Deposit one sphere in a slipper block/shuttle block to
track calibration.
f) Once the sphere has dropped into the metal
container, remove it from the vicinity of the aircraft.
g) Time ignition delay by measuring time of injection to
ignition. Repeat as necessary.
h) Check system for leaks.
i) Test PSD emergency water system.
j) Secure Machine
k) Fill hopper with spheres.
l) Check intercom communications and air-to-ground
communications.

Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 21 -
Inflight Operations
Dry Run over Burn Area Procedures
1. Check that ignition area is clear of personnel.
2. Identify burn area boundaries.
It is important that all parties (burn boss/ignition
specialist, pilot, and PLDO) understand where the
firing is to be done. This includes the starting points,
ending points, and desired placement and spacing.
3. Ensure communication with ground personnel.
4. Make practice run of the first firing sequence.
5. Coordinate machine speed and sphere spacing to be
used on first run with RXB1/2 or FIRB
6. Identify helispots and emergency landing areas.
7. After a dry run and prior to aerial firing the crew will
evaluate the risk assessment mitigations and readjust as
necessary. The RXB1/2 or FIRB will confirm that all ground
personnel are clear of the area and that firing may
commence.
Once the dry run is complete and personnel are clear of the
area
RXB1/2 or FIRB communicates to PLDO, “Prepare to fire;
activate machine.”
1. Operator actions:
a. Activates machine
b. PLDO communicates toRXB1/2 or FIRB,
“Ready to fire.”
2. RXB1/2 or FIRB communicates to PLDO to “Start
firing/Number of chutes or machine speed”
3. PLDO replies, “Firing/Number of chutes or machine
speed.”
4. Operator monitors machine operation and refills hopper
as needed. Operator observes spheres after they have
made contact with the ground to confirm ignition.
5. When appropriate, RXB1/2 or FIRB communicates,

Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 22 -
“Prepare to stop firing.”
6. PLDO places hand on controls and communicates,
“Ready to stop.”
7. RXB1/2 or FIRB gives the order “Stop firing.”
8. PLDO closes chutes and responds, “Firing stopped.”
9. PLDO observes last sphere clear of the PSD and relays,
“Machine cleared.”
Clear communication is critical to prevent inadvertent
dropping of spheres outside of burn area boundaries.
10. RXB1/2 or FIRB gives order to PLDO to “secure
machine” or “prepare to fire.”
o If securing the machine, operator actions:
a. Hopper feed switch off
b. Drive motor off
c. Glycol pump off
11. PLDO responds appropriately.
12. Conduct a post mission debriefing that includes a
review and update of hazards and risk mitigations.
Emergency Procedures
PLDO notifies Pilot of problem and gives brief description.
1. Pilot should maintain aircraft flight in the burn area until
emergency is resolved.
2. PLDO closes chute feed handles.
3. Jammed Machine: PLDO pulls manual assist wheel
outward and rotates forward then backward. If
obstruction clears, turn on drive motor, check circuit
breaker, and notify Pilot and RXB 1/2 FIRB crew before
resuming operations.
4. Fire in the Machine: PLDO pushes red button
(emergency water) and holds button depressed for up to
30 seconds. If necessary, uses additional container of
water to extinguish fire by pouring down feed chutes in
hopper. If problem persists, land as soon as possible

Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 23 -
5. PLDO notifies Pilot of problem status and takes
appropriate actions.
Although there are two types of machine malfunctions that can
leave a live sphere in the machine and will cause a fire inside,
the emergency corrective procedure is the same.
Post Operations
1. Conduct and After Action Review (AAR) to identify
areas for improvement and highlight the strengths of
the operation.
2. Remove and clean the PSD Machine according to
manufacturer’s instructions.
3. Complete the PSD Log for use.
Complete required documentation: Unit log, training
documentation, flight use invoice, and SAFECOM if applicable.
Interaction/Activity: REVIEW QUESTION
Question: What are the two actions to be taken if a fire occurs
in the machine?
Answer:
1. Notify the Pilot
2. Press the Emergency Water Switch
Segue to next module: Fuels and Fire Behavior
An understanding of the fire environment will help PLDO’s
understand the advantages of using the PSD machine to
achieve specific burn objectives.

Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 24 -
Est. Instruction
Time: XX min.
Module 3: Fuels and Fire Behavior
PPT – Module 3
Introduce the module/topic:
An understanding of the fire environment will help PLDO’s
understand the advantages of using the PSD machine to
achieve specific burn objectives.
PPT – Objectives
Objective:
After completing this module, participants should be able to:
7. List three advantages of using the PSD machine
versus the helitorch aerial ignition device.
Key teaching points to accomplish module objectives:
Discuss advantages and disadvantage of using the PSD
versus the helitorch.
PPT – Title of
Slide
PPT – Title of
Slide
Est. Time for
Activity: XX min.
PW Page: XX
Fire Environment
Aerial ignition can utilize firing patterns that could not be
implemented by ground forces due to safety concerns.
The PSD machine was developed to provide a method of
igniting ground fuels, in a short time, on large acreage without
causing undue damage to the over story.
Faster speed, additional chutes and strip spacing/timing could
create a more intense burn pattern. Likewise a slower speed,
fewer chutes and strip spacing/timing could produce a lower
intensity burn pattern.
PSD operators should maintain situational awareness of the
flight pattern as it relates to approaching fuel types, the ignition
pattern, and unit boundaries.
Fuels, weather, topography, fire behavior and ignition pattern
interact to create fire effects.
The desired objectives of the plan will determine the fire type:
1. surface fire
2. crown fire
Adjustments to firing patterns can be made to produce fire

Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 25 -
effects that will meet burn objectives.
If the objective is to burn the over story with a rate of high
mortality, the helitorch would be a more effective tool to create
that desired condition.
Advantages of PSD versus the Helitorch Aerial Ignition
Device
Better Control
Firing Boss onboard helicopter
Operator can assess / address problems
Operator can monitor quantity of spheres remaining
Less Complex
Separate helibase is not required
Spheres safer to transport and handle
Lower Cost
Lower equipment cost
Less support staff
Fire Behavior
Minimum damage to the tree canopy
Possible to lay very long ignition lines
Disadvantages of PSD versus the Helitorch Aerial Ignition
Device
Fire Behavior
Spheres burn for a shorter time
Cannot duplicate the helitorch drop pattern
Fire lines take longer to form
Safety
Possible fire in PSD
Requires constant operator attention
Pilot cannot jettison PSD
Instructor Note:
Additional training of fire behavior and ignition operations can
be found in the following NWCG Training Courses:
http://training.nwcg.gov/
S-290 Intermediate Wildland Fire Behavior
S-219 Firing Operations

Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 26 -
Interaction/Activity: REVIEW QUSTION
Question: Aerial ignition can utilize firing patterns that could
not be implemented by ground forces due to safety concerns.
True or False?
Answer: True.
Segue to next module: PSD Function and Maintenance
Let’s take a look at the function of each PSD Machine.
Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 27 -
Est. Instruction
Time: XX min.
Module 4: PSD Function and Maintenance
PPT – Module 4
Introduce the module/topic:
This unit covers all the PSD Machines approved for use. Focus
the learning objective to the machine(s) on site for bench
testing. (Example: If the Premo Mark III is the only machine for
use and bench testing, that is all that is covered – the
additional sections are OPTIONAL to cover for
informational purposes only.)
The Missoula Technology and Development Center has the
latest information for Aerial Ignition.
http://www.fs.fed.us/t-d/aerial_ign/plsphere/training/index.htm
This site is your information source for:
o Equipment and spare parts information
o Operating manuals and guides
o Links to training sites
o Mixing instructions and Material Safety Data Sheets
(MSDS)
o Ignition system residue reports
o Links to aviation, D.O.T. (Department of Transportation),
and other Web sites
PPT – Objectives
Objective(s):
After completing this module, participants should be able to:
8. Identify the parts and basic functions of each PSD
machine.
9. Demonstrate knowledge to perform routine
maintenance on the PSD machine.
10. Demonstrate knowledge and perform a bench-test of
the PSD machine.
11. Demonstrate knowledge and perform the operational
functions of the Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator
(PLDO) duties as identified in the position Task book.
Key teaching points to accomplish module objectives:
Identify the individual parts of the PSD Machine.
Identify the basic functions of the PSD Machine.

Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 28 -
Identify the routine maintenance procedures for the PSD
Machine.
Identify the steps to bench test the PSD Machine.
Identify the steps to perform the operational functions of
the PLDO duties as identified in the position Task book
located in Appendix C.
PPT – Title of
Slide
PPT – Title of
Slide
Est. Time for
Activity: XX min.
PW Page: XX
Premo Mark III Aerial Ignition Device
The Premo Mark III is the most common machine in use for
PSD operations.
Incorporated into the mainframe of the Premo Mark III are the
power train, glycol pump, glycol tank, separate water reservoir
and pump, slipper blocks and injection mechanism.
The dispenser contains four slipper blocks and chutes. The
drive motor speed and the number of chutes open can be
varied to determine the number and spacing of ignition sources
on the ground.
Power is supplied to the dispenser from the aircraft power
supply (24V DC) through a quick-disconnect fitting. A central
control panel contains all the electrical components and
switches to operate the different stations such as the main
drive, glycol pump, slow-fast speed and the emergency water
supply. The switches are series wired so that the drive motor
can be operated independently of the pump but the pump will
not operate unless the drive motor is turned on. This allows
cycling of unprimed spheres for testing. Caution however,
should always be taken, as a small amount of glycol may enter
a sphere even if the glycol pump is not on. Care should be
taken to dispose of these test spheres appropriately.
(See Section 6 of Premo PSD manual for electrical
schematics.)
Parts of the dispenser and function
A. Main frame: Constructed of heavy gauge aluminum, 61
pounds with glycol.
B. Cap for glycol tank: Must be tight, leak proof, and vented.
Check seal. Note: Ethylene Glycol is corrosive to the airframe.
Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 29 -
C. Feed chute: Feeds balls from hopper to injection assembly.
D. Hopper: Holds 450 spheres. Separate unit that mounts on
the mainframe. Contains motorized shaker that prevents the
balls from jamming.
E. Tie down straps: Two-inch wide nylon webbing used to
secure machine to aircraft. (Longer straps will be required for
some types of aircraft.)
F. Power cable: From aircraft. 12- or 24-volt.
G. Emergency water tank: Holds .8 gallons. The emergency
water supply is for extinguishing fires in the PSD.
H. Feed control: Four levers control ball entry to slipper blocks.
Determines number of spheres ejected. Newer models have
locking levers.
I. Manual assist: Gear used to manually cycle injection
mechanism. It is used to clear PSD following a power loss or
jam.
J. Exit chute: Ensures all spheres will fall clear of aircraft.
Ensure knurled nuts and wing nuts are tight. Extensions are
used in some aircraft.
K. Control panel: Switches, fuses and breakers to control
pumps, emergency water, main power, and slipper block speed.
L. Hopper power cord: Provides power to shaker assembly in
the hopper.
M. Hopper controls: Switches, fuses and breakers.
N. Transparent plastic lid: Must be on Premo Mark III.
Specifications
o Main frame mass, glycol full 27.5 kg 61.0 lb.
o Hopper and chutes 10.5 kg 23.0 lb.
o Emergency water tank full 3.8 kg 8.5 lb.
o Hopper capacity (450 spheres) 2.7 kg 6.0 lb.
o Approximate operational weight 44.5 kg 98.0 lb.
o Glycol tank volume 9.0 liters 2.4 US
o Emergency water tank volume 3.2 liters 0.8 US

Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 30 -
Instructor Note: Emergency water is power dependent.
Cleaning and Maintenance
A. Tool Kit
1. 1/8 and 3/16 Slot screwdrivers
2. No.0, No.1 and No.2 Philips Screwdrivers
3. No.1 Robertson screwdriver (square drive)
4. Set of Imperial Allen keys
5. Set of wrenches (5/16, 3/8, 7/16, ½, 9/16, 5/8, 11/16)
6. Adjustable pliers and adjustable wrench
7. Wire cutters and wire strippers
8. Soldering iron and solder
9. Small smooth file for emergency touch up to the needles
10. Cleaner or degreaser
11. Small can of lubricant (Tri-Flow or Never-Seize)
12. Permatex No.2 form-a-gasket sealant for all pipe threads
(non-hardening)
13. Brass wool for cleaning
14. Small brush for cleaning
15. Special rubber tool to remove light bulbs
B. Spare Parts
1. Fuses 5A, 2A, 2 amp circuit breakers (Klixon)
2. Needles (set of four)
3. Valve springs (set of four)
“O” rings for valve stems (set of four)
4. Pump
5. Drive motor
6. Bulbs for indicator lights
7. Solenoid
Instructor Note: The motors used for the main drive and the
hopper are identical, however, the hopper motor uses the
high-speed wire for its operation. The pumps used for the
glycol and the emergency water are also identical. It is
therefore only necessary to carry one of each to ensure rapid
replacement.
C. Cleaners and Lubricants
Use a citrus based cleaner / degreaser to clean (Simple Green®
or equivalent).

Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 31 -
D. Daily Cleaning for Multiple Day Operations
1. Wipe down hopper
2. Check linkages for wear
3. Inspect glycol & water pumps and hose connections
4. Clean using cloth and cleaner / degreaser as required
5. Check condition of needles and sharpen as required
6. Check pump(s) operation
7. Clean needle block assembly area regularly
8. Clean using a cloth and cleaner / degreaser
9. Check for smooth operation and signs of wear
10. Wipe tank surfaces with cloth to remove any glycol
11. Check tanks and lines for signs of leakage
E. Long Term Storage
1. Drain the glycol tank
2. Drain the water tank
3. Store PSD indoors at room temperature
4. Store PSD spheres in a dry location to avoid humidity
5. Confirmed, specific shelf life is not currently known
exactly but reducing stored spheres from exposure to
humidity can extend the life of the spheres and see
consistent performance over many years.
http://www.premofire.com
http://www.sei-ind.com/fireignition
Interaction/Activity: REVIEW – HANDS ON
Ask students to demonstrate how to perform the bench
test and maintenance on the PSD machine.
PPT – Title of
Slide
Red Dragon
In 2006 SEI Industries introduced its Red Dragon Dispenser
and Dragon Egg Spheres aerial ignition spheres.
Parts of the dispenser and function
A. Mounting System
o Removable adapter fits the body contour of Bell 206

Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 32 -
PPT – Title of
Slide
Est. Time for
Activity: XX min.
PW Page: XX
series aircraft. For aircraft with flat cabin floors, an
adapter is not required.
o Nylon “Y” strap secures dispenser to the aircraft.
Standard strap suits all type III helicopters.
B. Tank Assembly
o Acts as a frame to which other components are mounted
o Contains the water and glycol tanks.
o Drain valves for tanks
C. Hopper
o Stores 950 unprimed spheres.
o Agitator provides a constant supply of spheres to the
feed gates.
o Receives power from gate assembly via an automatically
mating plug.
D. Feed Gate Assembly
o Controls the flow of spheres from the Hopper into the
Injection Head.
o Easily removable from the Injection Head.
o Feed gate position controlled by a toggle switch on the
remote control.
o Manual override to close and lock the feedgate.
E. Injection Head
o Injects the spheres with glycol.
o One reciprocating shuttle with two sphere cavities.
o Two constant displacement glycol pumps that inject the
same amount of glycol regardless of drop rate. No need
to calibrate.
o Water nozzles connected to the emergency water tank
and pump to direct water into the injection chamber.
o Manual hand wheel to drive cam and shuttle in case of
power failure. Machine can be turned in either direction.
F. Outlet Chute
o Guides primed spheres from the Injection Head to a
point below the aircraft.
G. Main Control Panel
o Houses the main control board, switches and indicators.
o “RUN/STOP” switch controls the hopper motor and
enables the injection drive motor.
o “RUN/STOP” indicator illuminates when the hopper
motor is turned on. It flashes when the injection drive
motor is running.

Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 33 -
o “WATER” switch activates the emergency water pump.
This switch is always active because of battery backup.
o “LOW WATER” indicator illuminates when the water level
is too low and the machine will not start.
o “RESET” switch controls the count display. Pushing the
switch toggles between trip count and lifetime count.
Pushing and holding resets the trip count.
o “POWER” indicator illuminates when the machine is
connected to an external power source.
o “MOTOR FAULT” indicator illuminates when the injection
drive is jammed.
o Pump indicator illuminates when the emergency water
pump is operating.
o Segment LED displays the sphere count and low battery
warning message.
H. Tethered Remote Control
o Controls the feed gates and adjusts the drop rate.
o Seven-position “SPEED” knob to adjust the drop rate.
o “FEED GATE” momentary toggle switch opens and
closes the feed gates and controls the injection drive
motor.
o “POWER” indicator illuminates when dispenser is
connected to an external power source.
o “RUN/STOP” indicator illuminates when hopper motor is
turned on. It flashes when injection drive motor is
running.
o “FAULT” indicator flashes when there is a problem.
I. Power Cords
o The main power cord connects dispenser to aircraft’s
power system using a standard MS3116F-12-3P plug.
o The auxiliary power cord connects to the auxiliary power
supply or to batteries.
Dispenser Specifications
1. Performance
# of Speeds 7
Min Drop Rate 25 spheres per minute
Max Drop Rate 175 spheres per minute
Hopper Capacity 950 spheres
2. Power
Voltage 24-324 – 32 VDC2 VDC
Connector MS3116F-12-3P (A +28, B Gnd)
Circuit Breaker 5A, MS3320
3. Fluid Volumes

Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 34 -
Glycol Tank 0.8 gal 3.2 liter (5000 spheres)
Water Tank (Full) 0.5 gal 1.9 liter
Water Tank(Min) 0.4 gal 1.5 liter
4. Weights
Red Dragon 48.0 lb. 21.8 kg
Spheres (950) 10.0 lb. 4.5 kg
Ethylene Glycol 7.9 lb. 3.6 kg
Emergency Water 4.1 lb. 1.9 kgl Weight 70.0 lb. 31.8 kg
5. Dimensions
Length 24.5 in 63 cm
Width 10.8 in 27 cm
Height (No Base) 19.0 in 61 cm
Cleaning and Maintenance
A. Tool Kit
1. 1/4” Slotted Screwdriver
2. #1 Phillips Screwdriver
3. 7/16” Combination Wrenches
4. Long Nose Pliers
5. 1/8” Allen Key Wrench
6. 2.5 mm Allen Key Wrench
7. Tip Cleaner Set
8. Metal Bristle Brush
9. Scotch Brite® Abrasive Pad
B. Spare Parts
1. (2) Injection Needles
2. 6mm x 12” Blue Tube
3. 6mm x 12” Red Tube
4. 8mm x 32” Red Drain Tube
5. (2) 6mm Tube Caps
C. Cleaners and Lubricants
1. Use a citrus based cleaner / degreaser to clean the Red
Dragon (Simple Green® or equivalent).
2. The running surfaces of the injection head are self-
lubricating. Do not lubricate with WD-40® or light
machine oil. These will cause potassium permanganate
residue to accumulate and may cause mechanical
seizure.
D. Daily Cleaning for Multiple Day Operations
1. Hopper
(a) Remove the hopper from the Red Dragon
(b) Empty any remaining spheres.
(c) Wipe down interior of hopper

Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 35 -
(d) Check agitator and linkage for signs of wear.
2. Gate Assembly
(a) Unlock gate and remove assembly from
injection head.
(b) Unlock the feed gate control rod using
screwdriver.
(c) Clean the sphere paths using a cloth and a
citrus based cleaner / degreaser.
(d) Close gates using manual knob and check
lock.
3. Glycol Pumps
(a) Remove glycol pump assemblies from
injection head
(b) Clean using cloth and cleaner / degreaser as
required
(c) Check condition of needles and sharpen as
required.
(d) Check the pump operation.
4. Injection Head
(a) Loosen any potassium permanganate residue
from the shuttle and injection block using the
wire brush provided.
(b) Clean the surfaces of the injection block and
shuttle using a cloth and cleaner / degreaser
as required.
(c) Rotate the handwheel and check for smooth
operation
(d) Check cam guides and shuttle guides for signs
of wear.
(e) Replace the glycol pumps.
5. Tank Assembly
(a) Wipe down surfaces with cloth to remove and
glycol
(b) Check tanks and lines for signs of leakage.
E. Long Term Storage
1. Drain the glycol tank.
(a) Insert drain tubing into drain valve.
(b) Using screwdriver, rotate drain valve so slot is
vertical.
(c) Close drain valve when empty.
2. Drain the water tank.
(a) Insert drain tubing into drain valve.
(b) Using screwdriver, rotate drain valve so slot is
vertical.
(c) Close drain valve when empty.

Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 36 -
Interaction/Activity: REVIEW – HANDS ON
Ask students to demonstrate how to perform the bench
test and maintenance on the PSD machine.
Aerostat PSDS Mark V
Aerostat introduced the PSDS Mark V which has the same
footprint at the Premo Mark III but with a stronger hopper and
chassis and lighter gross weight. The parts of the dispenser
and function are the same as the Premo Mark III. It uses the
same diameter sphere as the Premo Mark III.
Dispenser Specifications
1. Dispenser weight fully assembled less glycol and
water 65 lbs.
2. Power source 24 – 28 VDC
3. Dimensions fully assembled
length 27.25 inches
width 10.50 inches
height 26.00 inches
4. Hopper capacity (approx.) 450 spheres
5. Glycol tank capacity 2.4 gal.
6. Emergency water tank capacity .8 gal.
7. Sphere Diameter 1.25 inches
8. Sphere shell material High Impact Polystyrene
Cleaning and Maintenance
A. Tool Kit (Comes with PSDS Mark V)
1. Screw Drivers
2. Cleaning Brushes
3. Tape
4. Pliers
5. Spare Hose and Fitting
6. Scotch Brite® Abrasive Pad
7. Hex Keys
8. Knife
9. Wrenches
10. Spare Hardware
B. Spare Parts

Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 37 -
Provided in the tool kit listed above.
C. Cleaners and Lubricants
To clean the MARK V it is recommended that the user
purchase a bottle of white vinegar and a bottle of 3%
hydrogen peroxide.
Prepare a mixture containing:
1 part water
2 parts white vinegar
1 part 3% hydrogen peroxide
For lubricating the machine, a non-drying, oily film lubricant
such as LPS2 in aerosol form along with an extension tube
that can be inserted in the nozzle is ideal.
1. Liberally apply the lubricant to the slipper block
assembly then use the manual assist wheel to move
the blocks several times to spread the lubricant
around evenly.
2. Using an extension tube on the lubricant can spray
each plunger in the manifold block close to where the
plunger enters the block. Then depress each plunger
several times to spread the lubricant.
3. Insert the extension tube behind the manual assist
wheel into the chain drive cover and spray. Turn the
manual assist wheel about a half turn and spray
again. This will get lubricant on to the drive chain and
drive gears.
Keep in mind that a machine can never be over lubricated
providing the right lubricant is used.
SAFETY NOTE: Do not store the cleaning solution near
aerial ignition spheres as contact between the two may
result in ignition.
Contact Aerostat, Inc. at (352) 787-1348 for support if
needed.
D. Daily Cleaning for Multiple Day Operations
1. In a well-ventilated area using rubber gloves and
goggles apply the solution to the machine (i.e., use a
spray bottle, a brush, cloth, etc.).
2. Work the solution into heavily soiled spots with a
brush and then let it stand for no more than 15
minutes [Note: If left on more than 15 minutes the
Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 38 -
solution may begin to corrode some metal parts.]
3. Spray the machine with a water hose to remove all of
the solution. Once it is completely rinsed [Note: Don’t
forget the rinse the bottom of the machine.] move it to
a dry location and allow it to air dry.
E. Long Term Storage
Carefully remove the dispenser from the helicopter and place it
on a solid surface.
1. Empty any spheres that may be remaining in the
hopper and inspect the four chutes to be certain no
spheres are left in them.
2. Remove the hopper from the mainframe section of
the dispenser.
3. Drain the water tank by removing the cap and then
lifting it from the PSD and turning it over.
4. Drain the glycol by positioning the machine so that
the drain valve located at the bottom of the glycol
tank is accessible. Open the valve and allow the
glycol to flow out into a container.
5. Place the stabilization tray into the transit case so
that it will sit under the mainframe.
6. Place the mainframe and hopper in their respective
places in the transit container. (NOTE: When properly
placed in the container the tops of both the
mainframe and hopper should be parallel to the upper
edge of the case.)
7. Place the drop chute extension in the case making
certain it is properly placed in the designated spot.
8. Close the transit case lid and make sure it latches.
[NOTE: If the lid does not drop down easily and latch
the machine is not properly positioned in the case.]
Interaction/Activity: REVIEW – HANDS ON
Ask students to demonstrate how to perform the bench
test and maintenance on the PSD machine.
Segue to next module: References and Resources
Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 39 -
Est. Instruction
Time: XX min.
Module 5: References and Resources
PPT – Module 5
Introduce the module/topic:
The Aerial Ignition Unit is committed to providing up-to-date
information to the users in the field.
PPT – Title of
Slide
PPT – Title of
Slide
Est. Time for
Activity: XX min.
PW Page: XX
Resources
The Missoula Technology and Development Center has the
latest information for Aerial Ignition.
http://www.fs.fed.us/t-d/aerial_ign/plsphere/training/index.htm
This site is your information source for:
o Equipment and spare parts information
o Operating manuals and guides
o Links to training sites
o Mixing instructions and Material Safety Data Sheets
(MSDS)
o Ignition system residue reports
o Links to aviation, D.O.T. (Department of Transportation),
and other Web sites
The Bureau of Land Management’s Aviation Website also
provides limited information related to aerial ignition training.
http://www.blm.gov/nifc/st/en/prog/fire/Aviation/training.html

Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 40 -
Est. Instruction
Time: XX min.
PPT – Summary
PPT – Objectives
Review
Summary
Review the course objectives and address any remaining
questions.
Objectives:
1. Identify the approved Plastic Sphere Dispenser
(PSD) machines approved for use as identified in the
Interagency Aerial Ignition Guide.
2. Identify the organization required for a safe operation.
3. Identify the requirements for safely working with the
hazardous materials involved with PSD operations.
4. Demonstrate knowledge of the operational functions
before, during and after the project.
5. Demonstrate knowledge of the firing commands and
actions of a PSD operator.
6. Demonstrate knowledge of emergency procedures.
7. List three advantages of using the PSD machine
versus the helitorch aerial ignition device.
8. Identify the parts and basic functions of each PSD
machine.
9. Demonstrate knowledge to perform routine
maintenance on the PSD machine.
10. Demonstrate knowledge and perform a bench-test of
the PSD machine.
11. Demonstrate knowledge and perform the operational
functions of the Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator
(PLDO) duties as identified in the position Task book.
PPT - Exam
PPT - Questions
and Evaluations
Distribute and administer the course exam.
Once again, ask students if they have any remaining questions.
If you have any questions, contact your agency representative
of the Aerial Ignition Unit.

Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 41 -
APPENDIX A: Helibase Briefing Checklist (HJA-1)

Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 42 -

Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 43 -
Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 44 -

Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 45 -

Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 46 -

Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 47 -
Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 48 -
APPENDIX B: MTDC Drawing # 993

Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 49 -
Appendix C: Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator (PLDO)
Position Task book
(When available, place here.)

Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 50 -
Appendix D: PLDO Exam

Revised January 29, 2015
PLDO Plastic Sphere Dispenser Operator Instructor Guide - 51 -
Appendix E: PLDO Exam ANSWER KEY
