
Guidance Document on Federal Interim
Groundwater Quality Guidelines for Federal
Contaminated Sites
November 2012
Update of the May 2010 version
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

LIBRARY AND ARCHIVES CANADA CATALOGUING IN PUBLICATION
Guidance Document on Federal Interim Groundwater Quality Guidelines for Federal Contaminated Sites
also in French under title:
Recommandations fédérales intérimaires pour la qualité des eaux souterraines sur les sites contaminés
fédéraux
ISBN no. 978-1-100-22281-3
Cat. no. En14-91/2013E-PDF
DISCLAIMER
Her Majesty is not responsible for the accuracy or completeness of the information contained in the
reproduced material. Her Majesty shall at all times be indemnified and held harmless against any and
all claims whatsoever arising out of negligence or other fault in the use of the information contained in
this publication or product.
The information in this document does not constitute legal advice; following this guidance will not
necessarily ensure compliance with federal, provincial, or any other regulatory requirements. In case
of discrepancy between this information and any Acts of Parliament, most notably the Canadian
Environmental Protection Act, 1999 or the Fisheries Act or regulations made under these Acts, the Acts
of Parliament and associated regulations take precedence. Notwithstanding any other regulatory or
permitting requirements, any deposits, discharges and releases from your operations or activities must
comply with all applicable federal Acts and regulations.
COPYRIGHT
Information contained in this publication or product may be reproduced, in part or in whole, and by
any means, for personal or public non-commercial purposes, without charge or further permission,
unless otherwise specified.
You are asked to:
Exercise due diligence in ensuring the accuracy of the materials reproduced;
Indicate both the complete title of the materials reproduced, as well as the author organization;
and
Indicate that the reproduction is a copy of an official work that is published by the Government of
Canada and that the reproduction has not been produced in affiliation with or with the
endorsement of the Government of Canada.
Commercial reproduction and distribution is prohibited except with written permission from the
Government of Canada's copyright administrator, Public Works and Government Services of Canada
(PWGSC). For more information, please contact PWGSC at 613-996-6886 or at
droitdauteur.copyright@tpsgc-pwgsc.gc.ca.
© Her Majesty the Queen in Right of Canada, represented by the Minister of the Environment, 2013.
Aussi disponible en français.
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080
Preface
The Federal Contaminated Sites Action Plan (FCSAP) was established to help federal
departments, agencies and consolidated Crown corporations (referred to as custodians)
address federal contaminated sites, so as to reduce environmental and human health risks as
well as federal financial environmental liability associated with the higher risk federal
contaminated sites.
The Federal Interim Groundwater Quality Guidelines presented in this report were developed to
assist federal custodians in assessing, remediating/risk managing federal contaminated sites
funded under the FCSAP. Federal custodians are advised to use these interim guidelines as an
interim measure until Canadian groundwater quality guidelines are available.
This report was developed based on a study conducted for Environment Canada by Meridian
Environmental Inc. to review existing approaches for deriving groundwater quality guidelines
used by other jurisdictions in Canada and other countries, and recommended one of them that
can be adapted for use at federal contaminated sites. The study was conducted under the
guidance of an Environment Canada working group of experts, and reviewed by the Expert
Support Science Department of Health Canada and Fisheries and Oceans.
An update of the May 2010 version of this guidance document is required as it contains a
number of groundwater guidelines that were calculated based on The Rationale for the
Development of Soil and Groundwater Standards for Use at Contaminated Site in Ontario
(2009) developed by the Ontario Ministry of the Environment. These guidelines have been
revised since then. In addition, comments were solicited from custodians and consultants
based on their experiences in applying the May 2010 version of the Federal Interim
Groundwater Quality Guidelines at their contaminated sites. These comments were considered
and addressed where appropriate in the current version of the guidelines.
November 2012
Update of the May 2010 Version
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080
OVERVIEW OF CHANGES MADE SINCE THE MAY 2010 VERSION OF THE GUIDANCE
DOCUMENT ON FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES FOR
FEDERAL CONTAMINATED SITES (FIGWQGS)
Clarified that the 2012 update supersedes the May 2010 version of the this document
Updated year of publication for guidelines where applicable
Removed sentence “and in many cases may not discharge to nearby surface water
bodies” from 5th paragraph under the “Background on Groundwater” section (Section 2)
Removed 4th bullet on The Canadian Water Quality Guidelines for the Protection of
Agricultural Water Uses as an additional set of guidelines that is relevant for
groundwater at federal contaminated sites as these guidelines are already incorporated
in Table 1-3 (Section 3)
Removed 7th bullet on “use of groundwater for human consumption (i.e. drinking water)”
as a potential receptors and exposure pathways considered under the Federal Interim
Groundwater Quality Guidelines. The protection of drinking water is addressed
separately by the Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality that should be used in
conjunction the FIGWQGs (Section 3)
Added a section on “Guidelines Lower than Detection Limits” as a special considerations
on the application of the numerical guidelines (Section 4.3)
Added a paragraph that clarified situations when the FIGWQGs apply to dissolved or
total concentrations in groundwater (Section 4.3)
Revised section on Application on First Nation Lands to state that “For contaminated
sites on settlement lands, First Nations (e.g. in Yukon Territory) may have the right to
request more stringent standards/guidelines for water quality than those provided in
Federal or Territorial laws (Section 4.3)
Clarified the “Drinking water” section under “Pathways Elimination” that protection of
drinking water may also need to be considered if contaminated groundwater may impact
surface water used for drinking water supply (Section 5.2)
Revised “Protection of freshwater/marine life” section under “Pathways Elimination” to
provide clarification and guidance on when to eliminate this pathway (Section 5.2)
Clarified and clearly define “conservative solute” (Section 5.2)
Added FCSAP Ecological Risk Assessment guidance documents to current list of
references relevant while conducting site-specific risk assessments (Section 6)
Reviewed and updated all federal interim groundwater quality guidelines adopted from
Ontario MOEE 1997 to be in line with the newly released OMOEE groundwater
guidelines (Appendix A, Table 1-3)
Revised Appendix B to include models, equations and default model parameters used to
calculate Tier 2 guidelines (Appendix B)
Provided additional guidance for the derivation of Tier 2 adjustment factors (calculated
using the Tier 2 model assuming steady-state conditions and no biodegradation, with all
other parameters at Tier 1 default values) (B.3 Groundwater Transport)
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Glossary i
1 INTRODUCTION 1
2 BACKGROUND ON GROUNDWATER 2
3 BASIS FOR THE GUIDELINES 4
4 APPLICATION OF THE TIER 1 AND TIER 2 NUMERICAL GUIDELINES 5
4.1 Factors to Consider 8
4.2 Limitations of the Use of the Numerical Guidelines 10
4.3 Special Considerations on the Application of the Numerical Guidelines 11
5 CONSIDERATION OF SITE-SPECIFIC CONDITIONS (FOR TIER 2) 11
5.1 Guidelines Modification based on Site-Specific Conditions 12
5.2 Pathways Elimination 12
6 SITE-SPECIFIC RISK ASSESSMENT (TIER 3) 14
APPENDIX A
A FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES 15
APPENDIX B 63
MODELS, EQUATIONS AND DEFAULT MODEL PARAMETERS USED TO CALCULATE TIER 1 AND TIER 2
GUIDELINES
REFERENCES 75
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080
i
GLOSSARY
Active layer: The soil layer in Northern regions with permafrost that melts in the summer and
re-freezes in the fall or winter.
Aquifer: A geologic formation(s) that has the ability to store and/or transmit water, such as to
springs. Use of the term is usually restricted to water-bearing formations capable of yielding
water in significant quantities sufficient to constitute a usable supply for people’s uses.
Background concentration: Representative, naturally occurring level of a contaminant in the
environment. Reflects natural geologic variations.
Coarse-grained soil: Soil which contains greater than 50% by mass particles greater than 75
μm mean diameter (D50 > 75 μm).
Confined aquifer: A region of soil or rock below the land surface that is saturated with water.
There are impermeable material layers above and below it and it is under pressure so that when
the aquifer is penetrated by a well, the water will rise above the top of the aquifer.
Dilution factor: A constant applied to groundwater guidelines to address the decrease in
concentration as contaminants are transported to surface water due to dilution.
Ecological receptor: A non-human organism potentially experiencing adverse effects from
exposure to contaminated media either directly or indirectly (food chain transfer).
Ecosystem: A dynamic complex of plant, animal and micro-organism communities and their
non-living environment interacting as a functional unit.
Fine-grained soil: Soil which contains greater than 50% by mass particles less than 75 μm
mean diameter (D50 < 75 μm).
Groundwater: Subsurface water beneath the water table in fully saturated geologic formations.
Hypolentic zone: Transition zone between groundwater and surface water beneath lakes and
wetlands.
Hyporheic zone: Transition zone between groundwater and surface water beneath streams
and rivers.
Offset distances: A minimum distance from a receptor where guidelines do not apply, due to
limitations in transport models or other invalidated guideline assumptions.
Receptor: A receptor is the person or organism exposed to a chemical. For
human health risk assessment, it is common to define a critical receptor as the person
expected to experience the most severe exposure (due to age, sex, diet, lifestyle, etc.) or most
severe effects (due to state of health, genetic disposition, sex, age, etc.) as a result of that
exposure.
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080
ii
Recharge: Process which occurs when the water content of the unsaturated zone becomes
high enough to cause excess water to percolate downward to the water table, usually as a result
of the infiltration of snow melt or rainwater into surface soils. Using a water balance approach,
recharge is equal to the total amount of precipitation less the amount of surface runoff and
evapotranspiration.
Pore water: The water occupying the space between particles of sediment or soil.
Solubility: The maximum concentration of a chemical that can be dissolved in water when that
water is both in contact and at equilibrium with the pure chemical.
Subsurface: Unconsolidated regolith material above the water table not subject to soil forming
processes.
Transition zone: The area where groundwater enters a surface water body.
Unconfined aquifer: A region of saturated ground material not overlain by an impermeable or
low-permeability layer such as clay, whose upper water surface (water table) is at atmospheric
pressure, and thus is able to rise and fall. These systems allow for the draining of pore water
and the subsequent movement of air (or water) to fill the spaces vacated by the moving water.
Water table: Depth below which soil is saturated with groundwater.
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080
1
1 INTRODUCTION
The Federal Contaminated Sites Action Plan (FCSAP) was established in 2005 as a 15-year
program with a commitment of $3.5 billion from the Government of Canada. The program helps
federal departments, agencies, and consolidated Crown corporations (referred to as custodians)
determine if a site is contaminated and, if so, to what extent. Where appropriate, it provides
financial assistance to deal with the environmental and human health risks that these sites may
pose.
Federal contaminated sites are generally evaluated using the Canadian Environmental Quality
Guidelines (CEQG) (CCME 1999) developed by the Canadian Council of Ministers of the
Environment (CCME). The CEQGs are primarily risk-based numerical guidelines set at levels at
which it is believed that unacceptable adverse effects on environmental or human health will not
occur. These were developed for various media: water, soil, and sediments, and biological
tissue. For some media (e.g. surface water, soil), there is a multi-tier framework that allows for
the application of generic numerical guidelines, the modification of guidelines based on site-
specific conditions, or the use of site-specific risk assessment. While the Canadian Soil Quality
Guidelines (CCME 1999) include consideration of the protection of groundwater for organic
chemicals, there are currently no Canadian Environmental Quality Guidelines for groundwater.
In the absence of national groundwater guidelines, provincial guidelines are sometimes applied
at federal contaminated sites, or in other cases, potable water guidelines, and/or surface water
quality guidelines are often applied for groundwater – either directly or with an arbitrary
adjustment factor. In recognizing the need for a nationally-consistent approach for assessing
and managing groundwater at federal contaminated sites, Environment Canada conducted a
study to develop a federal approach that would be based on a critical review and evaluation of
existing approaches used by other jurisdictions in Canada and in other countries. Meridian
Environmental Inc. conducted such a review for Environment Canada, and recommended
Federal Interim Groundwater Quality Guidelines, presented in this report, that should be used
by custodians to assess, remediate/risk manage contaminated groundwater at federal sites
funded under FCSAP. This report was prepared for the FCSAP Secretariat of Environment
Canada and is based on the recommendations provided by Meridian Environmental Inc. in their
study.
The Federal Interim Groundwater Quality Guidelines are intended to be used as an interim
measure until CEQGs for groundwater are available. This update supersedes the May 2010
version of the Federal Interim Groundwater Quality Guidelines. A draft CCME protocol for the
derivation of groundwater quality guidelines for contaminated sites has recently been
developed; once that protocol is finalized, guidelines developed under the CCME protocol would
supersede the Federal Interim Groundwater Quality Guidelines presented herein. Until such
time, the Federal Interim Groundwater Quality Guidelines are to be used in connection with
groundwater investigation and remediation activities at federal contaminated sites.
An update of the May 2010 version of this guidance document is required as it contains a
number of groundwater guidelines that were calculated based on The Rationale for the
Development of Soil and Groundwater Standards for Use at Contaminated Site in Ontario
(2009) developed by the Ontario Ministry of the Environment. These guidelines have been
revised since then. In addition, comments were solicited from custodians and consultants
based on their experiences in applying the May 2010 version of the Federal Interim
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080
2
Groundwater Quality Guidelines at their contaminated sites. These comments were considered
and addressed where appropriate in the current version of the guidelines.
These guidelines are intended as assessment and remediation criteria for contaminated sites,
and should not be construed as “pollute up to” levels. The Federal Interim Groundwater Quality
Guidelines follow a tiered framework, consistent with the Canadian Soil Quality Guidelines
development through the CCME. The tiers are:
Tier 1: direct application of the generic numerical guidelines; specifically, application of
the lowest guideline for any pathway
Tier 2: allows for the development of site-specific remediation objectives through the
consideration of site-specific conditions, by modifying (within limits) the numerical
guidelines based on site-specific conditions and focusing on exposure pathways and
receptors that are applicable to the site
Tier 3: use of site-specific risk assessment to develop Site-Specific Remediation
Objectives
The Federal Interim Groundwater Quality Guidelines presented in this report have been adopted
from other jurisdictions, with some modifications, and are based on common risk assessment
methods. Quantitative human health and environmental risk assessments involve a number of
uncertainties and limitations. As a consequence, the use of the recommendations presented
herein may either be overly protective or may not necessarily provide complete protection of
human and environmental receptors or prevent damage of property in all circumstances. The
generic (i.e. Tier 1) guidelines are not intended for application at all sites without consideration
of the sensitivity of the site and its characteristics, as discussed below. However, it is expected
that the generic guidelines will be protective of the majority of federal contaminated sites. Sites
that are more sensitive than what was assumed for the derivation of the generic guidelines must
be assessed at higher tiers; at other sites of lower sensitivity it may be advantageous to proceed
to the higher tiers.
This report is organized in six sections. Section 1 provides general background information on
the FCSAP program and the Federal Interim Groundwater Quality Guidelines. Section 2
provides general background on groundwater. Section 3 describes the basis of the Federal
Interim Groundwater Quality Guidelines. Section 4 describes how the generic numerical
guidelines (Tier 1) are to be applied and their limitations. Section 5 explains how these Tier 1
guidelines can be modified for site-specific conditions to generate Tier 2 values. Section 6
provides relevant reference guidance documents that can be used to derive site-specific risk
assessment guidelines (Tier 3). The Federal Interim Groundwater Quality Guidelines are
provided in Appendix A, for the agricultural, residential/parkland, commercial and industrial land
uses. Finally, Appendix B provides the equations and default model parameters that were used
to derive the Tier 1 generic numerical guidelines, so that Tier 2 numbers can be derived if
required.
2 BACKGROUND ON GROUNDWATER
The term “groundwater”, in its most basic sense, refers to water beneath the ground surface.
For purposes of this document, groundwater refers primarily to water beneath the surface of the
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080
3
water table (i.e. in the saturated zone) in either unconsolidated soils (e.g., gravel or sand) or
bedrock, including both shallow groundwater and deeper aquifers. Groundwater is part of the
hydrologic cycle, and groundwater can be transported to surface water bodies. For
contaminated sites, the most important interaction between groundwater and surface water is
direct discharge of groundwater into surface water bodies such as streams, lakes or wetlands.
Groundwater may also be discharged to the surface (e.g., spring or seepage) and subsequently
reach surface water bodies via surface run-off.
The transition between groundwater and surface water is not a sharp or distinct boundary;
rather, there is a dynamic transition zone from groundwater to surface water. This transition
zone is considered to be an important component of the surface water ecosystem (US EPA
2008). Transition zones beneath streams and rivers are referred to as hyporheic zones, while
those beneath lakes and wetlands are referred to as hypolentic zones (US EPA 2008). The
transition zone includes the sediment-water interface and sediment beneath and adjacent to the
surface water where surface water conditions may affect groundwater and where surface water
biota (particularly invertebrates, larvae and microbial communities) spend at least part of their
time. The transition zone plays a major role in nutrient and energy cycling in surface water
bodies (Hayashi and Rosenberry 2002), and in some cases has been shown to contribute
significantly to the biodegradation of contaminants (US EPA 2008). Since groundwater typically
has a more stable temperature than surface water, the transition zone can provide a thermal
refuge for fish in summer or winter (Hayashi and Rosenberry 2002). The extent of the transition
zone can vary over time; since groundwater and surface water often have very different
chemical characteristics, the extent can often be determined from water chemistry (Hayashi and
Rosenberry 2002).
Groundwater is also present beneath surface water bodies; for purposes of this document,
water beneath the hyporheic zone or beneath the hypolentic zone is considered to be
groundwater (i.e. the transition zone is not considered as groundwater).
Water within soil pores in the unsaturated zone is referred to herein as pore water. For purposes
of this document, water bodies which support macroscopic life (e.g. fish) in subterranean
caverns are not considered to be groundwater, but rather would be potential receptors.
In areas of Northern Canada with permafrost, water may also be present at least part of the
year in the active layer (the soil layer that thaws during the summer and re-freezes in the fall or
winter). This water is also treated as groundwater for purposes of this document. Some of the
exposure pathways evaluated herein may not apply for the active layer; these pathways could
be excluded on a site-specific basis. For example, the active layer is unlikely to be used as a
source of potable water. Furthermore, permafrost may also thaw near surface water bodies; this
thawed permafrost would also be considered as groundwater for purposes of these guidelines.
The term “aquifer” is used to describe a subsurface formation which can produce enough water
when tapped by a well to be useful (e.g., as a drinking water source). Water in aquifers can
move either through pores or through fractures. In rare cases, particularly in limestone, fractures
may be enlarged to form larger channels or caverns. Aquifers can be unconfined, meaning the
water table is present within the unit, or confined, meaning a relatively impermeable layer forms
the upper boundary of the aquifer.
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

4
3 BASIS FOR THE GUIDELINES
The Federal Interim Groundwater Quality Guidelines have been adopted from other
jurisdictions, with some modifications; however, these guidelines have generally been
developed using methods consistent with nationally approved protocols published by CCME,
and in particular A Protocol for the Derivation of Environmental and Human Health Soil Quality
Guidelines (CCME 2006) and the Canada-Wide Standard for Petroleum Hydrocarbons (PHC) in
Soil: Scientific Rationale and User Guidance (CCME 2008a, CCME 2008b). The Guidelines for
Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada 2008) and the Canadian Water Quality
Guidelines for the Protection of Agricultural Water Uses (CCME 1999) were applied for the
protection of potable water.
In addition to the Federal Interim Groundwater Quality Guidelines, three other sets of guidelines
may be relevant for groundwater at federal contaminated sites:
The Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada 2010 and available
online at http://www.hc-sc.gc.ca/ewh-semt/pubs/water-eau/index-eng.php) apply for
potable water sources; the most recent version of the guidelines should be consulted.
While they are intended to be applied at the point of exposure (e.g., tap), it is
recommended that, at federal contaminated sites, these guidelines be used when
investigating groundwater that could be used as a potable water source. The
determination of a particular aquifer as a potable water source is often under provincial
jurisdiction. In the absence of Federal guidelines for a particular chemical, applicable
provincial guidelines for the protection of potable groundwater should also be applied.
The Canadian Water Quality Guidelines for the Protection of Aquatic Life, summarized in
the Canadian Environmental Quality Guidelines (CCME 1999 and available online at
http://ceqg-rcqe.ccme.ca/) should be applied to the receiving water body, groundwater
within 10 m of a surface water body, and to the groundwater-surface water transition
zone (as defined in Section 2).
The Canadian Sediment Quality Guidelines for the Protection of Aquatic Life,
summarized in the Canadian Environmental Quality Guidelines (CCME 1999 and
available online at http://ceqg-rcqe.ccme.ca/), should be applied for sediments in the
groundwater-surface water transition zone for contaminants that are expected to be
associated with sediments. If both pore water and bulk sediment samples are collected
for comparison with aquatic life and sediment guidelines respectively, both guidelines
should be met.
The Federal Interim Groundwater Quality Guidelines are based on the consideration of several
potential receptors and exposure pathways, including:
groundwater transport to surface water at least 10 m from the contamination and
subsequent exposure of freshwater and marine life
direct contact of soil organisms with contaminated groundwater
use of groundwater for irrigation water
use of groundwater for livestock watering
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080
5
groundwater transport to surface water at least 10 m from the contamination and
subsequent ingestion by wildlife
migration of contaminant vapours to indoor air and subsequent inhalation by humans.
The generic guidelines are point estimates of a chemical concentration in groundwater
associated with an approximate no- to low- effects level based on toxicological information
about the chemical, along with a screening-level evaluation of environmental fate and transport
and estimated intake rates, or exposure, by potential receptors. The assumed receptor
characteristics and fate models are generally the same as those used to derive Canadian Soil
Quality Guidelines (CCME 2006). Details on the models used and model input parameters
applied for guidelines are provided in Appendix B, so that Tier 2 site-specific modification of the
guidelines can be performed.
For inorganic substances, the Canadian Water Quality guidelines for the Protection of Aquatic
Life are applied directly to groundwater, due to the high level of variability in the behaviour of
inorganic substances in groundwater and the lack of biodegradation of these substances.
Inorganic substances could alternatively be evaluated on a site-specific basis. Additionally, for
many organic substances without appropriate groundwater biodegradation rates defined by
CCME or other Canadian regulatory agencies, the groundwater quality guidelines are
essentially equal to the water quality guidelines for the protection of aquatic life because
dispersion alone does not provide significant dilution over the default distance of 10 m. These
substances can also be evaluated on a site-specific basis; it should be stressed that applied
biodegradation rates should be based on site-specific data or data that conservatively reflect
potentially anaerobic degradation in groundwater (not surface water or aerobic degradation
rates).
4 APPLICATION OF THE TIER 1 AND TIER 2 NUMERICAL GUIDELINES
At Tier 1, the generic numerical guidelines are directly applied. It is expected that most sites
would be addressed using the generic numerical guidelines. The Tier 1 numerical guidelines are
presented in Tables 1 to 3 for the agricultural, residential/parkland, commercial and industrial
land uses, respectively.
The Tier 2 approach allows for consideration of site-specific conditions by either modifying
(within limits) the guidelines based on site-specific conditions and/or removing exposure
pathways that may not be applicable to the site.
The columns in Tables 1 to 3 are as follows:
Lowest Guideline – the lowest guideline available selected from all exposure pathways
for that land use.
The existing exposure pathways are:
Inhalation – the guideline based on indoor inhalation by humans.
Soil Organisms: Direct Contact – the guideline for direct contact by plants and soil
invertebrates, calculated from a Canadian Soil Quality Guideline for these receptors.
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080
6
Freshwater Life – the guideline for the protection of freshwater life in a surface water
body at least 10 m from the contamination. For soluble organic chemicals, this value is
calculated from the Canadian Water Quality Guideline for the Protection of Aquatic Life
(freshwater) based on groundwater transport modelling; for other chemicals (e.g.,
inorganics), it is equal to the Canadian Water Quality Guideline for the Protection of
Aquatic Life (freshwater).
Marine Life – the guideline for the protection of marine life in a surface water body at
least 10 m from the contamination. These values are calculated the same way as the
freshwater life values, but using the Canadian Water Quality Guideline for the Protection
of Aquatic Life (marine).
Irrigation – the Canadian Water Quality Guideline for the Protection of Agricultural Water
Uses; Irrigation Water guideline values are used directly.
Livestock – the Canadian Water Quality Guideline for the Protection of Agricultural
Water Uses; Livestock Watering guideline values are used directly.
Wildlife Watering – the guideline for the protection of wildlife watering in surface water at
least 10 m from the contamination.
The “lowest guideline” presented in the first two column of Tables 1 to 3 were provided for
convenience purposes, and represent the lowest guideline values if all the pathways presented
in these tables are present at a site. However, this will often not be the case, and in particular
relatively few sites will have both freshwater and marine water bodies nearby; the use of the
lowest guideline may therefore result in a guideline that is overly conservative. Further
discussion of the applicable pathways is provided in Section 5.2.
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080
7
It is possible that multiple guidelines will apply at a single location. As a general rule, the
following should be applied:
Table 1. Summary of Applicable Groundwater Quality Guidelines
Federal
Interim
Groundwater
Quality
Guidelines
Canadian
Water Quality
Guidelines for
the Protection
of Aquatic Life
Guidelines for
Canadian
Drinking Water
Quality
Canadian
Sediment
Quality
Guidelines for
the Protection
of Aquatic Life
Canadian
Water Quality
Guidelines for
the Protection
of Agricultural
Water Uses
Groundwater as
defined in
Section 2
(including the
active zone in
permafrost
areas)
√
√
(where
applicable)
√
(where
applicable)
Groundwater
within 10 m of a
water body
√
√
(where
applicable)
√
(where
applicable)
Groundwater-
surface water
transition zone
√
√
(where
applicable)
√
(where
applicable)
Sediment pore
water in
groundwater-
surface water
transition zone
√
√
(where
applicable)
√
(where
applicable)
Sediments in
groundwater-
surface water
transition zone
√
(apply to the
sediments)
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

8
The following Figure 1 provides a visual representation of the groundwater and of where the
various guidelines would apply near a surface water body.
Note: Canadian Water Quality Guidelines for the Protection of Agricultural Water Uses and the
Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality may also be applicable where appropriate
Figure 1. Illustration of groundwater cross-section near a surface water body.
4.1 Factors to Consider
In order to apply the numerical Tier 1 and Tier 2 guidelines, the following factors should be
considered.
Soil Type Assessment
Groundwater quality guidelines are presented for both coarse (e.g. sand) and fine (e.g. silt or
clay) soils. Consistent with Canadian Soil Quality Guidelines, coarse soils are defined as having
a median particle diameter greater than or equal to 75 μm, while fine soils have a median
particle diameter less than 75 μm (CCME 2006). The hydraulic conductivity for coarse soils is
typically greater than 33 m/year, while the hydraulic conductivity for fine soils is typically less
than 33 m/year.
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080
9
Groundwater quality guidelines for coarse soils are generally lower than guidelines for fine soils,
and therefore the coarse soil guidelines should be applied unless it can be demonstrated that
site soils are fine-grained, with no coarse layers which could potentially govern contaminant
migration. Even a relatively thin coarse layer in the saturated zone may govern transport
towards downgradient receptors such as surface water bodies. Similarly, a layer of coarse soil
beneath a building foundation may govern the transport of vapours into the building. There are a
few chemicals, however, for which interim guidelines for the protection of soil organisms are
lower for fine soils than coarse soils. Therefore, the lower of the guidelines for coarse and fine
soils should be applied unless thorough investigation of site stratigraphy has been undertaken,
supported by laboratory classification of the soil type, and it can clearly be demonstrated that
the chosen soil type is appropriate.
Distance from Surface Water Bodies
As noted above, the groundwater guidelines as presented in Tables 1 to 3 can only be applied if
the groundwater is taken at least 10 m away from the receiving water body. Canadian Water
Quality Guidelines for the Protection of Aquatic Life are applied within 10 m of a surface water
body and to the transition zone, particularly the part of the transition zone where aquatic and
benthic organisms may reside. The 10 m lateral offset distance should be applied from the
ordinary high water mark or edge of the 1 in 100 year flood zone (see Figure 1). For marine
water bodies, the point of compliance should be established on a site-specific basis, taking into
consideration the maximum expected high tide mark so as to ensure that there is at least a 10
m lateral separation between the contamination and potential habitat for marine aquatic or
benthic organisms. Based on historical practices, it is expected that the extent of the transition
zone will not be regularly determined at federal contaminated sites, although site-specific
determination is recommended.
Water and Land Use Assessment
In order to apply these numerical guidelines, the appropriate land use should be determined. In
many jurisdictions, current uses of groundwater as well as potential future uses must also be
considered. The same land uses specified for Canadian Soil Quality Guidelines (agricultural,
residential/parkland, commercial and industrial) are used for groundwater quality guidelines for
consistency, because soil and groundwater are generally investigated together. These land
uses are defined as follows (CCME 2006):
Agricultural: where the primary land use is growing crops or tending livestock. This also
includes agricultural lands that provide habitat for resident and transitory wildlife and
native flora.
Residential/Parkland: where the primary activity is residential or recreational activity;
parkland is defined as a buffer between areas of residency, and also includes
campground areas, but excludes wild lands such as national or provincial parks.
Commercial: where the primary activity is commercial (e.g., shopping mall) and not
residential or manufacturing; access to the site is generally not restricted. This does not
include zones where food is grown.
Industrial: where the primary activity involves the production, manufacture, or
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080
10
construction of goods. Access to the site is generally restricted.
Groundwater guidelines are generally less dependent on land use than soil guidelines, because
many of the groundwater uses and pathways are independent of human uses of the land. In the
event that none of the defined land uses is appropriate for the site, use of the agricultural
guidelines is generally conservative.
4.2 Limitations of the Use of the Numerical Guidelines
As discussed above, the numerical guidelines were developed using a specific set of
assumptions and models. In some cases, the assumptions used to derive these guidelines may
not be protective for particularly sensitive sites. Any of the following conditions may invalidate
the assumptions used to develop the Federal Interim Groundwater Quality Guidelines, and
therefore would invalidate the use of the numerical groundwater quality guidelines:
Contaminated groundwater within 10 m of a surface water body
For contaminated groundwater within 10 m of a surface water body, accounting for potential
seasonal fluctuations in water and the transition zone, the Canadian Water Quality Guidelines
for the Protection of Aquatic Life should be applied directly.
Groundwater flow to stagnant water bodies
If contaminated groundwater is discharging into a stagnant water body (a water body without
significant outflow), persistent contaminants may be concentrated through evaporation. A site-
specific risk assessment is normally required in this scenario.
Fractured bedrock or fractured silt/clay
The transport models used to develop the numerical guidelines assume that contaminant
transport occurs through unconsolidated soils. If transport between the contaminant source and
receptor (e.g. surface water body) is through fractures instead of unconsolidated soils, either a
transport distance of zero should be assumed (i.e. the Canadian Water Quality Guidelines for
the Protection of Aquatic Life should be applied to groundwater), or a site-specific risk
assessment should be conducted.
Very coarse textured soils enhancing transport or high groundwater velocity
Very coarse (e.g. gravel) soils may result in enhanced contaminant transport compared to what
was assumed in the derivation of the numerical guidelines. Other scenarios resulting in a high
groundwater velocity (e.g. tidal influences close to a marine water body) may also enhance
contaminant transport. If the Darcy groundwater velocity exceeds 3x10
-7
m/s, the groundwater
transport modelling conducted for the numerical guidelines may not be protective of nearby
surface water bodies; in this case, a site-specific adjustment of the guidelines will likely be
necessary. Similarly, if the soil vapour permeability exceeds 6x10
-8
cm
2
, the vapour transport
guidelines may need to be adjusted on a site-specific basis.
Contaminated groundwater within 30 cm of a building foundation
The models used to evaluate vapour intrusion are not considered valid if the source of
contamination is very close to the building; contaminated groundwater in direct contact with a
building in particular is considered to be a high risk situation. In the event that contaminated
groundwater is present within 30 cm of a building foundation, a site-specific risk assessment is
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080
11
normally required.
Earthen Floors or Other Unusual Structural Features
The vapour intrusion model assumes a typical residential or commercial/industrial building with
a concrete foundation slab. The presence of a building with an earthen floor within 10 m of
groundwater contamination indicates that a site-specific risk assessment is required. Other
unusual building features (e.g. unusually low air exchange rate) may need to be addressed in a
site-specific risk assessment or site-specific guideline modification.
4.3 Special Considerations on the Application of the Numerical Guidelines
High Natural Background Concentration
In applying the Federal Interim Groundwater Quality Guideline, it is not expected that
remediation of a contaminated site would be done to levels below natural background
concentrations. However, in some cases where the naturally occurring background
concentrations of contaminants are higher than the Federal Interim Groundwater Quality
Guideline values, the guideline values may still need to be considered in the development of the
risk management approach that would be applied to the site so as to ensure that the site does
not continue to pose an unacceptable risk to human health. For example, groundwater in areas
with high naturally occurring background chemical concentrations (e.g. arsenic, radon, uranium)
may be restricted to non-potable water uses.
Guidelines Lower than Detection Limits
Some groundwater quality guidelines, such as guidelines for the protection of freshwater life for
pesticides, may be lower than detection limits normally achieved by analytical laboratories. In
most cases these guidelines have been adopted from existing CCME water quality guidelines.
The CCME guideline derivation approach does not limit guidelines to concentrations above
analytical detection limits; guidelines are set based on the concentrations which may pose a risk
to relevant receptors.
Dissolved vs. Total Concentrations
For inorganics, the Federal Interim Groundwater Quality Guidelines generally apply to dissolved
concentrations, and therefore filtration of groundwater samples is required. Appropriate
guidance on groundwater sampling methods should be consulted for proper filtration technique.
For organic chemicals, filtration is often not possible, particularly for volatile organic chemicals
which may be lost to volatilization during the filtration process, and therefore unfiltered
groundwater samples are normally used for organic chemicals.
Application on First Nation Lands
For contaminated sites on settlement lands, the First Nation (e.g. in Yukon Territory) may have
the right to request more stringent standards/guidelines for water quality than those provided in
Federal or Territorial laws.
5 CONSIDERATION OF SITE-SPECIFIC CONDITIONS (FOR TIER 2)
The development of site-specific remediation objectives through consideration of site-specific
conditions for deriving Tier 2 groundwater quality guidelines, often referred to as “Tier 2
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080
12
adjustment”, involves the re-calculation of groundwater quality guidelines using the same model
and pathways as for the generic guidelines, but adjusting certain stable, readily adjusted
parameters in the models or by focusing on the receptors that are applicable to the site to reflect
site-specific conditions; or the removal of exposure pathways that are not applicable at a site.
These adjustments may be undertaken either for sites where the generic guidelines are not
applicable, or for sites where it is believed that site-specific conditions may mitigate exposure for
the governing pathway.
5.1 Guidelines Modification based on Site-Specific Conditions
The equations used for site-specific modification of guidelines are presented in Appendix B,
along with default model parameters used to derive the generic guidelines. Further guidance on
site-specific modification of guidelines, including site characterization requirements, whose
parameters can be adjusted, and the adjustment procedures, can be found in the Alberta Tier 2
Soil and Groundwater Remediation Guidelines (AESRD 2010b) or Appendices C and D of the
Canada-Wide Standard for Petroleum Hydrocarbons (PHC) in Soil: User Guidance (CCME
2008b) and Guidance Manual for Developing Site-Specific Soil Quality Remediation Objectives
for Contaminated Sites in Canada (CCME 1996).
5.2 Pathways Elimination
To determine the groundwater quality guidelines that would be applied to a site, and thus to
select the appropriate Tables 1 to 3, the current and intended federal land uses need to be
identified first. Pathways that apply to the site would then be identified, considering both the
current site conditions and reasonably anticipated future federal uses of the site. In addition,
where potable water sources are present in a contaminated site, the Guidelines for Canadian
Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada 2008) should be applied. The groundwater quality
guidelines that apply at the site would be the lowest of the guidelines for all the applicable
pathways.
It should be noted that in some circumstances it may be theoretically possible to screen out all
pathways for a particular chemical. It is recommended that at least one pathway should be
retained unless a site-specific risk assessment can establish an acceptable concentration,
taking into consideration additional factors such as potential free-phase product formation and
other hazards from the chemical, and the possibility that remaining concentrations could act as
a source of further contamination. It is not the intent of these guidelines to allow for unlimited
groundwater contamination in the event that all pathways for which guidelines have been
calculated can be eliminated at a site.
Drinking water
The protection of drinking water is addressed separately by the Guidelines for Canadian
Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada 2010). The drinking water guidelines are applied to
groundwater that is used as a potable water source or to groundwater defined as a potential
potable water source by the province or other agency with jurisdiction over drinking water
issues. The protection of drinking water may also need to be considered if contaminated
groundwater may impact surface water used for drinking water supply. This pathway can likely
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080
13
be eliminated for groundwater in the active layer in permafrost areas.
Protection of freshwater/marine life
The protection of freshwater life can be excluded as a consideration for most contaminants if
there is no potential for contaminants to reach freshwater surface bodies at concentrations
exceeding the surface water quality guidelines. Similarly, marine life guidelines can be excluded
if there is no potential for contaminants to reach marine bodies at concentrations above surface
water quality guidelines. Potential situations where this may occur include:
For most contaminants, including petroleum hydrocarbons and metals, if there are no
surface water bodies within 500 m then the contaminants are unlikely to reach surface
water. Most petroleum hydrocarbon plumes are much less than 500 m and their
transport is generally limited by biodegradation. While metals do not biodegrade, the
transport times required to travel 500 m are in most cases very long. The 500 m distance
should not be automatically applied in very coarse (i.e. gravel) soils.
For chlorinated solvents, a distance of 500 m will not be protective in all cases; some
chlorinated solvent plumes are longer than this. If the plume can be demonstrated to be
stable or decreasing (i.e. it is not spreading and concentrations are not increasing) then
a distance of 500 m could still be used; if not, a distance of 2000 m may be more
appropriate for excluding this pathway.
For conservative solutes, which are defined as solutes which do not biodegrade and are
not significantly retarded (e.g. certain anions such as chloride and fluoride), the plume
size is limited primarily by the mass of contamination present at the site. For these
contaminants, the protection of aquatic life can be excluded if there are no surface water
bodies within 10 km.
If there are surface water bodies within the above distances, the protection of aquatic life
pathways can still be excluded if other lines of evidence such as Tier 2 site-specific
groundwater transport modelling demonstrate that, based on the maximum
concentrations present at the site and the current plume sizes, contamination would not
reach nearby surface water bodies at concentrations exceeding the surface water quality
guidelines.
If site-specific data demonstrate that contaminated groundwater does not have the
potential to discharge into a specific water body (i.e. there is no hydrological connection
between the contaminated groundwater and the surface water body) then that water
body does not need to be considered further.
Irrigation water and livestock watering guidelines
The irrigation water and livestock watering guidelines normally only apply with the agricultural
land use. They could be excluded if there is no aquifer suitable for this use, and groundwater
contamination is not present within the depth of typical agricultural dugouts (approximately 3-4
m).
Wildlife watering
The wildlife watering guidelines can be excluded if there are no surface water bodies within 500
m of the groundwater contamination, or 10 km for conservative solutes such as chloride. It may
also be possible to eliminate this pathway if it can be demonstrated that there is no hydrological
connection between the contaminated groundwater and nearby surface water bodies,
particularly when addressing contamination in the active layer in permafrost areas.
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080
14
Vapour intrusion
The vapour intrusion pathway can only be excluded if there are no occupied buildings present at
the site and no potential for future occupied buildings within 30 m of the groundwater
contamination.
6 SITE-SPECIFIC RISK ASSESSMENT (TIER 3)
The use of site-specific risk assessment to develop site-specific remediation objectives, which
are often referred to as “Tier 3”, is generally applied where neither Tier 1 nor Tier 2 guidelines
apply, or for large and complex sites.
Site-specific risk assessment, may involve the use of different models and assumptions, and
generally requires more site-specific data than application of the generic guidelines or site-
specific modification of guidelines. Detailed guidance on site-specific risk assessment is beyond
the scope of this document; guidance has been published by agencies such as Health Canada,
CCME and several international agencies. Particularly relevant documents include:
A Framework for Ecological Risk Assessment: General Guidance. (CCME 1996).
A Framework for Ecological Risk Assessment: Technical Appendices. (CCME 1997).
Federal Contaminated Sites Risk Assessment in Canada Part I: Guidance on Human
Health Preliminary Quantitative Risk Assessment (PQRA). (Health Canada 2010,
revised 2012).
Federal Contaminated Sites Risk Assessment in Canada Part II: Health Canada
Toxicological Reference Values (TRVs). (Health Canada 2010).
Federal Contaminated Sites Risk Assessment in Canada Part V: Guidance on Human
Health Detailed Quantitative Risk Assessment of Chemicals (DQRA). Draft. (Health
Canada 2010).
A Protocol for the Derivation of Environmental and Human Health Soil Quality
Guidelines. (CCME 2006).
Guidance on the Site-Specific Application of Water Quality Guidelines in Canada:
Procedures for Deriving Numerical Water Quality Objectives. (CCME 2003).
FCSAP Ecological Risk Assessment Guidance. (Environment Canada 2010 draft).
FCSAP Supplemental Guidance for Ecological Risk Assessment. Module A: Toxicity
Test Selection and Interpretation. (Environment Canada 2010 draft).
FCSAP Supplemental Guidance for Ecological Risk Assessment. Module B: Selection or
Development of Site-specific Toxicity Reference Values. (Environment Canada 2010
draft).
FCSAP Supplemental Guidance for Ecological Risk Assessment. Module C:
Standardization of Wildlife Receptor Characteristics. (Environment Canada 2011 draft).
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080
15
APPENDIX A
FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080
16
List of Tables
TABLE 1.0 – TABLE 1.15 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR AGRICULTURAL LAND USE
a
(mg/L)
TABLE 2.0 – TABLE 2.15 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR RESIDENTIAL/PARKLAND LAND USE
a
(mg/L)
TABLE 3.0 – TABLE 3.15 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL LAND USES
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

TABLE 1 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR AGRICULTURAL LAND USE
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
17
Table 1.0: Tier 1 (Generic Groundwater Guidelines), General and Inorganic Parameters, based on Soil Type (Fine Soil
and Coarse Soil)
Table 1.1: Tier 1 (Generic Groundwater Guidelines), Metals, based on Soil Type (Fine Soil and Coarse Soil)
Parameters
Lowest
Guideline
Fine
Lowest
Guideline
Coarse
Aluminium
See note e
See note e
Antimony
2.0
2.0
Arsenic
0.005
0.005
Barium
0.5
0.5
Beryllium
0.0053
0.0053
Boron
0.5
0.5
Cadmium
0.000017
0.000017
Chromium (Total)
See note e
See note e
Cobalt
0.05
0.05
Copper
See note e
See note e
Iron
0.3
0.3
Parameters
Lowest
Guideline
Fine
Lowest
Guideline
Coarse
pH
6.5-9
6.5-9
Ammonia
See note e
See note e
Chloride
100
100
Chlorine
0.002
0.002
Cyanide
0.001
0.001
Fluoride
0.12
0.12
Nitrate
13
13
Nitrate + Nitrite (as
nitrogen)
100
100
Nitrite (as nitrogen)
0.06
0.06
Sulphate
100
100
Sulphide (as H
2
S)
0.002
0.002
Total Dissolved Solids
(TDS)
3000
3000
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

TABLE 1 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR AGRICULTURAL LAND USE
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
18
Lead
See note e
See note e
Manganese
0.2
0.2
Mercury
See note e
See note e
Molybdenum
0.073
0.073
Nickel
See note e
See note e
Selenium
0.001
0.001
Silver
See note e
See note e
Thallium
0.0008
0.0008
Titanium
0.1
0.1
Uranium
0.01
0.01
Vanadium
0.1
0.1
Zinc
0.01
0.01
Table 1.2: Tier 1 (Generic Groundwater Guidelines), Hydrocarbons, based on Soil Type (Fine Soil and Coarse Soil)
Parameters
Lowest
Guideline
Fine
Lowest
Guideline
Coarse
Benzene
0.088
0.088
Toluene
4.9
0.083
Ethylbenzene
3.2
3.2
Xylenes
13
3.9
Styrene
0.072
0.072
F1
6.5
0.81
F2
1.8
1.3
Acenaphthene
0.0058
0.0058
Acenaphthylene
0.046
0.046
Anthracene
0.000012
0.000012
Fluoranthene
0.00004
0.00004
Fluorene
0.003
0.003
Methylnaphthalenes
0.18
0.18
Naphthalene
0.0011
0.0011
Phenanthrene
0.0004
0.0004
Pyrene
0.000025
0.000025
Benz[a]anthracene
g
0.000018
0.000018
Benzo[b+j]fluoranthene
g
0.00048
0.00048
Benzo[k]fluoranthene
g
0.00048
0.00048
Benzo[g,h,i]perylene
g
0.00021
0.00017
Benzo[a]pyrene
g
0.00001
0.00001
Chrysene
g
0.0001
0.0001
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

TABLE 1 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR AGRICULTURAL LAND USE
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
19
Dibenz[a,h]anthracene
g
0.00028
0.00026
Indeno[1,2,3-c,d]pyrene
g
0.00023
0.00021
Table 1.3: Tier 1 (Generic Groundwater Guidelines), Halogenated Aliphatics, based on Soil Type (Fine Soil and Coarse
Soil)
Parameters
Lowest
Guideline
Fine
Lowest
Guideline
Coarse
Vinyl chloride
0.018
0.0011
1,1-Dichloroethene
0.68
0.039
cis-1,2-Dichloroethene
0.017
0.0016
trans-1,2-Dichloroethene
0.017
0.0016
Trichloroethene
(Trichloroethylene, TCE)
0.05
0.02
Tetrachloroethene
(Tetrachloroethylene,
Perchloroethylene, PCE)
0.11
0.11
1,1-Dichloroethane
3.1
0.32
1,2-Dichloroethane
0.005
0.005
Dichloromethane
(Methylene chloride)
0.05
0.05
1,1,1,2-Tetrachloroethane
0.028
0.0033
1,1,2,2-Tetrachloroethane
0.015
0.0032
1,1,1-Trichloroethane
1.1
0.64
1,1,2-Trichloroethane
0.03
0.0047
Trichloromethane
(Chloroform)
0.0018
0.0018
Tetrachloromethane
(Carbon tetrachloride)
0.005
0.00056
1,2-Dichloropropane
0.14
0.016
1,3-Dichloropropene
0.045
0.0052
Bromoform
0.77
0.38
Bromomethane
0.056
0.0056
Bromodichloromethane
8.5
8.5
Dibromochloromethane
0.1
0.1
Ethylene dibromide
0.00083
0.00025
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

TABLE 1 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR AGRICULTURAL LAND USE
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
20
Table 1.4: Tier 1 (Generic Groundwater Guidelines), Chlorinated Aromatics, based on Soil Type (Fine Soil and Coarse
Soil)
Parameters
Lowest
Guideline
Fine
Lowest
Guideline
Coarse
Chlorobenzene
0.0013
0.0013
1,2-Dichlorobenzene
0.0007
0.0007
1,3-Dichlorobenzene
0.042
0.042
1,4-Dichlorobenzene
0.026
0.026
1,2,3-Trichlorobenzene
0.008
0.008
1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene
0.0054
0.0054
1,3,5-Trichlorobenzene
0.38
0.015
1,2,3,4-
Tetrachlorobenzene
0.0018
0.0018
1,2,3,5-
Tetrachlorobenzene
0.41
0.017
1,2,4,5-
Tetrachlorobenzene
0.21
0.0088
Pentachlorobenzene
0.006
0.006
Hexachlorobenzene
0.00052
0.00052
Table 1.5: Tier 1 (Generic Groundwater Guidelines), Phenols, based on Soil Type (Fine Soil and Coarse Soil)
Parameters
Lowest
Guideline
Fine
Lowest
Guideline
Coarse
2-Chlorophenol
0.33
0.33
2,4-Dichlorophenol
0.0002
0.0002
2,4-Dimethylphenol
3.9
3.9
2,4-Dinitrophenol
1.1
1.1
Phenol
0.002
0.002
2,4,5-Trichlorophenol
0.16
0.16
2,4,6-Trichlorophenol
0.018
0.018
2,3,4,6-Tetrachlorophenol
0.001
0.001
Pentachlorophenol
0.0005
0.0005
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

TABLE 1 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR AGRICULTURAL LAND USE
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
21
Table 1.6: Tier 1 (Generic Groundwater Guidelines), Pesticides, based on Soil Type (Fine Soil and Coarse Soil)
Parameters
Lowest
Guideline
Fine
Lowest
Guideline
Coarse
Aldicarb
0.00015
0.00015
Aldrin
0.003
0.003
Atrazine and metabolites
0.0018
0.0018
Azniphos-methyl
0.00001
0.00001
Bromacil
0.005
0.005
Bromoxynil
0.00033
0.00033
Captan
0.0013
0.0013
Carbaryl
0.0002
0.0002
Carbofuran
0.0018
0.0018
Chlordane
0.015
0.015
Chlorothalonil
0.00018
0.00018
Chlorpyrifos
0.000002
0.000002
Cyanazine
0.0005
0.0005
2,4-D (2,4-
Dichlorophenoxyacetic
acid) & other phenoxy
herbicides
0.004
0.004
DDAC (Didecyl dimethyl
ammonium chloride)
0.0015
0.0015
DDT (Dichloro-Diphenyl-
Trichloroethane) &
metabolites
0.000001
0.000001
Deltamethrin
0.0000004
0.0000004
Diazinon
0.000003
0.000003
Dicamba
0.000006
0.000006
Dichlofop-methyl
0.00018
0.00018
Dieldrin
0.000056
0.000056
Dimethoate
0.003
0.003
Dinoseb
0.00005
0.00005
Endosulfan
0.00002
0.00002
Endrin
0.000036
0.000036
Glyphosate
0.065
0.065
Heptachlor epoxide
0.0000038
0.0000038
Imidacloprid
0.00023
0.00023
IPBC (3-iodo-2-propynyl
butyl carbamate)
0.0019
0.0019
Lindane (γ-
0.00001
0.00001
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

TABLE 1 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR AGRICULTURAL LAND USE
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
22
hexachlorocyclohexane)
Linuron
0.000071
0.000071
Malathion
0.0001
0.0001
MCPA
0.000025
0.000025
Methoprene
0.00009
0.00009
Methoxychlor
0.00003
0.00003
Metolachlor
0.0078
0.0078
Metribuzin
0.0005
0.0005
Parathion
0.000013
0.000013
Permethrin
0.000001
0.000001
Picloram
0.029
0.029
Simazine
0.0005
0.0005
Tebuthiuron
0.00027
0.00027
Toxaphene
0.0000002
0.0000002
Triallate
0.00024
0.00024
Trifluarin
0.0002
0.0002
Table 1.7: Tier 1 (Generic Groundwater Guidelines), Other Organics, based on Soil Type (Fine Soil and Coarse Soil)
Parameters
Lowest
Guideline
Fine
Lowest
Guideline
Coarse
Acetone
13
13
Acridine
0.00005
0.00005
Aniline
0.0022
0.0022
Bis(2-chloroethyl)ether
30
30
Bis(2-chloroisopropyl)ether
30
30
Bis(2-ethyl-hexyl)phthalate
0.016
0.016
Chloroaniline, p-
0.04
0.04
Dibutyl phthalate
0.019
0.019
di-n-Butyltin
0.00008
0.00008
Diethylphthalate
0.0038
0.0038
Diisopropanolamine
1.6
1.6
2,4-Dinitrotoluene
0.29
0.29
Ethylene glycol
190
190
Hexachlorobutadiene
0.0013
0.0013
Methyl methacrylate
17
0.84
Methyl ethyl ketone
150
150
Methyl isobutyl ketone
58
58
Methyl mercury
0.000015
0.000015
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

TABLE 1 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR AGRICULTURAL LAND USE
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
23
MTBE (Methyl tert-butyl
ether)
5
0.34
Monochloramine
0.0005
0.0005
Nonylphenol + ethoxylates
0.0007
0.0007
Propylene glycol
500
500
Quinoline
0.0034
0.0034
Sulfolane
0.5
0.5
Tributyltin
0.000001
0.000001
Triethyltin
0.0004
0.0004
Triphenyltin
0.000022
0.000022
Table 1.8: Tier 2 (Site-Specific Guidelines), General and Inorganic Parameters, Water Use/Exposure Pathway, based on
Soil Type (Fine Soil and Coarse Soil)
Inhalation
Fine
Inhalation
Coarse
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Fine
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Coarse
Freshwater
Life
b
Fine
Freshwater
Life
b
Coarse
Marine
Life
c
Fine
Marine
Life
c
Coarse
Irriga-tion
j
All
Live-
stock
j
All
Wildlife
Watering
Fine
Wildlife
Watering
Coarse
pH
-
-
-
-
6.5-9
6.5-9
7-8.7
7-8.7
-
-
-
-
Ammonia
-
-
-
-
see note d
see note d
-
-
-
-
-
-
Chloride
-
-
-
-
120
120
-
-
100
-
-
-
Chlorine
-
-
-
-
0.002
h,i
0.002
h,i
0.003
h,i
0.003
h,i
-
-
-
-
Cyanide
-
-
-
-
0.005
0.005
0.001
h,i
0.001
h,i
-
-
-
-
Fluoride
-
-
-
0.12
0.12
1.5
h,i
1.5
h,i
1
1
-
-
Nitrate
-
-
-
-
13
13
16
16
-
-
-
-
Nitrate +
Nitrite (as
nitrogen)
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
100
-
-
Nitrite (as
nitrogen)
-
-
-
-
0.06
0.06
-
-
-
10
-
-
Sulphate
-
-
-
-
100
h,i
100
h,i
-
-
-
1000
-
-
Sulphide (as
H
2
S)
-
-
-
-
0.002
0.002
0.002
h,i
0.002
h,i
-
-
-
-
Total
Dissolved
Solids (TDS)
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
3000
-
-
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

TABLE 1 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR AGRICULTURAL LAND USE
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
24
Table 1.9: Tier 2 (Site-Specific Guidelines), Metals, Water Use/Exposure Pathway, based on Soil Type (Fine Soil and
Coarse Soil)
Inhalation
Fine
Inhalation
Coarse
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Fine
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Coarse
Freshwater
Life
b
Fine
Freshwater
Life
b
Coarse
Marine
Life
c
Fine
Marine
Life
c
Coarse
Irriga-tion
j
All
Live-
stock
j
All
Wildlife
Watering
Fine
Wildlife
Watering
Coarse
Aluminium
-
-
-
-
see note d
see note d
-
-
5
5
-
-
Antimony
-
-
-
-
2.0
f,i
2.0
f,i
-
-
-
-
-
-
Arsenic
-
-
-
-
0.005
0.005
0.0125
0.0125
0.1
0.025
-
-
Barium
-
-
-
-
2.9
f,i
2.9
f,i
0.5
h,i
0.5
h,i
-
-
-
-
Beryllium
-
-
-
-
0.0053
h,i
0.0053
h,i
0.1
h,i
0.1
h,i
0.1
0.1
-
-
Boron
-
-
-
-
-
-
5
h,i
5
h,i
0.5
5
-
-
Cadmium
-
-
-
-
0.000017
0.000017
0.0001
2
0.00012
0.0051
0.08
-
-
Chromium
(Total)
-
-
-
-
0.0089
0.0089
0.056
0.056
-
0.05
-
-
Cobalt
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
0.05
1
-
-
Copper
-
-
-
-
see note d
see note d
0.002
h,i
0.002
h,i
0.2
0.5
-
-
Iron
-
-
-
-
0.3
0.3
-
-
5
-
-
-
Lead
-
-
-
-
see note d
see note d
0.002
h,i
0.002
h,i
0.2
0.1
-
-
Manganese
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
0.2
-
-
-
Mercury
-
-
-
-
0.000026
0.000026
0.0000
16
0.00001
6
-
0.003
-
-
Molybdenum
-
-
-
-
0.073
0.073
-
-
-
-
-
-
Nickel
-
-
-
-
see note d
see note d
0.083
h,i
0.083
h,i
0.2
1
-
-
Selenium
-
-
-
-
0.001
0.001
0.054
h,i
0.054
h,i
0.02
0.05
-
-
Silver
-
-
-
-
0.0001
0.0001
0.0015
h,i
0.0015
h,i
0.02
0.05
-
-
Thallium
-
-
-
-
0.0008
0.0008
-
-
-
-
-
-
Titanium
-
-
-
-
0.1
h,i
0.1
h,i
-
-
-
-
-
-
Uranium
-
-
-
-
0.015
0.015
-
-
0.01
0.2
-
-
Vanadium
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
0.1
0.1
-
-
Zinc
-
-
-
-
0.03
0.03
0.01
h,i
0.01
h,i
1
50
-
-
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

TABLE 1 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR AGRICULTURAL LAND USE
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
25
Table 1.10: Tier 2 (Site-Specific Guidelines), Hydrocarbons, Water Use/Exposure Pathway, based on Soil Type (Fine Soil
and Coarse Soil)
Inhalation
Fine
Inhalation
Coarse
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Fine
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Coarse
Freshwater
Life
b
Fine
Freshwater
Life
b
Coarse
Marine
Life
c
Fine
Marine
Life
c
Coarse
Irriga-tion
j
All
Live-
stoc
k
j
All
Wildlife
Watering
Fine
Wildlife
Watering
Coarse
Benzene
2.8
0.14
100
61
33
0.69
9.8
0.2
-
0.088
6.8
0.14
Toluene
NGR
74
82
59
NGR
0.083
NGR
8.9
-
4.9
NGR
180
Ethylbenze
ne
NGR
16
42
20
NGR
41
NGR
11
-
3.2
NGR
NGR
Xylenes
80
3.9
21
31
NGR
18
-
-
-
13
NGR
NGR
Styrene
90
4.3
-
-
0.072
0.072
-
-
-
-
-
-
F1
19
0.81
6.5
7.1
NGR
9.8
-
-
-
53
NGR
NGR
F2
NGR
1.5
1.8
1.8
NGR
1.3
-
-
-
NGR
NGR
NGR
Acenaphthe
ne
NGR
NGR
-
-
0.0058
0.0058
-
-
-
NGR
NGR
NGR
Acenaphthy
lene
-
-
-
-
0.046
0.046
-
-
-
-
-
-
Anthracene
NGR
NGR
0.025
0.025
0.000012
0.000012
-
-
-
NGR
NGR
NGR
Fluoranthen
e
NGR
NGR
0.24
0.24
0.00004
0.00004
-
-
-
NGR
NGR
NGR
Fluorene
NGR
NGR
-
-
0.003
0.003
0.012
h,i
0.012
h,i
-
NGR
NGR
NGR
Methylnaph
thalenes
35
f
6.2
f
-
-
0.18
f,i
0.18
f,i
-
-
-
-
-
-
Naphthalen
e
14
0.6
-
-
0.0011
0.0011
0.0014
0.0014
-
NGR
NGR
NGR
Phenanthre
ne
-
-
-
-
0.0004
0.0004
-
-
-
NGR
NGR
NGR
Pyrene
NGR
NGR
-
-
0.000025
0.000025
-
-
-
NGR
NGR
NGR
Benz[a]anth
racene
g
-
-
-
-
0.000018
0.000018
-
-
-
NGR
NGR
NGR
Benzo[b+j]fl
uoranthene
g
-
-
-
-
0.00048
0.00048
-
-
-
NGR
NGR
NGR
Benzo[k]flu
oranthene
g
-
-
-
-
0.00048
0.00048
-
-
-
NGR
NGR
NGR
-
-
-
-
0.00021
0.00017
-
-
-
-
-
-
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

TABLE 1 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR AGRICULTURAL LAND USE
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
26
Benzo[g,h,i]
perylene
g
Benzo[a]pyr
ene
g
-
-
0.0018
0.0018
0.000017
0.000015
0.00001
h,i
0.00001
h,i
-
NGR
NGR
NGR
Chrysene
g
-
-
-
-
0.0014
0.0014
0.0001
h,i
0.0001
h,i
-
NGR
NGR
NGR
Dibenz[
a,h]anth
racene
g
-
-
-
-
0.00028
0.00026
-
-
-
NGR
NGR
NGR
Indeno[
1,2,3-
c,d]pyre
ne
g
-
-
-
-
0.00023
0.00021
-
-
-
-
-
-
Table 1.11: Tier 2 (Site-Specific Guidelines), Halogenated Aliphatics, Water Use/Exposure Pathway, based on Soil Type
(Fine Soil and Coarse Soil)
Inhalation
Fine
Inhalation
Coarse
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Fine
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Coarse
Fresh
water
Life
b
Fine
Freshwa
ter Life
b
Coarse
Marine
Life
c
Fine
Marine
Life
c
Coarse
Irriga-
tion
j
All
Live-stock
j
All
Wildlife
Watering
Fine
Wildlife
Watering
Coarse
Vinyl chloride
0.018
0.0011
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
1,1-Dichloroethene
0.68
0.039
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
cis-1,2-Dichloroethene
0.017
f
0.0016
f
-
-
14
,i
14
,i
-
-
-
-
-
-
trans-1,2-Dichloroethene
0.017
f
0.0016
f
-
-
28
f,i
28
f,i
-
-
-
-
-
-
Trichloroethene
(Trichloroethylene, TCE)
0.41
0.02
4.4
5
0.27
0.029
-
-
-
0.05
-
-
Tetrachloroethene
(Tetrachloroethylene,
Perchloroethylene, PCE)
2.3
0.11
-
-
0.11
0.11
-
-
-
-
-
-
1,1-Dichloroethane
3.1
f
0.32
f
-
-
260
f,i
260
f,i
-
-
-
-
-
-
1,2-Dichloroethane
0.17
0.01
-
-
0.1
0.1
-
-
-
0.005
-
-
Dichloromethane
(Methylene chloride)
61
3.4
-
-
0.098
0.098
-
-
-
0.05
-
-
1,1,1,2-Tetrachloroethane
0.028
f
0.0033
f
-
-
2.5
f,i
2.5
f,i
-
-
-
-
-
-
1,1,2,2-Tetrachloroethane
0.015
f
0.0032
f
-
-
3.0
f,i
3.0
f,i
-
-
-
-
-
-
1,1,1-Trichloroethane
6.7
f
0.64
f
-
-
1.1
f,i
1.1
f,i
-
-
-
-
-
-
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

TABLE 1 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR AGRICULTURAL LAND USE
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
27
1,1,2-Trichloroethane
0.03
f
0.0047
f
-
-
12
f,i
12
f,i
-
-
-
-
-
-
Trichloromethane
(Chloroform)
0.05
0.003
-
-
0.0018
0.0018
-
-
-
0.1
-
-
Tetrachloromethane
(Carbon tetrachloride)
0.011
0.00056
-
-
0.013
0.013
-
-
-
0.005
-
-
1,2-Dichloropropane
0.14
f
0.016
f
-
-
7.2
f,i
7.2
f,i
-
-
-
-
-
-
1,3-Dichloropropene
0.045
f
0.0052
f
-
-
0.31
f,i
0.31
f,i
-
-
-
-
-
-
Bromoform
0.77
f
0.38
f
-
-
3.7
f,i
3.7
f,i
-
-
-
-
-
-
Bromomethane
0.056
f
0.0056
f
-
-
0.4
f,i
0.4
f,i
-
-
-
-
-
-
Bromodichloromethane
-
-
-
-
8.5
f,i
8.5
f,i
-
-
-
-
-
-
Dibromochloromethane
26
1.1
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
0.1
-
-
Ethylene dibromide
8.3E-4
f
0.00025
f
-
-
12
f,i
12
f,i
-
-
-
-
-
-
Table 1.12: Tier 2 (Site-Specific Guidelines), Chlorinated Aromatics, Water Use/Exposure Pathway, based on Soil Type
(Fine Soil and Coarse Soil)
Inhalation
Fine
Inhalation
Coarse
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Fine
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Coarse
Freshw
ater
Life
b
Fine
Freshw
ater
Life
b
Coarse
Marine
Life
c
Fine
Marine
Life
c
Coarse
Irriga-
tion
j
All
Live-stock
j
All
Wildlife
Watering
Fine
Wildlife
Watering
Coarse
Chlorobenzene
0.3
0.014
-
-
0.0013
0.0013
0.025
0.025
-
-
-
-
1,2-
Dichlorobenzene
116
5.4
-
-
0.0007
0.0007
0.042
0.042
-
-
-
-
1,3-
Dichlorobenzene
-
-
-
-
0.15
0.15
0.042
h,i
0.042
h,i
-
-
-
-
1,4-
Dichlorobenzene
4.6
0.22
-
-
0.026
0.026
-
-
-
-
-
-
1,2,3-
Trichlorobenzene
0.8
0.032
-
-
0.008
0.008
-
-
-
-
-
-
1,2,4-
Trichlorobenzene
0.71
0.028
-
-
0.024
0.024
0.0054
0.0054
-
-
-
-
1,3,5-
Trichlorobenzene
0.38
0.015
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
1,2,3,4-
Tetrachlorobenzene
NGR
0.14
-
-
0.0018
0.0018
-
-
-
-
-
-
1,2,3,5-
Tetrachlorobenzene
0.41
0.017
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
1,2,4,5-
Tetrachlorobenzene
0.21
0.0088
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

TABLE 1 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR AGRICULTURAL LAND USE
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
28
Pentachlorobenzen
e
NGR
0.038
-
-
0.006
0.006
-
-
-
-
-
-
Hexachlorobenzene
0.029
0.0012
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
0.00052
-
-
Table 1.13: Tier 2 (Site-Specific Guidelines), Phenols, Water Use/Exposure Pathway, based on Soil Type (Fine Soil and
Coarse Soil)
Inhalation
Fine
Inhalation
Coarse
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Fine
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Coarse
Freshwat
er Life
b
Fine
Fresh
water
Life
b
Coars
e
Marine
Life
c
Fine
Marine
Life
c
Coarse
Irriga-
tion
j
All
Live-stock
j
All
Wildlife
Watering
Fine
Wildlife
Watering
Coarse
2-Chlorophenol
-
-
-
-
0.33
f,i
0.33
f,i
-
-
-
-
-
-
2,4-Dichlorophenol
NGR
1500
-
-
0.0002
0.0002
-
-
-
-
-
-
2,4-Dimethylphenol
-
-
-
-
3.9
f,i
3.9
f,i
-
-
-
-
-
-
2,4-Dinitrophenol
-
-
-
-
1.1
f,i
1.1
f,i
-
-
-
-
-
-
Phenol
73000
3700
110
150
0.004
0.004
-
-
-
0.002
-
-
2,4,5-
Trichlorophenol
-
-
-
-
0.16
f,i
0.16
f,i
-
-
-
-
-
-
2,4,6-
Trichlorophenol
NGR
54
-
-
0.018
0.018
-
-
-
-
-
-
2,3,4,6-
Tetrachlorophenol
NGR
NGR
-
-
0.001
0.001
-
-
-
-
-
-
Pentachlorophenol
NGR
NGR
0.87
0.88
0.0005
0.0005
-
-
-
-
-
-
Table 1.14: Tier 2 (Site-Specific Guidelines), Pesticides, Water Use/Exposure Pathway, based on Soil Type (Fine Soil
and Coarse Soil)
Inhalation
Fine
Inhalation
Coarse
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Fine
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Coarse
Freshwat
er Life
b
Fine
Fresh
water
Life
b
Coars
e
Marine
Life
c
Fine
Marine
Life
c
Coarse
Irriga-
tion
j
All
Live-stock
j
All
Wildlife
Watering
Fine
Wildlife
Waterin
g
Coarse
Aldicarb
-
-
-
-
0.001
0.001
0.00015
0.00015
0.055
0.011
-
-
Aldrin
-
-
-
-
0.003
0.003
-
-
-
-
-
-
Atrazine and
metabolites
-
-
-
-
0.0018
0.0018
0.01
h,i
0.01
h,i
0.01
0.005
-
-
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

TABLE 1 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR AGRICULTURAL LAND USE
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
29
Azniphos-methyl
-
-
-
-
0.00001
0.0000
1
-
-
-
-
-
-
Bromacil
-
-
-
-
0.005
0.005
-
-
-
-
-
-
Bromoxynil
-
-
-
-
0.005
0.005
-
-
0.00033
0.011
-
-
Captan
-
-
-
-
0.0013
0.0013
-
-
-
-
-
-
Carbaryl
-
-
-
-
0.0002
0.0002
0.00032
0.00032
-
1.1
-
-
Carbofuran
-
-
-
-
0.0018
0.0018
-
-
-
0.045
-
-
Chlordane
0.086
f
0.058
f
-
-
0.015
f,i
0.015
f,i
-
-
-
-
-
-
Chlorothalonil
-
-
-
-
0.00018
0.0001
8
0.00036
0.00036
0.0058
0.17
-
-
Chlorpyrifos
-
-
-
-
0.0000035
0.0000
035
0.00000
2
0.00000
2
-
0.024
-
-
Cyanazine
-
-
-
-
0.002
0.002
-
-
0.0005
0.01
-
-
2,4-D (2,4-
Dichlorophenoxy
acetic acid) &
other phenoxy
herbicides
-
-
-
-
0.004
0.004
-
-
-
0.1
-
-
DDAC (Didecyl
dimethyl
ammonium
chloride)
-
-
-
-
0.0015
0.0015
-
-
-
-
-
-
DDT (Dichloro-
Diphenyl-
Trichloroethane)
& metabolites
-
-
-
-
0.000001
0.0000
01
-
-
-
0.1
-
-
Deltamethrin
-
-
-
-
0.0000004
0.0000
004
-
-
-
-
-
-
Diazinon
-
-
-
-
0.000003
h,i
0.0000
03
h,i
-
-
-
-
-
-
Dicamba
-
-
-
-
0.01
0.01
-
-
0.00000
6
0.12
-
-
Dichlofop-methyl
-
-
-
-
0.0061
0.0061
-
-
0.00018
0.009
-
-
Dieldrin
-
-
-
-
0.000056
0.0000
56
-
-
-
-
-
-
Dimethoate
-
-
-
-
0.0062
0.0062
-
-
-
0.003
-
-
Dinoseb
-
-
-
-
0.00005
0.0000
5
-
-
0.016
0.15
-
-
Endosulfan
-
-
-
-
0.00003
0.0000
3
0.00002
0.00002
-
-
-
-
Endrin
-
-
-
-
0.000036
0.0000
36
-
-
-
-
-
-
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

TABLE 1 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR AGRICULTURAL LAND USE
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
30
Glyphosate
-
-
-
-
0.065
0.065
-
-
-
0.28
-
-
Heptachlor
epoxide
0.0043
0.00024
-
-
0.0000038
0.0000
038
-
-
-
-
-
-
Imidacloprid
-
-
-
-
0.00023
0.0002
3
-
-
-
-
-
-
IPBC (3-iodo-2-
propynyl butyl
carbamate)
-
-
-
-
0.0019
0.0019
-
-
-
-
-
-
Lindane (γ-
hexachlorocycloh
exane)
-
-
-
-
0.00001
0.0000
1
-
-
-
0.004
-
-
Linuron
-
-
-
-
0.007
0.007
-
-
0.00007
1
-
-
-
Malathion
-
-
-
-
0.0001
0.0001
-
-
-
-
-
-
MCPA
-
-
-
-
0.0026
0.0026
0.0042
0.0042
0.00002
5
0.025
-
-
Methoprene
-
-
-
-
0.00009
0.0000
9
-
-
-
-
-
-
Methoxychlor
-
-
-
-
0.00003
0.0000
3
-
-
-
-
-
-
Metolachlor
-
-
-
-
0.0078
0.0078
-
-
0.028
0.05
-
-
Metribuzin
-
-
-
-
0.001
0.001
-
-
0.0005
0.08
-
-
Parathion
-
-
-
-
0.000013
0.0000
13
-
-
-
-
-
-
Permethrin
-
-
-
-
0.000004
0.0000
04
0.00000
1
0.00000
1
-
-
-
-
Picloram
-
-
-
-
0.029
0.029
-
-
-
0.19
-
-
Simazine
-
-
-
-
0.01
0.01
-
-
0.0005
0.01
-
-
Tebuthiuron
-
-
-
-
0.0016
0.0016
-
-
0.00027
0.13
-
-
Toxaphene
6.4
0.31
-
-
0.0000002
0.0000
002
-
-
-
-
-
-
Triallate
-
-
-
-
0.00024
0.0002
4
-
-
-
0.23
-
-
Trifluarin
-
-
-
-
0.0002
0.0002
-
-
-
0.045
-
-
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

TABLE 1 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR AGRICULTURAL LAND USE
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
31
Table 1.15: Tier 2 (Site-Specific Guidelines), Other Organics, Water Use/Exposure Pathway, based on Soil Type (Fine
Soil and Coarse Soil)
Inhalation
Fine
Inhalation
Coarse
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Fine
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Coarse
Freshwat
er Life
b
Fine
Fresh
water
Life
b
Coars
e
Marine
Life
c
Fine
Marine
Life
c
Coarse
Irriga-
tion
j
All
Live-stock
j
All
Wildlife
Watering
Fine
Wildlife
Waterin
g
Coarse
Acetone
7700
f
1800
f
-
-
13
f,i
13
f,i
-
-
-
-
-
-
Acridine
-
-
-
-
0.00005
h,i
0.0000
5
h,i
-
-
-
-
-
-
Aniline
1900
87
-
-
0.0022
0.0022
-
-
-
-
-
-
Bis(2-
chloroethyl)ethe
r
2800
f
810
f
-
-
30
f,i
30
f,i
-
-
-
-
-
-
Bis(2-
chloroisopropyl)
ether
1600
f
400
f
-
-
30
f,i
30
f,i
-
-
-
-
-
-
Bis(2-ethyl-
hexyl)phthalate
NGR
NGR
-
-
0.016
0.016
-
-
-
-
-
-
Chloroaniline, p-
-
-
-
-
0.04
f,i
0.04
f,i
-
-
-
-
-
-
Dibutyl
phthalate
NGR
NGR
-
-
0.019
0.019
-
-
-
-
-
-
di-n-Butyltin
-
-
-
-
0.00008
h,i
0.0000
8
h,i
-
-
-
-
-
-
Diethylphthalate
-
-
-
-
0.0038
f,i
0.0038
f,i
-
-
-
-
-
-
Diisopropanola
mine
-
-
160
160
1.6
1.6
-
-
2
-
-
-
2,4-
Dinitrotoluene
-
-
-
-
0.29
f,i
0.29
f,i
-
-
-
-
-
-
Ethylene glycol
NGR
NGR
9200
16000
190
190
-
-
-
-
-
-
Hexachlorobuta
diene
0.031
0.0013
-
-
0.0013
0.0013
-
-
-
-
-
-
Methyl
methacrylate
17
0.84
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Methyl ethyl
ketone
1700
f
470
f
-
-
150
f,i
150
f,i
-
-
-
-
-
-
Methyl isobutyl
ketone
600
f
140
f
-
-
58
f,i
58
f,i
-
-
-
-
-
-
Methyl mercury
-
-
-
-
0.000015
f,i
0.0000
15
f,i
-
-
-
-
-
-
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

TABLE 1 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR AGRICULTURAL LAND USE
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
32
MTBE (Methyl
tert-butyl ether)
6.1
0.34
-
-
10
10
5
5
-
-
-
-
Monochloramin
e
0.0005
h,i
0.0005
h,i
Nonylphenol +
ethoxylates
-
-
0.0081
0.0081
0.001
0.001
0.0007
0.0007
-
-
-
-
Propylene glycol
-
-
-
-
500
500
-
-
-
-
-
-
Quinoline
-
-
-
-
0.0034
h,i
0.0034
h,i
-
-
-
-
-
-
Sulfolane
-
-
1700
2800
50
50
-
-
0.5
-
-
-
Tributyltin
-
-
-
-
0.000008
0.0000
08
0.00000
1
0.00000
1
-
0.25
-
-
Triethyltin
-
-
-
-
0.0004
h,i
0.0004
h,i
-
-
-
-
-
-
Triphenyltin
-
-
-
-
0.000022
0.0000
22
-
-
-
0.8
-
-
a – all values adopted from Alberta Environment (AESRD) (2010a) unless otherwise specified
b – where AESRD (2010a) guideline was not based on the Canadian Water Quality Guidelines (CWQG) for the Protection of Aquatic Life for freshwater environments (CCME
1999), and a CWQG exists, the groundwater quality guideline was re-calculated based on the CWQG
c – based on Canadian Water Quality Guidelines (CWQG) for the Protection of Aquatic Life for the marine environments(CCME 1999) and groundwater transport model
d – the freshwater aquatic life guidelines vary depending on water pH, hardness etc. Therefore, see Canadian Water Quality Guidelines for the Protection of Aquatic Life
(CCME 1999) to determine the appropriate water quality guideline applicable to the site and calculate the groundwater guidelines using formulas provided in Appendix B
e – guideline is the lowest of all applicable pathways
f – adopted from Ontario Ministry of the Environment (OMOE) (2010)
g – for ecological receptors only
h – adopted from BC Contaminated Sites Regulation
i - 10x factor for dilution in surface water was removed from guideline value
j – adopted directly from CCME (1999)
NGR – no guideline required; calculated guideline exceeds solubility limit
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

TABLE 2 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR RESIDENTIAL/PARKLAND LAND USE
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
33
Table 2.0: Tier 1 (Generic Groundwater Guidelines), General and Inorganic Parameters, based on Soil Type (Fine Soil
and Coarse Soil)
Parameters
Fine
Coarse
pH
6.5-9
6.5-9
Ammonia
See note e
See note e
Chloride
120
120
Chlorine
0.002
0.002
Cyanide
0.001
0.001
Fluoride
0.12
0.12
Nitrate
13
13
Nitrite (as nitrogen)
0.06
0.06
Sulphate
100
100
Sulphide (as H
2
S)
0.002
0.002
Table 2.1: Tier 1 (Generic Groundwater Guidelines), Metals, based on Soil Type (Fine Soil and Coarse Soil)
Parameters
S
7
S e
S e
S e
S e
Fine
Coarse
Aluminium
ee note e
See note e
Antimony
2.0
2.0
Arsenic
0.005
0.005
Barium
0.5
0.5
Beryllium
0.0053
0.0053
Boron
5
5
Cadmium
0.00001
0.000017
Chromium (Total)
0.0089
0.0089
Copper
ee note
See note e
Iron
0.3
0.3
Lead
ee note
See note e
Mercury
ee note
See note e
Molybdenum
0.073
0.073
Nickel
ee note
See note e
Selenium
0.001
0.001
Silver
0.0001
0.0001
Thallium
0.0008
0.0008
Titanium
0.1
0.1
Uranium
0.015
0.015
Zinc
0.01
0.01
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

TABLE 2 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR RESIDENTIAL/PARKLAND LAND USE
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
34
Table 2.2: Tier 1 (Generic Groundwater Guidelines), Hydrocarbons, based on Soil Type (Fine Soil and Coarse Soil)
Parameters
Fine
Coarse
Benzene
2.8
0.14
Toluene
82
0.083
Ethylbenzene
42
11
Xylenes
21
3.9
Styrene
0.072
0.072
F1
6.5
0.81
F2
1.8
1.3
Acenaphthene
0.0058
0.0058
Acenaphthylene
0.046
0.046
Anthracene
0.000012
0.000012
Fluoranthene
0.00004
0.00004
Fluorene
0.003
0.003
Methylnaphthalenes
0.18
0.18
Naphthalene
0.0011
0.0011
Phenanthrene
0.0004
0.0004
Pyrene
0.000025
0.000025
Benz[a]anthracene
g
0.000018
0.000018
Benzo[b+j]fluoranthene
g
0.00048
0.00048
Benzo[k]fluoranthene
g
0.00048
0.00048
Benzo[g,h,i]perylene
g
0.00021
0.00017
Benzo[a]pyrene
g
0.00001
0.00001
Chrysene
g
0.0001
0.0001
Dibenz[a,h]anthracene
g
0.00028
0.00026
Indeno[1,2,3-c,d]pyrene
g
0.00023
0.00021
Table 2.3: Tier 1 (Generic Groundwater Guidelines), Halogenated Aliphatics, based on Soil Type (Fine Soil and Coarse
Soil)
Parameters
Fine
Coarse
Vinyl chloride
0.018
0.0011
1,1-Dichloroethene
0.68
0.039
cis-1,2-Dichloroethene
0.017
0.0016
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

TABLE 2 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR RESIDENTIAL/PARKLAND LAND USE
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
35
trans-1,2-Dichloroethene
0.017
0.0016
Trichloroethene
(Trichloroethylene, TCE)
0.27
0.02
Tetrachloroethene
(Tetrachloroethylene,
Perchloroethylene, PCE)
0.11
0.11
1,1-Dichloroethane
3.1
0.32
1,2-Dichloroethane
0.1
0.01
Dichloromethane
(Methylene chloride)
0.098
0.098
1,1,1,2-Tetrachloroethane
0.028
0.0034
1,1,2,2-Tetrachloroethane
0.015
0.0032
1,1,1-Trichloroethane
1.1
0.64
1,1,2-Trichloroethane
0.03
0.0047
Trichloromethane
(Chloroform)
0.0018
0.0018
Tetrachloromethane
(Carbon tetrachloride)
0.011
0.00056
1,2-Dichloropropane
0.14
0.016
1,3-Dichloropropene
0.045
0.0052
Bromoform
0.77
0.38
Bromomethane
0.056
0.0056
Bromodichloromethane
8.5
8.5
Dibromochloromethane
26
1.1
Ethylene dibromide
0.00083
0.00025
Table 2.4: Tier 1 (Generic Groundwater Guidelines), Chlorinated Aromatics, based on Soil Type (Fine Soil and Coarse
Soil)
Parameters
Fine
Coarse
Chlorobenzene
0.0013
0.0013
1,2-Dichlorobenzene
0.0007
0.0007
1,3-Dichlorobenzene
0.042
0.042
1,4-Dichlorobenzene
0.026
0.026
1,2,3-Trichlorobenzene
0.008
0.008
1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene
0.0054
0.0054
1,3,5-Trichlorobenzene
0.38
0.015
1,2,3,4-
Tetrachlorobenzene
0.0018
0.0018
1,2,3,5-
0.41
0.017
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

TABLE 2 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR RESIDENTIAL/PARKLAND LAND USE
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
36
Tetrachlorobenzene
1,2,4,5-
Tetrachlorobenzene
0.21
0.0088
Pentachlorobenzene
0.006
0.006
Hexachlorobenzene
0.029
0.0012
Table 2.5: Tier 1 (Generic Groundwater Guidelines), Phenols, based on Soil Type (Fine Soil and Coarse Soil)
Parameters
Fine
Coarse
2-Chlorophenol
0.33
0.33
2,4-Dichlorophenol
0.0002
0.0002
2,4-Dimethylphenol
3.9
3.9
2,4-Dinitrophenol
1.1
1.1
Phenol
0.004
0.004
2,4,5-Trichlorophenol
0.16
0.16
2,4,6-Trichlorophenol
0.018
0.018
2,3,4,6-Tetrachlorophenol
0.001
0.001
Pentachlorophenol
0.0005
0.0005
Table 2.6: Tier 1 (Generic Groundwater Guidelines), Pesticides, based on Soil Type (Fine Soil and Coarse Soil)
Parameters
Fine
Coarse
Aldicarb
0.00015
0.00015
Aldrin
0.003
0.003
Atrazine and metabolites
0.0018
0.0018
Azniphos-methyl
0.00001
0.00001
Bromacil
0.005
0.005
Bromoxynil
0.005
0.005
Captan
0.0013
0.0013
Carbaryl
0.0002
0.0002
Carbofuran
0.0018
0.0018
Chlordane
0.015
0.015
Chlorothalonil
0.00018
0.00018
Chlorpyrifos
0.000002
0.000002
Cyanazine
0.002
0.002
2,4-D (2,4-
0.004
0.004
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

TABLE 2 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR RESIDENTIAL/PARKLAND LAND USE
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
37
Dichlorophenoxyacetic
acid) & other phenoxy
herbicides
DDAC (Didecyl dimethyl
ammonium chloride)
0.0015
0.0015
DDT (Dichloro-Diphenyl-
Trichloroethane) &
metabolites
0.000001
0.000001
Deltamethrin
0.0000004
0.0000004
Diazinon
0.000003
0.000003
Dicamba
0.01
0.01
Dichlofop-methyl
0.0061
0.0061
Dieldrin
0.000056
0.000056
Dimethoate
0.0062
0.0062
Dinoseb
0.00005
0.00005
Endosulfan
0.00002
0.00002
Endrin
0.000036
0.000036
Glyphosate
0.065
0.065
Heptachlor epoxide
0.0000038
0.0000038
Imidacloprid
0.00023
0.00023
IPBC (3-iodo-2-propynyl
butyl carbamate)
0.0019
0.0019
Lindane (γ-
hexachlorocyclohexane)
0.00001
0.00001
Linuron
0.007
0.007
Malathion
0.0001
0.0001
MCPA
0.0026
0.0026
Methoprene
0.00009
0.00009
Methoxychlor
0.00003
0.00003
Metolachlor
0.0078
0.0078
Metribuzin
0.001
0.001
Parathion
0.000013
0.000013
Permethrin
0.000001
0.000001
Picloram
0.029
0.029
Simazine
0.01
0.01
Tebuthiuron
0.0016
0.0016
Toxaphene
0.0000002
0.0000002
Triallate
0.00024
0.00024
Trifluarin
0.0002
0.0002
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

TABLE 2 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR RESIDENTIAL/PARKLAND LAND USE
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
38
Table 2.7: Tier 1 (Generic Groundwater Guidelines), Other Organics, based on Soil Type (Fine Soil and Coarse Soil)
Parameters
Fine
Coarse
Acetone
13
13
Acridine
0.00005
0.00005
Aniline
0.0022
0.0022
Bis(2-chloroethyl)ether
30
30
Bis(2-chloroisopropyl)ether
30
30
Bis(2-ethyl-hexyl)phthalate
0.016
0.016
Chloroaniline, p-
0.04
0.04
Dibutyl phthalate
0.019
0.019
di-n-Butyltin
0.00008
0.00008
Diethylphthalate
0.0038
0.0038
Diisopropanolamine
1.6
1.6
2,4-Dinitrotoluene
0.29
0.29
Ethylene glycol
190
190
Hexachlorobutadiene
0.0013
0.0013
Methyl methacrylate
17
0.84
Methyl ethyl ketone
150
150
Methyl isobutyl ketone
58
58
Methyl mercury
0.000015
0.000015
MTBE (Methyl tert-butyl
ether)
5
0.34
Monochloramine
0.0005
0.0005
Nonylphenol + ethoxylates
0.0007
0.0007
Propylene glycol
500
500
Quinoline
0.0034
0.0034
Sulfolane
50
50
Tributyltin
0.000001
0.000001
Triethyltin
0.0004
0.0004
Triphenyltin
0.000022
0.000022
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

TABLE 2 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR RESIDENTIAL/PARKLAND LAND USE
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
39
Table 2.8: Tier 2 (Site-Specific Guidelines), General and Inorganic Parameters, Water Use/Exposure Pathway, based on
Soil Type (Fine Soil and Coarse Soil)
Parameters
Inhalation
Fine
Inhalation
Coarse
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Fine
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Coarse
Freshwater
Life
b
Fine
Freshwater
Life
b
Coarse
Marine
Life
c
Fine
Marine
Life
c
Coarse
pH
-
-
-
-
6.5-9
6.5-9
7-8.7
7-8.7
Ammonia
-
-
-
-
see note d
see note d
-
-
Chloride
-
-
-
-
120
120
-
-
Chlorine
-
-
-
-
0.002
h,i
0.002
h,i
0.003
h,i
0.003
h,i
Cyanide
-
-
-
-
0.005
0.005
0.001
h,i
0.001
h,i
Fluoride
-
-
-
-
0.12
0.12
1.5
h,i
1.5
h,i
Nitrate
-
-
-
-
13
13
16
16
Nitrite (as nitrogen)
-
-
-
-
0.06
0.06
-
-
Sulphate
-
-
-
-
100
h,i
100
h,i
-
-
Sulphide (as H
2
S)
-
-
-
-
0.002
0.002
0.002
h,i
0.002
h,i
Table 2.9: Tier 2 (Site-Specific Guidelines), Metals, Water Use/Exposure Pathway, based on Soil Type (Fine Soil and
Coarse Soil)
Parameters
Inhalation
Fine
Inhalation
Coarse
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Fine
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Coarse
Freshwater
Life
b
Fine
Freshwater
Life
b
Coarse
Marine
Life
c
Fine
Marine
Life
c
Coarse
Aluminium
-
-
-
-
see note d
see note d
-
-
Antimony
-
-
-
-
2.0
f,i
2.0
f,i
-
-
Arsenic
-
-
-
-
0.005
0.005
0.0125
0.0125
Barium
-
-
-
-
2.9
f,i
2.9
f,i
0.5
h,i
0.5
h,i
Beryllium
-
-
-
-
0.0053
h,i
0.0053
h,i
0.1
h,i
0.1
h,i
Boron
-
-
-
-
-
-
5
h,i
5
h,i
Cadmium
-
-
-
-
0.000017
0.000017
0.00012
0.00012
Chromium (Total)
-
-
-
-
0.0089
0.0089
0.056
0.056
Copper
-
-
-
-
see note d
see note d
0.002
h,i
0.002
h,i
Iron
-
-
-
-
0.3
0.3
-
-
Lead
-
-
-
-
see note d
see note d
0.002
h,i
0.002
h,i
Mercury
-
-
-
-
0.000026
0.000026
0.00001
6
0.000016
Molybdenum
-
-
-
-
0.073
0.073
-
-
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080
TABLE 2 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR RESIDENTIAL/PARKLAND LAND USE
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
40
Nickel
-
-
-
-
see note d
see note d
0.083
h,i
0.083
h,i
Selenium
-
-
-
-
0.001
0.001
0.054
h,i
0.054
h,i
Silver
-
-
-
-
0.0001
0.0001
0.0015
h,i
0.0015
h,i
Thallium
-
-
-
-
0.0008
0.0008
-
-
Titanium
0.1
h,i
0.1
h,i
Uranium
-
-
-
-
0.015
0.015
-
-
Zinc
-
-
-
-
0.03
0.03
0.01
h,i
0.01
h,i
Table 2.10: Tier 2 (Site-Specific Guidelines), Hydrocarbons, Water Use/Exposure Pathway, based on Soil Type (Fine Soil
and Coarse Soil)
Parameters
Inhalation
Fine
Inhalation
Coarse
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Fine
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Coarse
Freshwater
Life
b
Fine
Freshwater
Life
b
Coarse
Marine
Life
c
Fine
Marine
Life
c
Coarse
Benzene
2.8
0.14
100
61
33
0.69
9.8
0.2
Toluene
NGR
74
82
59
NGR
0.083
NGR
8.9
Ethylbenzene
NGR
16
42
20
NGR
41
NGR
11
Xylenes
80
3.9
21
31
NGR
18
-
-
Styrene
90
4.3
-
-
0.072
0.072
-
-
F1
19
0.81
6.5
7.1
NGR
9.8
-
-
F2
NGR
1.5
1.8
1.8
NGR
1.3
-
-
Acenaphthene
NGR
NGR
-
-
0.0058
0.0058
-
-
Acenaphthylene
-
-
-
-
0.046
0.046
-
-
Anthracene
NGR
NGR
0.025
0.025
0.000012
0.000012
-
-
Fluoranthene
NGR
NGR
0.24
0.24
0.00004
0.00004
-
-
Fluorene
NGR
NGR
-
-
0.003
0.003
0.012
h,i
0.012
h,i
Methylnaphthalenes
35
f
6.2
f
-
-
0.18
f,i
0.18
f,i
-
-
Naphthalene
14
0.6
-
-
0.0011
0.0011
0.0014
0.0014
Phenanthrene
-
-
-
-
0.0004
0.0004
-
-
Pyrene
NGR
NGR
-
-
0.000025
0.000025
-
-
Benz[a]anthracene
g
-
-
-
-
0.000018
0.000018
-
-
Benzo[b+j]fluoranthene
g
-
-
-
-
0.00048
0.00048
-
-
Benzo[k]fluoranthene
g
-
-
-
-
0.00048
0.00048
-
-
Benzo[g,h,i]perylene
g
-
-
-
-
0.00021
0.00017
-
-
Benzo[a]pyrene
g
-
-
0.0018
0.0018
0.000017
0.000015
0.00001
h,i
0.00001
h,i
Chrysene
g
-
-
-
-
0.0014
0.0014
0.0001
h,i
0.0001
h,i
Dibenz[a,h]anthracene
g
-
-
-
-
0.00028
0.00026
-
-
Indeno[1,2,3-c,d]pyrene
g
-
-
-
-
0.00023
0.00021
-
-
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

TABLE 2 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR RESIDENTIAL/PARKLAND LAND USE
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
41
Table 2.11: Tier 2 (Site-Specific Guidelines), Halogenated Aliphatics, Water Use/Exposure Pathway, based on Soil Type
(Fine Soil and Coarse Soil)
Parameters
Inhalation
Fine
Inhalation
Coarse
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Fine
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Coarse
Freshwater
Life
b
Fine
Freshwater
Life
b
Coarse
Marine
Life
c
Fine
Marine
Life
c
Coarse
Vinyl chloride
0.018
0.0011
-
-
-
-
-
-
1,1-Dichloroethene
0.68
0.039
-
-
-
-
-
-
cis-1,2-Dichloroethene
0.017
f
0.0016
f
-
-
18
f,i
18
f,i
-
-
trans-1,2-Dichloroethene
0.017
f
0.0016
f
-
-
28
f,i
28
f,i
-
-
Trichloroethene
(Trichloroethylene, TCE)
0.41
0.02
4.4
5
0.27
0.029
-
-
Tetrachloroethene
(Tetrachloroethylene,
Perchloroethylene, PCE)
2.3
0.11
-
-
0.11
0.11
-
-
1,1-Dichloroethane
3.1
f
0.32
f
-
-
260
f,i
260
f,i
-
-
1,2-Dichloroethane
0.17
0.01
-
-
0.1
0.1
-
-
Dichloromethane
(Methylene chloride)
61
3.4
-
-
0.098
0.098
-
-
1,1,1,2-Tetrachloroethane
0.028
f
0.0034
f
-
-
2.5
f,i
2.5
f,i
-
-
1,1,2,2-Tetrachloroethane
0.015
f
0.0032
f
-
-
3.0
f,i
3.0
f,i
-
-
1,1,1-Trichloroethane
6.7
f
0.64
f
-
-
1.1
f,i
1.1
f,i
-
-
1,1,2-Trichloroethane
0.03
f
0.0047
f
-
-
12
f,i
12
f,i
-
-
Trichloromethane
(Chloroform)
0.05
0.003
-
-
0.0018
0.0018
-
-
Tetrachloromethane
(Carbon tetrachloride)
0.011
0.00056
-
-
0.013
0.013
-
-
1,2-Dichloropropane
0.14
f
0.016
f
-
-
7.2
f,i
7.2
f,i
-
-
1,3-Dichloropropene
0.045
f
0.0052
f
-
-
0.31
f,i
0.31
f,i
-
-
Bromoform
0.77
f
0.38
f
-
-
3.7
f,i
3.7
f,i
-
-
Bromomethane
0.056
f
0.0056
f
-
-
0.4
f,i
0.4
f,i
-
-
Bromodichloromethane
-
-
-
-
8.5
f,i
8.5
f,i
-
-
Dibromochloromethane
26
1.1
-
-
-
-
-
-
Ethylene dibromide
8.3E-4
f
0.00025
f
-
-
12
f,i
12
f,i
-
-
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

TABLE 2 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR RESIDENTIAL/PARKLAND LAND USE
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
42
Table 2.12: Tier 2 (Site-Specific Guidelines), Chlorinated Aromatics, Water Use/Exposure Pathway, based on Soil Type
(Fine Soil and Coarse Soil)
Parameters
Inhalation
Fine
Inhalation
Coarse
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Fine
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Coarse
Freshwater
Life
b
Fine
Freshwater
Life
b
Coarse
Marine
Life
c
Fine
Marine
Life
c
Coarse
Chlorinated Aromatics
Chlorobenzene
0.3
0.014
-
-
0.0013
0.0013
0.025
0.025
1,2-Dichlorobenzene
116
5.4
-
-
0.0007
0.0007
0.042
0.042
1,3-Dichlorobenzene
-
-
-
-
0.15
0.15
0.042
h,i
0.042
h,i
1,4-Dichlorobenzene
4.6
0.22
-
-
0.026
0.026
-
-
1,2,3-Trichlorobenzene
0.8
0.032
-
-
0.008
0.008
-
-
1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene
0.71
0.028
-
-
0.024
0.024
0.0054
0.0054
1,3,5-Trichlorobenzene
0.38
0.015
-
-
-
-
-
-
1,2,3,4-
Tetrachlorobenzene
NGR
0.14
-
-
0.0018
0.0018
-
-
1,2,3,5-
Tetrachlorobenzene
0.41
0.017
-
-
-
-
-
-
1,2,4,5-
Tetrachlorobenzene
0.21
0.0088
-
-
-
-
-
-
Pentachlorobenzene
NGR
0.038
-
-
0.006
0.006
-
-
Hexachlorobenzene
0.029
0.0012
-
-
-
-
-
-
Table 2.13: Tier 2 (Site-Specific Guidelines), Phenols, Water Use/Exposure Pathway, based on Soil Type (Fine Soil and
Coarse Soil)
Parameters
Inhalation
Fine
Inhalation
Coarse
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Fine
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Coarse
Freshwater
Life
b
Fine
Freshwater
Life
b
Coarse
Marine
Life
c
Fine
Marine
Life
c
Coarse
2-Chlorophenol
-
-
-
-
0.33
f,i
0.33
f,i
-
-
2,4-Dichlorophenol
NGR
1500
-
-
0.0002
0.0002
-
-
2,4-Dimethylphenol
-
-
-
-
3.9
f,i
3.9
f,i
-
-
2,4-Dinitrophenol
-
-
-
-
1.1
f,i
1.1
f,i
-
-
Phenol
73000
3700
110
150
0.004
0.004
-
-
2,4,5-Trichlorophenol
-
-
-
-
0.16
f,i
0.16
f,i
-
-
2,4,6-Trichlorophenol
NGR
54
-
-
0.018
0.018
-
-
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080
TABLE 2 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR RESIDENTIAL/PARKLAND LAND USE
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
43
2,3,4,6-Tetrachlorophenol
NGR
NGR
-
-
0.001
0.001
-
-
Pentachlorophenol
NGR
NGR
0.87
0.88
0.0005
0.0005
-
-
Table 2.14: Tier 2 (Site-Specific Guidelines), Pesticides, Water Use/Exposure Pathway, based on Soil Type (Fine Soil
and Coarse Soil)
Parameters
Inhalation
Fine
Inhalation
Coarse
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Fine
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Coarse
Freshwater
Life
b
Fine
Freshwater
Life
b
Coarse
Marine
Life
c
Fine
Marine
Life
c
Coarse
Aldicarb
-
-
-
-
0.001
0.001
0.00015
0.00015
Aldrin
-
-
-
-
0.003
0.003
-
-
Atrazine and metabolites
-
-
-
-
0.0018
0.0018
0.01
h,i
0.01
h,i
Azniphos-methyl
-
-
-
-
0.00001
0.00001
-
-
Bromacil
-
-
-
-
0.005
0.005
-
-
Bromoxynil
-
-
-
-
0.005
0.005
-
-
Captan
-
-
-
-
0.0013
0.0013
-
-
Carbaryl
-
-
-
-
0.0002
0.0002
0.00032
0.00032
Carbofuran
-
-
-
-
0.0018
0.0018
-
-
Chlordane
0.086
f
0.058
f
-
-
0.015
f,i
0.015
f,i
-
-
Chlorothalonil
-
-
-
-
0.00018
0.00018
0.00036
0.00036
Chlorpyrifos
-
-
-
-
0.0000035
0.0000035
0.00000
2
0.000002
Cyanazine
-
-
-
-
0.002
0.002
-
-
2,4-D (2,4-
Dichlorophenoxyacetic
acid) & other phenoxy
herbicides
-
-
-
-
0.004
0.004
-
-
DDAC (Didecyl dimethyl
ammonium chloride)
-
-
-
-
0.0015
0.0015
-
-
DDT (Dichloro-Diphenyl-
Trichloroethane) &
metabolites
-
-
-
-
0.000001
0.000001
-
-
Deltamethrin
-
-
-
-
0.0000004
0.0000004
-
-
Diazinon
0.000003
h,i
0.000003
h,i
Dicamba
-
-
-
-
0.01
0.01
-
-
Dichlofop-methyl
-
-
-
-
0.0061
0.0061
-
-
Dieldrin
-
-
-
-
0.000056
0.000056
-
-
Dimethoate
-
-
-
-
0.0062
0.0062
-
-
Dinoseb
-
-
-
-
0.00005
0.00005
-
-
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

TABLE 2 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR RESIDENTIAL/PARKLAND LAND USE
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
44
Endosulfan
-
-
-
-
0.00003
0.00003
0.00002
0.00002
Endrin
-
-
-
-
0.000036
0.000036
-
-
Glyphosate
-
-
-
-
0.065
0.065
-
-
Heptachlor epoxide
0.0043
0.00024
-
-
0.0000038
0.0000038
-
-
Imidacloprid
-
-
-
-
0.00023
0.00023
-
-
IPBC (3-iodo-2-propynyl
butyl carbamate)
-
-
-
-
0.0019
0.0019
-
-
Lindane (γ-
hexachlorocyclohexane)
-
-
-
-
0.00001
0.00001
-
-
Linuron
-
-
-
-
0.007
0.007
-
-
Malathion
-
-
-
-
0.0001
0.0001
-
-
MCPA
-
-
-
-
0.0026
0.0026
0.0042
0.0042
Methoprene
-
-
-
-
0.00009
0.00009
-
-
Methoxychlor
-
-
-
-
0.00003
0.00003
-
-
Metolachlor
-
-
-
-
0.0078
0.0078
-
-
Metribuzin
-
-
-
-
0.001
0.001
-
-
Parathion
-
-
-
-
0.000013
0.000013
-
-
Permethrin
-
-
-
-
0.000004
0.000004
0.00000
1
0.000001
Picloram
-
-
-
-
0.029
0.029
-
-
Simazine
-
-
-
-
0.01
0.01
-
-
Tebuthiuron
-
-
-
-
0.0016
0.0016
-
-
Toxaphene
6.4
0.31
-
-
0.0000002
0.0000002
-
-
Triallate
-
-
-
-
0.00024
0.00024
-
-
Trifluarin
-
-
-
-
0.0002
0.0002
-
-
Table 2.15: Tier 2 (Site-Specific Guidelines), Other Organics, Water Use/Exposure Pathway, based on Soil Type (Fine
Soil and Coarse Soil)
Parameters
Inhalation
Fine
Inhalation
Coarse
Soil Organisms
Direct Contact
Fine
Soil Organisms
Direct Contact
Coarse
Freshwater
Life
b
Fine
Freshwater
Life
b
Coarse
Marine
Life
c
Fine
Marine
Life
c
Coarse
Acetone
7700
f
1800
f
-
-
13
f,i
13
f,i
-
-
Acridine
-
-
-
-
0.00005
h,i
0.00005
h,i
-
-
Aniline
1,900
87
-
-
0.0022
0.0022
-
-
Bis(2-chloroethyl)ether
2800
f
810
f
-
-
30
f,i
30
f,i
-
-
Bis(2-chloroisopropyl)ether
1600
f
400
f
-
-
30
f,i
30
f,i
-
-
Bis(2-ethyl-hexyl)phthalate
NGR
NGR
-
-
0.016
0.016
-
-
Chloroaniline, p-
-
-
-
-
0.04
f,i
0.04
f,i
-
-
Dibutyl phthalate
NGR
NGR
-
-
0.019
0.019
-
-
di-n-Butyltin
-
-
-
-
0.00008
h,i
0.00008
h,i
-
-
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

TABLE 2 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR RESIDENTIAL/PARKLAND LAND USE
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
45
Diethylphthalate
-
-
-
-
0.0038
f,i
0.0038
f,i
-
-
Diisopropanolamine
-
-
160
160
1.6
1.6
-
-
2,4-Dinitrotoluene
-
-
-
-
0.29
f,i
0.29
f,i
-
-
Ethylene glycol
NGR
NGR
9200
16000
190
190
-
-
Hexachlorobutadiene
0.031
0.0013
-
-
0.0013
0.0013
-
-
Methyl methacrylate
17
0.84
-
-
-
-
-
-
Methyl ethyl ketone
1700
f
470
f
-
-
150
f,i
150
f,i
-
-
Methyl isobutyl ketone
600
f
140
f
-
-
58
f,i
58
f,i
-
-
Methyl mercury
-
-
-
-
0.000015
f,i
0.000015
f,i
-
-
MTBE (Methyl tert-butyl
ether)
6.1
0.34
-
-
10
10
5
5
Monochloramine
-
-
-
-
0.0005
h,i
0.0005
h,i
-
-
Nonylphenol + ethoxylates
-
-
0.0081
0.0081
0.001
0.001
0.0007
0.0007
Propylene glycol
-
-
-
-
500
500
-
-
Quinoline
-
-
-
-
0.0034
h,i
0.0034
h,i
-
-
Sulfolane
-
-
1700
2800
50
50
-
-
Tributyltin
-
-
-
-
0.000008
0.000008
0.00000
1
0.00000
1
Triethyltin
-
-
-
-
0.0004
h,i
0.0004
h,i
-
-
Triphenyltin
-
-
-
-
0.000022
0.000022
-
-
a – all values adopted from Alberta Environment (AESRD) (2010a) unless otherwise specified
b – where AESRD (2010a) guideline was not based on the Canadian Water Quality Guidelines (CWQG) for the Protection of Aquatic Life for freshwater
environments (CCME 1999), and a CWQG exists, the groundwater quality guideline was re-calculated based on the CWQG
c – based on Canadian Water Quality Guidelines (CWQG) for the Protection of Aquatic Life for the marine environments(CCME 1999) and groundwater
transport model
d – the freshwater aquatic life guidelines vary depending on water pH, hardness etc. Therefore, see Canadian Water Quality Guidelines for the Protection of
Aquatic Life (CCME 1999) to determine the appropriate water quality guideline applicable to the site and calculate the groundwater guidelines using
formulas provided in Appendix B
e – guideline is the lowest of all applicable pathways
f – adopted from Ontario Ministry of the Environment (OMOE) (2009)
g – for ecological receptors only
h – adopted from BC Contaminated Sites Regulation
i - 10x factor for dilution in surface water was removed from guideline value
j – adopted directly from CCME (1999)
NGR – no guideline required; calculated guideline exceeds solubility limit
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

TABLE 3 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL LAND USES
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
46
Table 3.0: Tier 1 (Generic Groundwater Guidelines), General and Inorganic Parameters, based on Soil Type (Fine Soil
and Coarse Soil)
Parameters
Fine
Coarse
pH
6.5-9
6.5-9
Ammonia
See note e
See note e
Chloride
100
100
Chlorine
0.002
0.002
Cyanide
0.001
0.001
Fluoride
0.12
0.12
Nitrate
13
13
Nitrate + Nitrite (as nitrogen)
100
100
Nitrite (as nitrogen)
0.06
0.06
Sulphate
100
100
Sulphide (as H
2
S)
0.002
0.002
Total Dissolved Solids (TDS)
3000
3000
Table 3.1: Tier 1 (Generic Groundwater Guidelines), Metals, based on Soil Type (Fine Soil and Coarse Soil)
Parameters
Fine
Coarse
Aluminium
See note e
See note e
Antimony
2.0
2.0
Arsenic
0.005
0.005
Barium
0.5
0.5
Beryllium
0.0053
0.0053
Boron
0.5
0.5
Cadmium
0.000017
0.000017
Chromium (Total)
See note e
See note e
Cobalt
0.05
0.05
Copper
See note e
See note e
Iron
0.3
0.3
Lead
See note e
See note e
Manganese
0.2
0.2
Mercury
See note e
See note e
Molybdenum
0.073
0.073
Nickel
See note e
See note e
Selenium
0.001
0.001
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

TABLE 3 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL LAND USES
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
47
Silver
See note e
See note e
Thallium
0.0008
0.0008
Titanium
0.1
0.1
Uranium
0.01
0.01
Vanadium
0.1
0.1
Zinc
0.01
0.01
Table 3.2: Tier 1 (Generic Groundwater Guidelines), Hydrocarbons, based on Soil Type (Fine Soil and Coarse Soil)
Parameters
Fine
Coarse
Benzene
0.088
0.088
Toluene
4.9
0.083
Ethylbenzene
3.2
3.2
Xylenes
13
3.9
Styrene
0.072
0.072
F1
6.5
0.81
F2
1.8
1.3
Acenaphthene
0.0058
0.0058
Acenaphthylene
0.046
0.046
Anthracene
0.000012
0.000012
Fluoranthene
0.00004
0.00004
Fluorene
0.003
0.003
Methylnaphthalenes
0.18
0.18
Naphthalene
0.0011
0.0011
Phenanthrene
0.0004
0.0004
Pyrene
0.000025
0.000025
Benz[a]anthracene
g
0.000018
0.000018
Benzo[b+j]fluoranthene
g
0.00048
0.00048
Benzo[k]fluoranthene
g
0.00048
0.00048
Benzo[g,h,i]perylene
g
0.00021
0.00017
Benzo[a]pyrene
g
0.00001
0.00001
Chrysene
g
0.0001
0.0001
Dibenz[a,h]anthracene
g
0.00028
0.00026
Indeno[1,2,3-c,d]pyrene
g
0.00023
0.00021
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

TABLE 3 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL LAND USES
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
48
Table 3.3: Tier 1 (Generic Groundwater Guidelines), Halogenated Aliphatics, based on Soil Type (Fine Soil and Coarse
Soil)
Parameters
Fine
Coarse
Vinyl chloride
0.018
0.0011
1,1-Dichloroethene
0.68
0.039
cis-1,2-Dichloroethene
0.017
0.0016
trans-1,2-Dichloroethene
0.017
0.0016
Trichloroethene (Trichloroethylene,
TCE)
0.05
0.02
Tetrachloroethene
(Tetrachloroethylene,
Perchloroethylene, PCE)
0.11
0.11
1,1-Dichloroethane
3.1
0.32
1,2-Dichloroethane
0.005
0.005
Dichloromethane
(Methylene chloride)
0.05
0.05
1,1,1,2-Tetrachloroethane
0.028
0.0033
1,1,2,2-Tetrachloroethane
0.015
0.0032
1,1,1-Trichloroethane
1.1
0.64
1,1,2-Trichloroethane
0.03
0.0047
Trichloromethane (Chloroform)
0.0018
0.0018
Tetrachloromethane
(Carbon tetrachloride)
0.005
0.00056
1,2-Dichloropropane
0.14
0.016
1,3-Dichloropropene
0.045
0.0052
Bromoform
0.77
0.38
Bromomethane
0.056
0.0056
Bromodichloromethane
8.5
8.5
Dibromochloromethane
0.1
0.1
Ethylene dibromide
0.00083
0.00025
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080
TABLE 3 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL LAND USES
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
49
Table 3.4: Tier 1 (Generic Groundwater Guidelines), Chlorinated Aromatics, based on Soil Type (Fine Soil and Coarse
Soil)
Parameters
Fine
Coarse
Chlorobenzene
0.0013
0.0013
1,2-Dichlorobenzene
0.0007
0.0007
1,3-Dichlorobenzene
0.042
0.042
1,4-Dichlorobenzene
0.026
0.026
1,2,3-Trichlorobenzene
0.008
0.008
1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene
0.0054
0.0054
1,3,5-Trichlorobenzene
0.38
0.015
1,2,3,4-Tetrachlorobenzene
0.0018
0.0018
1,2,3,5-Tetrachlorobenzene
0.41
0.017
1,2,4,5-Tetrachlorobenzene
0.21
0.0088
Pentachlorobenzene
0.006
0.006
Hexachlorobenzene
0.00052
0.00052
Table 3.5: Tier 1 (Generic Groundwater Guidelines), Phenols, based on Soil Type (Fine Soil and Coarse Soil)
Parameters
Fine
Coarse
2-Chlorophenol
0.33
0.33
2,4-Dichlorophenol
0.0002
0.0002
2,4-Dimethylphenol
3.9
3.9
2,4-Dinitrophenol
1.1
1.1
Phenol
0.004
0.004
2,4,5-Trichlorophenol
0.16
0.16
2,4,6-Trichlorophenol
0.018
0.018
2,3,4,6-Tetrachlorophenol
0.001
0.001
Pentachlorophenol
0.0005
0.0005
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

TABLE 3 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL LAND USES
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
50
Table 3.6: Tier 1 (Generic Groundwater Guidelines), Pesticides, based on Soil Type (Fine Soil and Coarse Soil)
Parameters
Fine
Coarse
Aldicarb
0.00015
0.00015
Aldrin
0.003
0.003
Atrazine and metabolites
0.0018
0.0018
Azniphos-methyl
0.00001
0.00001
Bromacil
0.005
0.005
Bromoxynil
0.00033
0.00033
Captan
0.0013
0.0013
Carbaryl
0.0002
0.0002
Carbofuran
0.0018
0.0018
Chlordane
0.015
0.015
Chlorothalonil
0.00018
0.00018
Chlorpyrifos
0.000002
0.000002
Cyanazine
0.0005
0.0005
2,4-D (2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic
acid) & other phenoxy herbicides
0.004
0.004
DDAC (Didecyl dimethyl ammonium
chloride)
0.0015
0.0015
DDT (Dichloro-Diphenyl-
Trichloroethane) & metabolites
0.000001
0.000001
Deltamethrin
0.0000004
0.0000004
Diazinon
0.000003
0.000003
Dicamba
0.000006
0.000006
Dichlofop-methyl
0.00018
0.00018
Dieldrin
0.000056
0.000056
Dimethoate
0.003
0.003
Dinoseb
0.00005
0.00005
Endosulfan
0.00002
0.00002
Endrin
0.000036
0.000036
Glyphosate
0.065
0.065
Heptachlor epoxide
0.0000038
0.0000038
Imidacloprid
0.00023
0.00023
IPBC (3-iodo-2-propynyl butyl
carbamate)
0.0019
0.0019
Lindane (γ-hexachlorocyclohexane)
0.00001
0.00001
Linuron
0.000071
0.000071
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

TABLE 3 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL LAND USES
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
51
Malathion
0.0001
0.0001
MCPA
0.000025
0.000025
Methoprene
0.00009
0.00009
Methoxychlor
0.00003
0.00003
Metolachlor
0.0078
0.0078
Metribuzin
0.0005
0.0005
Parathion
0.000013
0.000013
Permethrin
0.000001
0.000001
Picloram
0.029
0.029
Simazine
0.0005
0.0005
Tebuthiuron
0.00027
0.00027
Toxaphene
0.0000002
0.0000002
Triallate
0.00024
0.00024
Trifluarin
0.0002
0.0002
Table 3.7: Tier 1 (Generic Groundwater Guidelines), Other Organics, based on Soil Type (Fine Soil and Coarse Soil)
Parameters
Fine
Coarse
Acetone
13
13
Acridine
0.00005
0.00005
Aniline
0.0022
0.0022
Bis(2-chloroethyl)ether
30
30
Bis(2-chloroisopropyl)ether
30
30
Bis(2-ethyl-hexyl)phthalate
0.016
0.016
Chloroaniline, p-
0.04
0.04
Dibutyl phthalate
0.019
0.019
di-n-Butyltin
0.00008
0.00008
Diethylphthalate
0.0038
0.0038
Diisopropanolamine
1.6
1.6
2,4-Dinitrotoluene
0.29
0.29
Ethylene glycol
190
190
Hexachlorobutadiene
0.0013
0.0013
Methyl methacrylate
17
0.84
Methyl ethyl ketone
150
150
Methyl isobutyl ketone
58
58
Methyl mercury
0.000015
0.000015
MTBE (Methyl tert-butyl ether)
5
0.34
Monochloramine
0.0005
0.0005
Nonylphenol + ethoxylates
0.0007
0.0007
Propylene glycol
500
500
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

TABLE 3 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL LAND USES
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
52
Quinoline
0.0034
0.0034
Sulfolane
0.5
0.5
Tributyltin
0.000001
0.000001
Triethyltin
0.0004
0.0004
Triphenyltin
0.000022
0.000022
Table 3.8: Tier 2 (Site-Specific Guidelines), General and Inorganic Parameters, Water Use/Exposure Pathway, based on
Soil Type (Fine Soil and Coarse Soil)
Parameters
Inhalation
Fine
Inhalation
Coarse
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Fine
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Coarse
Freshwater
Life
b
Fine
Freshwater
Life
b
Coarse
Marine
Life
c
Fine
Marine
Life
c
Coarse
pH
-
-
-
-
6.5-9
6.5-9
7-8.7
7-8.7
Ammonia
-
-
-
-
see note d
see note d
-
-
Chloride
-
-
-
-
120
120
-
-
Chlorine
-
-
-
-
0.002
h,i
0.002
h,i
0.003
h,i
0.003
h,i
Cyanide
-
-
-
-
0.005
0.005
0.001
h,i
0.001
h,i
Fluoride
-
-
-
-
0.12
0.12
1.5
h,i
1.5
h,i
Nitrate
-
-
-
-
13
13
16
16
Nitrite (as
nitrogen)
-
-
-
-
0.06
0.06
-
-
Sulphate
-
-
-
-
100
h,i
100
h,i
-
-
Sulphide (as H
2
S)
-
-
-
-
0.002
0.002
0.002
h,i
0.002
h,i
Table 3.9: Tier 2 (Site-Specific Guidelines), Metals, Water Use/Exposure Pathway, based on Soil Type (Fine Soil and
Coarse Soil)
Parameters
Inhalation
Fine
Inhalation
Coarse
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Fine
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Coarse
Freshwater
Life
b
Fine
Freshwater
Life
b
Coarse
Marine
Life
c
Fine
Marine
Life
c
Coarse
Metals
Aluminium
-
-
-
-
see note d
see note d
-
-
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

TABLE 3 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL LAND USES
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
53
Parameters
Inhalation
Fine
Inhalation
Coarse
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Fine
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Coarse
Freshwater
Life
b
Fine
Freshwater
Life
b
Coarse
Marine
Life
c
Fine
Marine
Life
c
Coarse
Antimony
-
-
-
-
2.0
f,i
2.0
f,i
-
-
Arsenic
-
-
-
-
0.005
0.005
0.0125
0.0125
Barium
-
-
-
-
2.9
f,i
2.9
f,i
0.5
h,i
0.5
h,i
Beryllium
-
-
-
-
0.0053
h,i
0.0053
h,i
0.1
h,i
0.1
h,i
Boron
-
-
-
-
-
-
5
h,i
5
h,i
Cadmium
-
-
-
-
0.000017
0.000017
0.00012
0.00012
Chromium (Total)
-
-
-
-
0.0089
0.0089
0.056
0.056
Copper
-
-
-
-
see note d
see note d
0.002
h,i
0.002
h,i
Iron
-
-
-
-
0.3
0.3
-
-
Lead
-
-
-
-
see note d
see note d
0.002
h,i
0.002
h,i
Mercury
-
-
-
-
0.000026
0.000026
0.000016
0.000016
Molybdenum
-
-
-
-
0.073
0.073
-
-
Nickel
-
-
-
-
see note d
see note d
0.083
h,i
0.083
h,i
Selenium
-
-
-
-
0.001
0.001
0.054
h,i
0.054
h,i
Silver
-
-
-
-
0.0001
0.0001
0.0015
h,i
0.0015
h,i
Thallium
-
-
-
-
0.0008
0.0008
-
-
Titanium
-
-
-
-
0.1
h,i
0.1
h,i
-
-
Uranium
-
-
-
-
0.015
0.015
-
-
Zinc
-
-
-
-
0.03
0.03
0.01
h,i
0.01
h,i
Table 3.10: Tier 2 (Site-Specific Guidelines), Hydrocarbons, Water Use/Exposure Pathway, based on Soil Type (Fine Soil
and Coarse Soil)
Parameters
Inhalation
Fine
Inhalation
Coarse
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Fine
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
oarse
Freshwater
Life
b
Fine
Freshwater
Life
b
Coarse
Marine
Life
c
Fine
Marine
Life
c
Coarse
Hydrocarbons
Benzene
19
1.8
540
350
33
0.69
9.8
0.2
Toluene
NGR
NGR
240
200
NGR
0.083
NGR
8.9
Ethylbenzene
NGR
NGR
150
110
NGR
41
NGR
11
Xylenes
NGR
48
74
120
NGR
18
-
-
Styrene
NGR
51
-
-
0.072
0.072
-
-
F1
NGR
9.1
9.9
11
NGR
9.8
-
-
F2
NGR
17
3.1
3.1
NGR
1.3
-
-
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080
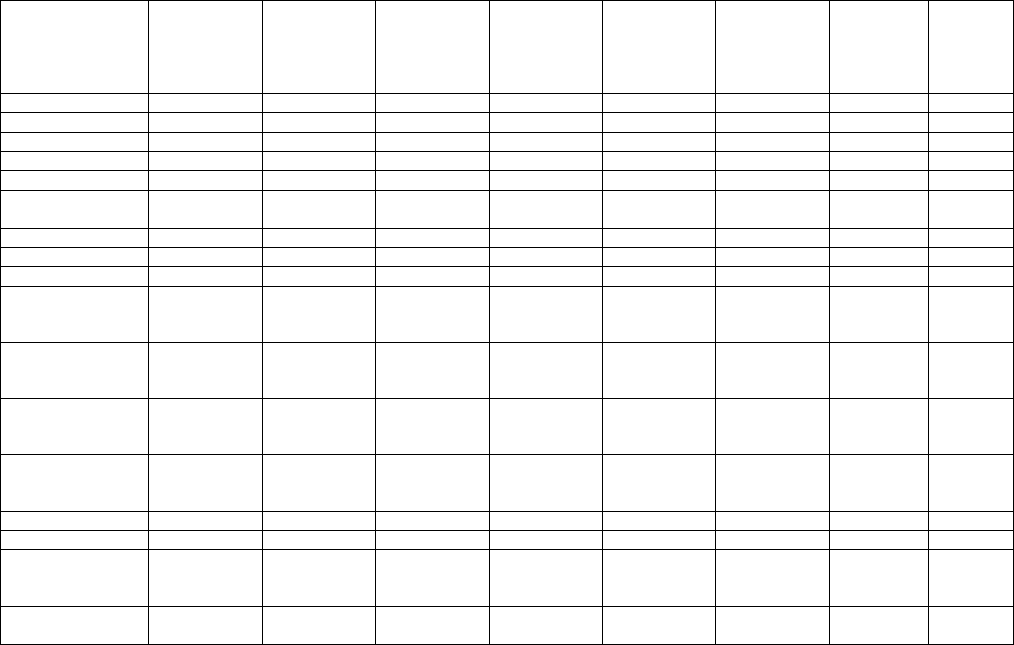
TABLE 3 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL LAND USES
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
54
Parameters
Inhalation
Fine
Inhalation
Coarse
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Fine
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
oarse
Freshwater
Life
b
Fine
Freshwater
Life
b
Coarse
Marine
Life
c
Fine
Marine
Life
c
Coarse
Acenaphthene
NGR
NGR
-
-
0.0058
0.0058
-
-
Acenaphthylene
-
-
-
-
0.046
0.046
-
-
Anthracene
NGR
NGR
0.32
0.32
0.000012
0.000012
-
-
Fluoranthene
NGR
NGR
0.86
0.86
0.00004
0.00004
-
-
Fluorene
NGR
NGR
-
-
0.003
0.003
-
-
Methylnaphthalen
es
150
f
38
f
-
-
0.18
f,i
0.18
f,i
-
-
Naphthalene
NGR
7
-
-
0.0011
0.0011
0.0014
0.0014
Phenanthrene
-
-
-
-
0.0004
0.0004
-
-
Pyrene
NGR
NGR
-
-
0.000025
0.000025
-
-
Benz[a]anthracen
e
g
-
-
-
-
0.000018
0.000018
-
-
Benzo[b+j]fluoran
thene
g
-
-
-
-
0.00048
0.00048
-
-
Benzo[k]fluoranth
ene
g
-
-
-
-
0.00048
0.00048
-
-
Benzo[g,h,i]peryle
ne
g
-
-
-
-
0.00021
0.00017
-
-
Benzo[a]pyrene
g
-
-
0.0066
0.0066
0.000017
0.000015
-
-
Chrysene
g
-
-
-
-
0.0014
0.0014
-
-
Dibenz[a,h]an
thracene
g
-
-
-
-
0.00028
0.00026
-
-
Indeno[1,2,3-
c,d]pyrene
g
-
-
-
-
0.00023
0.00021
-
-
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

TABLE 3 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL LAND USES
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
55
Table 3.11: Tier 2 (Site-Specific Guidelines), Halogenated Aliphatics, Water Use/Exposure Pathway, based on Soil Type
(Fine Soil and Coarse Soil)
Parameters
Inhalation
Fine
Inhalation
Coarse
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Fine
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Coarse
Freshwater
Life
b
Fine
Freshwater
Life
b
Coarse
Marine
Life
c
Fine
Marine
Life
c
Coarse
Halogenated
Aliphatics
Vinyl chloride
0.12
0.013
-
-
-
-
-
-
1,1-
Dichloroethene
4.5
0.49
-
-
-
-
-
-
cis-1,2-
Dichloroethene
0.23
f
0.03
f
-
-
18
f,i
18
f,i
-
-
trans-1,2-
Dichloroethene
0.23
f
0.03
f
-
-
28
f,i
28
f,i
-
-
Trichloroethene
(Trichloroethylen
e, TCE)
2.8
0.25
73
83
0.27
0.029
-
-
Tetrachloroethe
ne
(Tetrachloroethy
lene,
Perchloroethyle
ne, PCE)
16
1.3
-
-
0.11
0.11
-
-
1,1-
Dichloroethane
44
f
6.6
f
-
-
260
f,i
260
f,i
1,2-
Dichloroethane
1.2
0.13
-
-
0.1
0.1
-
-
Dichloromethan
e
(Methylene
chloride)
410
43
-
-
0.098
0.098
-
-
1,1,1,2-
Tetrachloroetha
ne
0.38
f
0.066
f
-
-
2.5
f,i
2.5
f,i
-
-
1,1,2,2-
Tetrachloroetha
ne
0.21
f
0.063
f
-
-
3.0
f,i
3.0
f,i
-
-
1,1,1-
Trichloroethane
95
f
13
f
-
-
1.1
f,i
1.1
f,i
-
-
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

TABLE 3 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL LAND USES
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
56
Parameters
Inhalation
Fine
Inhalation
Coarse
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Fine
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Coarse
Freshwater
Life
b
Fine
Freshwater
Life
b
Coarse
Marine
Life
c
Fine
Marine
Life
c
Coarse
1,1,2-
Trichloroethane
0.41
f
0.091
f
-
-
12
f,i
12
f,i
-
-
Trichloromethan
e (Chloroform)
0.35
0.04
-
-
0.0018
0.0018
-
-
Tetrachlorometh
ane
(Carbon
tetrachloride)
0.078
0.0068
-
-
0.013
0.013
-
-
1,2-
Dichloropropane
2
f
0.33
f
-
-
7.2
f,i
7.2
f,i
-
-
1,3-
Dichloropropene
0.61
f
0.1
f
-
-
0.31
f,i
0.31
f,i
-
-
Bromoform
13
f
8.4
f
-
-
3.7
f,i
3.7
f,i
-
-
Bromomethane
0.23
f
0.033
f
-
-
0.4
f,i
0.4
f,i
-
-
Bromodichlorom
ethane
-
-
-
-
8.5
f,i
8.5
f,i
-
-
Dibromochlorom
ethane
250
10
-
-
-
-
-
-
Ethylene
dibromide
0.012
f
0.0051
f
-
-
12
f,i
12
f,i
-
-
Table 3.12: Tier 2 (Site-Specific Guidelines), Chlorinated Aromatics, Water Use/Exposure Pathway, based on Soil Type
(Fine Soil and Coarse Soil)
Parameters
Inhalation
Fine
Inhalation
Coarse
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Fine
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Coarse
Freshwater
Life
b
Fine
Freshwater
Life
b
Coarse
Marine
Life
c
Fine
Marine
Life
c
Coarse
Chlorinated
Aromatics
Chlorobenzene
2.2
0.18
-
-
0.0013
0.0013
0.025
0.025
1,2-
Dichlorobenzen
NGR
64
-
-
0.0007
0.0007
0.042
0.042
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080
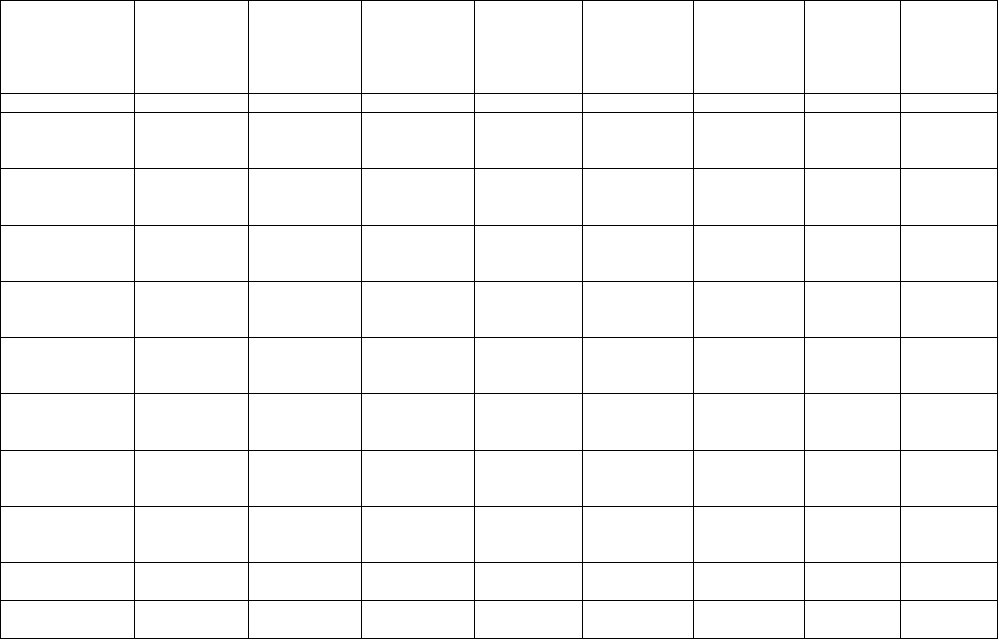
TABLE 3 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL LAND USES
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
57
Parameters
Inhalation
Fine
Inhalation
Coarse
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Fine
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Coarse
Freshwater
Life
b
Fine
Freshwater
Life
b
Coarse
Marine
Life
c
Fine
Marine
Life
c
Coarse
e
1,3-
Dichlorobenzen
e
-
-
-
-
0.15
0.15
0.042
h,i
0.042
h,i
1,4-
Dichlorobenzen
e
32
2.6
-
-
0.026
0.026
-
-
1,2,3-
Trichlorobenze
ne
6.9
0.33
-
-
0.008
0.008
-
-
1,2,4-
Trichlorobenze
ne
6.1
0.29
-
-
0.024
0.024
0.0054
0.0054
1,3,5-
Trichlorobenze
ne
3.3
0.15
-
-
-
-
-
-
1,2,3,4-
Tetrachloroben
zene
NGR
NGR
-
-
0.0018
0.0018
-
-
1,2,3,5-
Tetrachloroben
zene
NGR
0.16
-
-
-
-
-
-
1,2,4,5-
Tetrachloroben
zene
NGR
0.08
-
-
-
-
-
-
Pentachloroben
zene
NGR
0.44
-
-
0.006
0.006
-
-
Hexachloroben
zene
0.21
0.014
-
-
-
-
-
-
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

TABLE 3 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL LAND USES
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
58
Table 3.13: Tier 2 (Site-Specific Guidelines), Phenols, Water Use/Exposure Pathway, based on Soil Type (Fine Soil and
Coarse Soil)
Parameters
Inhalation
Fine
Inhalation
Coarse
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Fine
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Coarse
Freshwater
Life
b
Fine
Freshwater
Life
b
Coarse
Marine
Life
c
Fine
Marine
Life
c
Coarse
Phenols
2-Chlorophenol
-
-
-
-
0.33
f,i
0.33
f,i
-
-
2,4-
Dichlorophenol
NGR
NGR
-
-
0.0002
0.0002
-
-
2,4-
Dimethylphenol
-
-
-
-
3.9
f,i
3.9
f,i
-
-
2,4-
Dinitrophenol
-
-
-
-
1.1
f,i
1.1
f,i
-
-
Phenol
NGR
45000
110
150
0.004
0.004
-
-
2,4,5-
Trichlorophenol
-
-
-
-
0.16
f,i
0.16
f,i
-
-
2,4,6-
Trichlorophenol
NGR
540
-
-
0.018
0.018
-
-
2,3,4,6-
Tetrachlorophe
nol
NGR
NGR
-
-
0.001
0.001
-
-
Pentachlorophe
nol
NGR
NGR
2.2
2.2
0.0005
0.0005
-
-
Table 3.14: Tier 2 (Site-Specific Guidelines), Pesticides, Water Use/Exposure Pathway, based on Soil Type (Fine Soil
and Coarse Soil)
Parameters
Inhalation
Fine
Inhalation
Coarse
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Fine
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Coarse
Freshwater
Life
b
Fine
Freshwater
Life
b
Coarse
Marine
Life
c
Fine
Marine
Life
c
Coarse
Aldicarb
-
-
-
-
0.001
0.001
0.00015
0.00015
Aldrin
-
-
-
-
0.003
0.003
-
-
Atrazine and
metabolites
-
-
-
-
0.0018
0.0018
0.01
h,i
0.01
h,i
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

TABLE 3 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL LAND USES
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
59
Parameters
Inhalation
Fine
Inhalation
Coarse
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Fine
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Coarse
Freshwater
Life
b
Fine
Freshwater
Life
b
Coarse
Marine
Life
c
Fine
Marine
Life
c
Coarse
Azniphos-
methyl
-
-
-
-
0.00001
0.00001
-
-
Bromacil
-
-
-
-
0.005
0.005
-
-
Bromoxynil
-
-
-
-
0.005
0.005
-
-
Captan
-
-
-
-
0.0013
0.0013
-
-
Carbaryl
-
-
-
-
0.0002
0.0002
0.00032
0.00032
Carbofuran
-
-
-
-
0.0018
0.0018
-
-
Chlordane
1.7
f
1.6
f
-
-
0.015
f,i
0.015
f,i
-
-
Chlorothalonil
-
-
-
-
0.00018
0.00018
0.00036
0.00036
Chlorpyrifos
-
-
-
-
0.0000035
0.0000035
0.00000
2
0.000002
Cyanazine
-
-
-
-
0.002
0.002
-
-
2,4-D (2,4-
Dichlorophenox
yacetic acid) &
other phenoxy
herbicides
-
-
-
-
0.004
0.004
-
-
DDAC (Didecyl
dimethyl
ammonium
chloride)
-
-
-
-
0.0015
0.0015
-
-
DDT (Dichloro-
Diphenyl-
Trichloroethane
) & metabolites
-
-
-
-
0.000001
0.000001
-
-
Deltamethrin
-
-
-
-
0.0000004
0.0000004
-
-
Diazinon
0.000003
h,i
0.000003
h,i
Dicamba
-
-
-
-
0.01
0.01
-
-
Dichlofop-
methyl
-
-
-
-
0.0061
0.0061
-
-
Dieldrin
-
-
-
-
0.000056
0.000056
-
-
Dimethoate
-
-
-
-
0.0062
0.0062
-
-
Dinoseb
-
-
-
-
0.00005
0.00005
-
-
Endosulfan
-
-
-
-
0.00003
0.00003
0.00002
0.00002
Endrin
-
-
-
-
0.000036
0.000036
-
-
Glyphosate
-
-
-
-
0.065
0.065
-
-
Heptachlor
epoxide
0.051
0.002
-
-
0.0000038
0.0000038
-
-
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

TABLE 3 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL LAND USES
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
60
Parameters
Inhalation
Fine
Inhalation
Coarse
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Fine
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Coarse
Freshwater
Life
b
Fine
Freshwater
Life
b
Coarse
Marine
Life
c
Fine
Marine
Life
c
Coarse
Imidacloprid
-
-
-
-
0.00023
0.00023
-
-
IPBC (3-iodo-2-
propynyl butyl
carbamate)
-
-
-
-
0.0019
0.0019
-
-
Lindane (γ-
hexachlorocyclo
hexane)
-
-
-
-
0.00001
0.00001
-
-
Linuron
-
-
-
-
0.007
0.007
-
-
Malathion
-
-
-
-
0.0001
0.0001
-
-
MCPA
-
-
-
-
0.0026
0.0026
0.0042
0.0042
Methoprene
-
-
-
-
0.00009
0.00009
-
-
Methoxychlor
-
-
-
-
0.00003
0.00003
-
-
Metolachlor
-
-
-
-
0.0078
0.0078
-
-
Metribuzin
-
-
-
-
0.001
0.001
-
-
Parathion
-
-
-
-
0.000013
0.000013
-
-
Permethrin
-
-
-
-
0.000004
0.000004
0.00000
1
0.000001
Picloram
-
-
-
-
0.029
0.029
-
-
Simazine
-
-
-
-
0.01
0.01
-
-
Tebuthiuron
-
-
-
-
0.0016
0.0016
-
-
Toxaphene
75
2.9
-
-
0.0000002
0.0000002
-
-
Triallate
-
-
-
-
0.00024
0.00024
-
-
Trifluarin
-
-
-
-
0.0002
0.0002
-
-
Table 3.15: Tier 2 (Site-Specific Guidelines), Other Organics, Water Use/Exposure Pathway, based on Soil Type (Fine
Soil and Coarse Soil)
Parameters
Inhalation
Fine
Inhalation
Coarse
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Fine
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Coarse
Freshwater
Life
b
Fine
Freshwater
Life
b
Coarse
Marine
Life
c
Fine
Marine
Life
c
Coarse
Acetone
1.1E+5
f
39000
f
-
-
13
f,i
13
f,i
-
-
Acridine
-
-
-
-
0.00005
h,i
0.00005
h,i
-
-
Aniline
13,000
1,000
-
-
0.0022
0.0022
-
-
Bis(2-
12000
f
810
f
-
-
30
f,i
30
f,i
-
-
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080
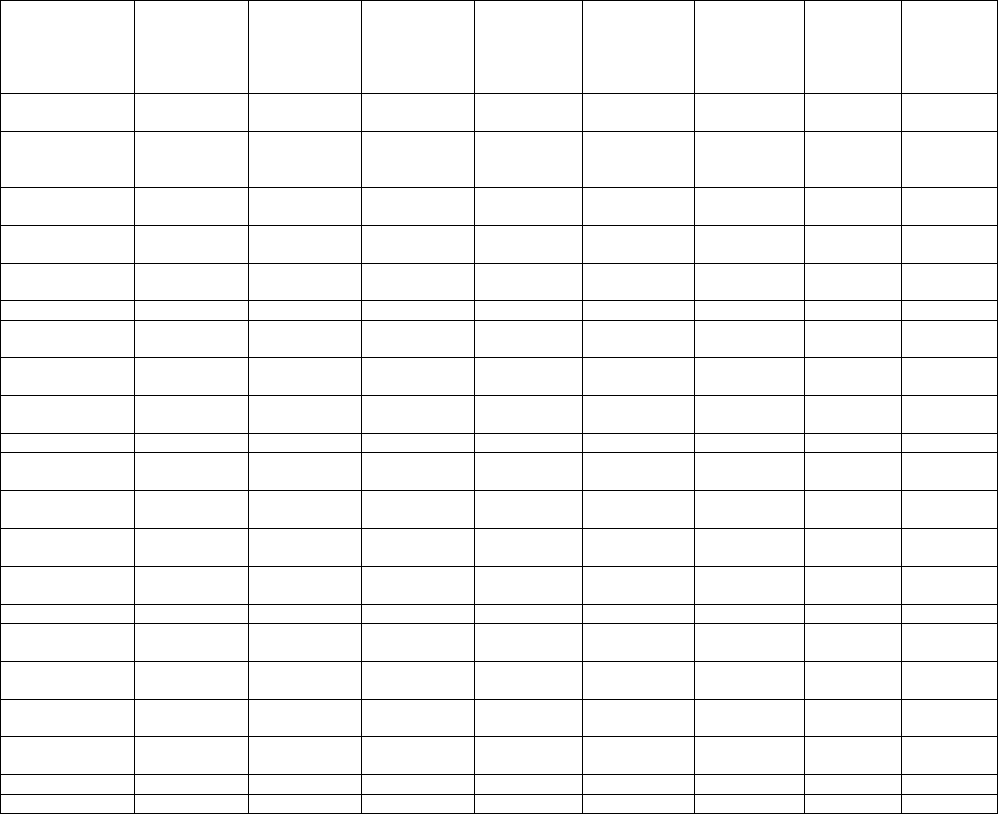
TABLE 3 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL LAND USES
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
61
Parameters
Inhalation
Fine
Inhalation
Coarse
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Fine
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Coarse
Freshwater
Life
b
Fine
Freshwater
Life
b
Coarse
Marine
Life
c
Fine
Marine
Life
c
Coarse
chloroethyl)eth
er
Bis(2-
chloroisopropyl
)ether
7100
f
400
f
-
-
30
f,i
30
f,i
-
-
Bis(2-ethyl-
hexyl)phthalate
NGR
NGR
-
-
0.016
0.016
-
-
Chloroaniline,
p-
-
-
-
-
0.04
f,i
0.04
f,i
-
-
Dibutyl
phthalate
NGR
NGR
-
-
0.019
0.019
-
-
di-n-Butyltin
-
-
-
-
0.00008
h,i
0.00008
h,i
-
-
Diethylphthalat
e
-
-
-
-
0.0038
f,i
0.0038
f,i
-
-
Diisopropanola
mine
-
-
160
160
1.6
1.6
-
-
2,4-
Dinitrotoluene
-
-
-
-
0.29
f,i
0.29
f,i
-
-
Ethylene glycol
NGR
NGR
9200
16000
190
190
-
-
Hexachlorobuta
diene
0.22
0.015
-
-
0.0013
0.0013
-
-
Methyl
methacrylate
120
10
-
-
-
-
-
-
Methyl ethyl
ketone
7200
f
2900
f
-
-
150
f,i
150
f,i
-
-
Methyl isobutyl
ketone
2500
f
830
f
-
-
58
f,i
58
f,i
-
-
Methyl mercury
-
-
-
-
0.000015
f,i
0.000015
f,i
-
-
MTBE (Methyl
tert-butyl ether)
40
4.3
-
-
10
10
5
5
Monochloramin
e
0.0005
h,i
0.0005
h,i
Nonylphenol +
ethoxylates
-
-
0.0081
0.0081
0.001
0.001
0.0007
0.0007
Propylene
glycol
-
-
-
-
500
500
-
-
Quinoline
0.0034
h,i
0.0034
h,i
Sulfolane
-
-
1700
2800
50
50
-
-
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

TABLE 3 FEDERAL INTERIM GROUNDWATER QUALITY GUIDELINES
GENERIC GUIDELINES FOR COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL LAND USES
a
(mg/L)
Note: Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality (Health Canada, 2010) may also apply
Guidelines may not apply if underlying assumptions are not met (see Section 4.2)
62
Parameters
Inhalation
Fine
Inhalation
Coarse
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Fine
Soil
Organisms
Direct
Contact
Coarse
Freshwater
Life
b
Fine
Freshwater
Life
b
Coarse
Marine
Life
c
Fine
Marine
Life
c
Coarse
Tributyltin
-
-
-
-
0.000008
0.000008
0.000001
0.000001
Triethyltin
-
-
-
-
0.0004
h,i
0.0004
h,i
-
-
Triphenyltin
-
-
-
-
0.000022
0.000022
-
-
a – all values adopted from Alberta Environment (AESRD) (2010a) unless otherwise specified
b – where AESRD (2010a) guideline was not based on the Canadian Water Quality Guidelines (CWQG) for the Protection of Aquatic Life for freshwater
environments (CCME 1999), and a CWQG exists, the groundwater quality guideline was re-calculated based on the CWQG
c – based on Canadian Water Quality Guidelines (CWQG) for the Protection of Aquatic Life for the marine environments(CCME 1999) and groundwater
transport model
d – the freshwater aquatic life guidelines vary depending on water pH, hardness etc. Therefore, see Canadian Water Quality Guidelines for the Protection of
Aquatic Life (CCME 1999) to determine the appropriate water quality guideline applicable to the site and calculate the groundwater guidelines using
formulas provided in Appendix B
e – guideline is the lowest of all applicable pathways
f – adopted from Ontario Ministry of the Environment (OMOE) (2010)
g – for ecological receptors only
h – adopted from BC Contaminated Sites Regulation
i - 10x factor for dilution in surface water was removed from guideline value
j – adopted directly from CCME (1999)
NGR – no guideline required; calculated guideline exceeds solubility limit
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080
63
APPENDIX B
MODELS, EQUATIONS AND DEFAULT MODEL PARAMETERS
USED TO CALCULATE TIER 1 AND TIER 2 GUIDELINES
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

64
This appendix provides the equations and default model parameters used to derive most of the
generic groundwater guidelines; these same equations and model parameters should be used
as the starting point for site-specific modification in the derivation of Tier 2 guidelines. All
equations presented herein were adopted from Alberta Environment and Sustainable Resource
Development (AESRD) (AESRD 2010a, 2010b) unless otherwise specified.
For more comprehensive guidance on using the models presented herein, including which
parameters can be adjusted at Tier 2, appropriate ranges within which these parameters can be
adjusted, and data requirements to support Tier 2 adjustment, refer to Appendices C and D of
the Canada-Wide Standard for Petroleum Hydrocarbons in Soil: User Guidance (CCME,
2008b).
B.1 Human Exposure Pathways
Vapour Inhalation
Groundwater guidelines protective of the indoor infiltration and inhalation pathway were
calculated using the equations from the CCME (2006) protocol adapted for groundwater.
Consistent with the approach taken in CCME (2008a), an adjustment factor of 10 is applied in
the equations below for petroleum hydrocarbons (including benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene and
xylenes), to account for empirical evidence that measured indoor air concentrations are typically
lower by at least an order of magnitude than concentrations predicted from the models below.
The adjustment factor takes the value of 1 for all other chemicals, reflecting the lack of any
empirical data to support such a factor for these chemicals. Default parameter values are
summarized in Tables 4 to 8. Separate calculations are made for carcinogens and non-
carcinogenic chemicals.
Groundwater Guidelines for Non-Carcinogens
3
10'
ETH
AFDFSAFCTC
GWQG
ia
I
Where: GWQG
I
= groundwater quality guideline for indoor infiltration (mg/L);
TC = tolerable concentration (mg/m
3
);
C
a
= background air concentration (mg/m
3
);
SAF = allocation factor (dimensionless);
DF
i
= dilution factor from soil gas to indoor air (calculated below);
AF = adjustment factor (10, hydrocarbons; 1, all other chemicals);
H’ = dimensionless Henry’s Law Constant (dimensionless);
ET = exposure term (dimensionless);
10
3
= conversion factor from m
3
to L; and,
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

65
Groundwater Guidelines for Carcinogens
3
10'
ETH
AFDFRsC
GWQG
i
I
Where: GWQG
I
= groundwater quality guideline for indoor infiltration (mg/L);
RsC = risk-specific concentration (mg/m
3
);
DF
i
= dilution factor from soil gas to indoor air (calculated below);
AF = adjustment factor (10, hydrocarbons; 1, all other chemicals);
H’ = dimensionless Henry’s Law Constant (dimensionless);
ET = exposure term (dimensionless);
10
3
= conversion factor from m
3
to L; and,
Note that in contrast to the CCME (2006) protocol, an exposure term of 0.2747 was used for
commercial and industrial land use for carcinogens.
Dilution Factor Calculation
The dilution factor (DF
i
) was calculated as follows:
1
DF
i
Where: DF
i
= dilution factor from soil gas concentration to indoor air
concentration (unitless); and,
= attenuation coefficient (unitless; see derivation below).
1
AD
LQ
exp
LQ
AD
LQ
AD
AD
LQ
exp
AD
LQ
exp
LQ
AD
crackcrack
cracksoil
Tsoil
B
eff
T
TB
B
eff
T
crackcrack
cracksoil
crackcrack
cracksoil
TB
B
eff
T
where:
= attenuation coefficient (dimensionless);
D
T
eff
= effective porous media diffusion coefficient (cm
2
/s);
A
B
= building area (cm
2
);
Q
B
= building ventilation rate (cm
3
/s);
L
T
= distance from contaminant source to foundation (cm);
Q
soil
= volumetric flow rate of soil gas into the building (cm
3
/s);
L
crack
= thickness of the foundation (cm);
D
crack
= effective vapour diffusion coefficient through the crack (cm
2
/s);
and,
A
crack
= area of cracks through which contaminant vapours enter the
building (cm
2
).
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

66
Calculation of D
T
eff
:
2
3
10
t
a
a
eff
T
DD
Where: D
T
eff
= overall effective porous media diffusion coefficient based on
vapour-phase concentrations for the region between the source
and foundation (cm
2
/s);
D
a
= diffusion coefficient in air (cm
2
/s);
a
= soil vapour-filled porosity (dimensionless); and,
t
= soil total porosity (dimensionless).
Note that this equation assumes that the dominant form of diffusion is through air and therefore
cannot be applied to scenarios where diffusion in water may become a dominant form of the
transport equation. Therefore, moisture content must always be set to an unsaturated condition
in order to apply this equation.
For Tier 1 and Tier 2 guideline adjustments where more than 1 stratum exists, the calculation of
D
T
eff
must be based on the most conservative stratum in zone of contaminant migration (e.g.,
the stratum with the highest diffusion coefficient must be used). An exception is allowed for sites
where a surficial fine grained deposit exists over a coarse grained deposit. In the event that
1. Sufficient borehole information is provided to support the presence of a continuous fine
grained layer over the entire site,
2. Sufficient borehole information is provided to support estimation of the minimum
thickness of the fine grained layer and
3. The minimum thickness of the fine grained layer is at least 1 m deeper than the depth of
typical excavations at the site in the event of construction and at least 1 m deeper than
the maximum depth of basements or potential basements at the site
then the fine grained layer can be applied to the calculation of D
T
eff
. However, the depth to the
contaminant layer or the groundwater cannot be set at a depth greater than the minimum
thickness of the layer.
For more detailed site specific risk assessments and in the event that sufficient data is available
to determine continuous presence of several layers and minimum and maximum thickness of
these layers, it may be possible to estimate the effective diffusion coefficient based on a
combination of all layers present at the site. However, this requires a site specific risk
assessment and is not allowed for simple model changes at Tier 2.
Where site-specific risk assessments are used, and in the event that there is more than one soil
type through which the contaminant must diffuse, D
T
eff
can be calculated separately for each soil
stratum (stratum-specific diffusion coefficients are referred to as D
i
eff
below) and averaged using
the following equation:
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

67
i
eff
i
T
eff
T
LD
L
D
Where: D
T
eff
= overall effective porous media diffusion coefficient based on
vapour-phase concentrations for the region between the source
and foundation (cm
2
/s);
D
i
eff
= effective porous media diffusion coefficient for stratum ‘i’,
calculated as above;
L
T
= distance from contaminant source to foundation (cm); and,
L
i
= thickness of stratum ‘i’ through which the contaminant travels.
Calculation of D
crack
:
D
crack
is calculated in exactly the same way as D
T
eff
, with the exception that the assumption is
made that the soil material in the cracks is dry (CCME, 2006a), and accordingly, the air filled
porosity is the same as the total porosity, and the equation becomes:
2
3
10
t
t
acrack
DD
Where: D
crack
= effective porous media diffusion coefficient in floor cracks (cm
2
/s);
D
a
= diffusion coefficient in air (cm
2
/s);
t
= total porosity for underlying soil (dimensionless).
In this equation, it is always assumed that the soil properties are based on the properties of the
soil surrounding the building foundation.
Calculation of Q
B
:
600,3
ACHHWL
Q
BBB
B
Where: Q
B
= building ventilation rate (cm
3
/s);
L
B
= building length (cm);
W
B
= building width (cm);
H
B
= building height (cm 3);
ACH = air exchanges per hour (h
-1
); and,
3,600 = conversion factor from hours to seconds.
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

68
Calculation of Q
soil
:
crack
crack
crackv
soil
r
Z2
ln
XPk2
Q
Where Q
soil
= volumetric flow rate of soil gas into the building (cm
3
/s);
P = pressure differential (g/cms
2
);
k
v
= soil vapour permeability to vapour flow (cm
2
) for soil adjacent to
building foundation;
X
crack
= length of idealized cylinder (cm);
= vapour viscosity (0.000173 g/cms; CCME, 2006a);
Z
crack
= distance below grade to idealized cylinder (cm); and,
r
crack
= radius of idealized cylinder (cm; calculated as A
crack
/X
crack
).
B.2 Ecological Exposure Pathways
Direct Contact by Soil organisms
Groundwater guidelines based on direct contact by soil organisms for non-polar organic
compounds and salts are based on soil quality guidelines for this pathway:
Non-polar organic compounds
abococw
b
DCDC
HfK
SQGGWQG
'
Where: GWQG
DC
= groundwater remediation guideline protective of direct contact with
plants and soil invertebrates in areas of shallow groundwater
(mg/L);
SQG
DC
= soil quality guideline protective of direct contact with plants and
soil invertebrates (mg/kg);
b
= dry soil bulk density (g/cm
3
);
w
= moisture-filled porosity (dimensionless);
K
oc
= organic carbon partition coefficient (L/kg);
f
oc
= fraction of organic carbon (g/g);
H’ = dimensionless Henry’s Law Constant (dimensionless); and,
a
= vapour-filled porosity (dimensionless).
Salt Compounds
Salt compounds do not interact significantly with soil organic carbon, are not present to a
significant extent in the vapour phase, and are present in pore water or loosely bound to clay
mineral surfaces. These guidelines are presented in terms of the electrical conductivity (in
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

69
dS/m) of a saturated paste of the soil. The groundwater guideline for this exposure pathway for
salts is calculated from the AESRD (2001b) ecological soil contact soil quality guidelines, for
coarse and fine soils, using the following equation. It is assumed that the water content of the
soil in a saturated paste sample may be approximated by the total porosity of the soil.
t
SQGGWQG
b
DCDC
000,1
where:
GWQG
DC
= groundwater remediation objective protective of ecological soil
contact in surface soil (S/cm);
SQG
DC
= soil quality guideline for salts protective of eco-soil contact (2
dS/m, agricultural and residential; 4 dS/m commercial and
industrial);
1,000 = conversion factor from dS/m to S/cm (dimensionless);
b
= dry soil bulk density (g/cm
3
); and,
t
= total porosity (dimensionless).
It should be noted that this calculation only applies to the groundwater quality guideline that is
calculated for soil-based ecological receptors and cannot be used to screen any other pathways
or receptors. It should also be noted that the above calculation only applies to the total ionic
concentration in the soil. All pathways and receptors, including soil ecological pathways and
receptors, must still be screened for potential effects from exposure of the individual ions that
comprise the total electrical conductivity regardless of calculations from this equation.
B.3 Groundwater Transport
Lateral groundwater transport (e.g. to a nearby surface water body) is modelled using a
transport model and equations from the CCME (2006) protocol. At this time, transport modelling
for inorganic substances is not conducted due to the uncertainties associated with the
partitioning of metals between the adsorbed and dissolved phase and the lack of biodegradation
of these substances; transport of inorganic substances could be assessed on a site-specific
basis where appropriate.
For the protection of aquatic life or wildlife watering, it is assumed that there is a minimum 10 m
lateral separation between the point of measurement and the surface water body; this distance
can be modified at Tier 2. The model used to calculate the groundwater guidelines for these
water uses is simply the lateral transport part of the CCME (2006) model used to calculate the
corresponding soil guideline.
The groundwater remediation guideline protective of aquatic life and wildlife watering is
calculated using the following equations.
GWQG
GR
= SWQG x DF4
where: GWQG
GR
= groundwater quality guideline protective of groundwater pathways
(mg/kg);
SWQG
FL
= corresponding surface water quality guideline (aquatic life, or
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

70
wildlife watering) (mg/L);
DF4 = dilution factor for lateral transport (L/kg).
Assumptions implicit in the model include the following:
the soil is physically and chemically homogeneous;
depletion of the contaminant source is not considered (i.e., infinite source mass);
contaminant is not present as a free phase product;
groundwater aquifer is unconfined;
groundwater flow is uniform and steady;
co-solubility and oxidation/reduction effects are not considered;
attenuation of the contaminant in the saturated zone is assumed to be one-dimensional
with respect to sorption-desorption, dispersion, and biological degradation;
dispersion in groundwater is assumed to occur in the longitudinal and transverse
directions only and diffusion is not considered;
dilution of the plume by groundwater recharge down-gradient of the source is not
included.
Dilution Factor 4
Dilution factor 4 (DF4) from the CCME (2006) model accounts for the processes of dispersion
and biodegradation as groundwater travels downgradient from beneath the source of
contamination, and is the ratio of the concentration of a chemical in groundwater beneath the
source, to the concentration in groundwater at a distance (10 m for generic aquatic life and
wildlife watering guidelines) downgradient of the source. For distances less than 10 m, a value
of 1 should be used for DF4. Consistent with CCME (2008a,b), the time independent (steady
state) version of the equation to calculate DF4 was used:
)]()([)exp(
2
4
DerfCerfA
DF
2/1
xs
x
v
DL4
11
D2
x
A
2/1
y
xD2
2Yy
C
2/1
y
xD2
2Yy
D
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

71
d
t
L
s
s
07.0exp
6931.0
2/1
st
R
V
v
t
ococb
s
fK
1R
x1.0D
x
xD
y
01.0
where:
DF4 = dilution factor 4 (dimensionless);
erf = the error function;
A = dimensionless group A (dimensionless);
C = dimensionless group C (dimensionless);
D = dimensionless group D (dimensionless);
x = lateral distance between source and receptor (m);
D
x
= dispersivity in the direction of groundwater flow (m);
L
s
= decay constant (1/year);
v = velocity of the contaminant (m/year);
y = distance to receptor perpendicular to groundwater flow (m);
Y = source width (m);
D
y
= dispersivity perpendicular to the direction of groundwater flow
(m);
t
1/2s
= decay half-life of contaminant in saturated zone of aquifer (years);
d = water table depth (m);
V = Darcy velocity in groundwater (m/year);
t
= total soil porosity (dimensionless) in the aquifer;
R
s
= retardation factor in saturated zone (dimensionless);
b
= dry soil bulk density in the aquifer (g/cm
3
);
K
oc
= organic carbon partition coefficient (mL/g); and,
f
oc
= fraction organic carbon (g/g) in the aquifer.
It should be noted that the decay half-life is assumed to be infinite unless a value has been
approved by the CCME. Most published half-life data reflect aerobic conditions or surface
water/surface soil, and may be unconservative for potentially anaerobic groundwater conditions.
Site-specific half-lives may be considered in a site-specific risk assessment.
For screening purposes, a series of distance-based “adjustment factors” have been calculated
using the above model, with all inputs set at the default values for Tier 1 with the exception of
distance to surface water. These adjustment factors are based on a chemical that does not
biodegrade (i.e. decay constant is set to 0); in the absence of biodegradation, the results are
independent of most soil properties and chemical properties. The adjustment factors were
calculated using the distance at the lower end of each range in the table below (e.g. the factor
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080
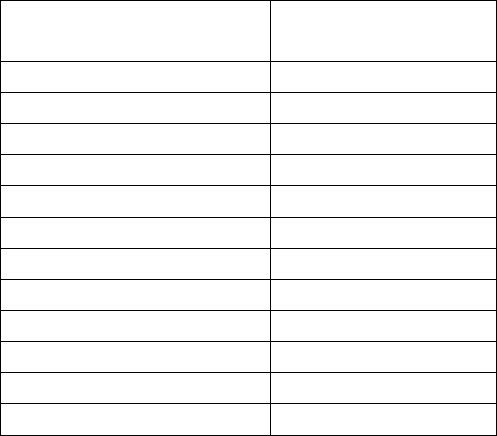
72
for 100-149 m is based on a distance of 100 m). The results are dependent on the plume width,
and therefore should not be applied for contaminant plumes that are significantly wider than the
Tier 1 default.
These adjustment factors can be applied by multiplying the generic guideline for the protection
of aquatic life by the factor for the distance to the nearest surface water body. These factors
could also be conservatively applied to biodegrading substances, although use of the full model
incorporating biodegradation would result in higher guidelines. For example, the Tier 1 guideline
for the protection of freshwater life for naphthalene is 0.0011 mg/L. If the nearest surface water
body is at least 250 m away, the guideline could be adjusted by a factor of 8.9, resulting in a
Tier 2 guideline for freshwater aquatic life of 0.0011 mg/L x 8.9 = 0.0098 mg/L.
Distance to Surface
Water (m)
Adjustment Factor
<50
1
50-74
1.9
75-99
2.75
100-149
3.6
150-199
5.4
200-249
7.1
250-299
8.9
300-349
10.6
350-399
12.4
400-449
14.2
450-499
16
500-1000
17.7
These adjustment factors should only be used at sites where the Tier 1 guidelines could be
applied, and are intended to serve as a preliminary screening-level approach for deriving site-
specific guidelines for the protection of aquatic life in situations where using the full Tier 2 model
may not be warranted. They could be conservatively applied for biodegrading as well as non-
biodegrading contaminants, but generally if a chemical has a biodegradation rate then a much
higher guideline can be derived using the full model.
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

73
B.4 Model Input Parameters
Table 4: Model Input Parameters for Human Receptor Characteristics
a
Parameter
Symbol
Infant
(0 – 6
mo)
Toddler
(7 mo - 4
y)
Child
(5 – 11
y)
Teen
(12 – 19 y)
Adult
(20+ y)
Body Weight (kg)
BW
8.2
16.5
32.9
59.7
70.7
Air Inhalation Rate
(m
3
/d)
IR
2.1
9.3
14.5
15.8
15.8
Water Ingestion
Rate (L/d)
WIR
0.3
0.6
0.8
1.0
1.5
a – from CCME 2006
Table 5: Soil and Hydrogeological Model Input Parameters
a
Parameter
Symbol
Soil Type
Coarse-
grained
Fine-
grained
Saturated Hydraulic Conductivity (m/y)
K
H
320
32
Hydraulic Gradient
i
0.028
0.028
Recharge (Infiltration rate) (m/y)
I
0.28
0.20
Organic Carbon Fraction (g/g)
foc
0.005
0.005
Soil Bulk Density (g/cm3)
ρ
b
1.7
1.4
Water Content (Mw/Ms)
M
W
/M
S
0.07
0.12
Total Soil Porosity
n
0.36
0.47
Vapour-Filled Porosity
θ
a
0.241
0.302
Moisture-Filled Porosity
θ
w
0.119
0.168
Soil Vapour Permeability (cm2)
k
v
6x10
-8
10
-9
a – from CCME 2008a
Table 6: Model Input Parameters for Site Characteristics
a
PARAMETER
SYMBOL
VALUE
Contaminant Source Width (m)
Y
10
Contaminant Source Depth (m)
Z
3
Contaminant Source Length (m)
X
10
Distance to Surface Water (m)
x
10
Distance to Potable Water User (m)
x
0
Distance to Agricultural Water User (m)
x
0
Distance from Groundwater to Building Slab (cm)
L
T
30
Depth to Groundwater (water table) (m)
d
3
Depth of unconfined aquifer (m)
d
a
5
a – from CCME 2006
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

74
Table 7: Model Input Parameters for Building
a
Parameter
Symbol
Residential
Basement
Residential
Slab-On-
Grade
Commercial
Slab-On-
Grade
Building Length (cm)
L
B
1225
1225
2000
Building Width (cm)
W
B
1225
1225
1500
Building Substructure Area (cm
2
)
A
B
2.7x10
6
1.5x10
6
3.0x10
6
Mixing Height (cm)
a
H
B
360
360
300
Thickness of Building Foundation
(cm)
L
crack
11.25
11.25
11.25
Depth Below Grade of Foundation
(cm)
Z
crack
244
11.25
11.25
Area of Crack (cm
2
)
A
crack
1790
994.5
1846
Length of Idealized Cylinder (cm)
X
crack
4900
4900
7000
Air Exchanges per Hour (1/h)
ACH
0.5
0.5
0.9
Pressure Differential (g/cm-s
2
)
ΔP
40
40
20
a – from CCME 2008a
Table 8: Model Input Parameters for Livestock and Wildlife Receptor Characteristics
a
Parameter
Symbol
Unit
Livestock
(Cow)
Wildlife
(Meadow
Vole)
Body Weight
BW
kg
550
0.017
Soil Ingestion Rate
SIR
kg/d
0.747
0.000058
Water Ingestion Rate
WIR
L/d
100
0.00357
a – from AESRD (2010a)
B.5 Chemical-Specific Parameters
A variety of chemical physical-chemical and toxicological parameters are also needed for
guideline calculation. The physical-chemical parameters applied to derive the generic guidelines
have been summarized in AESRD (2010a) and OMOE (2010). Human toxicological parameters
should be based on the latest guidance from Health Canada.
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080
75
REFERENCES
AESRD (Alberta Environment and Sustainable Resources Development). 2001. Salt
Contamination Assessment & Remediation Guidelines. Pub no.: T/606.
AESRD. 2010a. Alberta Tier 1 Soil and Groundwater Remediation Guidelines.
AESRD. 2010b. Alberta Tier 2 Soil and Groundwater Remediation Guidelines.
BC (British Columbia). 1996. BC Regulation 375/96: Contaminated Sites Regulation.
CCME (Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment). 1996. A Framework for Ecological
Risk Assessment: General Guidance. The National Contaminated Sites Remediation Program.
PN 1195.
CCME. 1997. A Framework for Ecological Risk Assessment: Technical Appendices. PN 1274.
CCME. 1999. Canadian Environmental Quality Guidelines. Canadian Council of Ministers of
the Environment. Publication No. 1299.
CCME. 2003. Guidance on the Site-Specific Application of Water Quality Guidelines in
Canada: Procedures for Deriving Numerical Water Quality Objectives.
CCME. 2006. A Protocol for the Derivation of Environmental and Human Health Soil Quality
Guidelines. PN 1332.
CCME. 2008a. Canada-Wide Standard for Petroleum Hydrocarbons (PHC) in Soil: Scientific
Rationale. Supporting Technical Document. PN 1399.
CCME. 2008b. Canada-Wide Standard for Petroleum Hydrocarbons (PHC) in Soil: User
Guidance. Prepared by O'Connor Associates Environmental Inc. (2001) and Meridian
Environmental Inc. (2001, 2007) for Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment. PN
1398.
Environment Canada. 2006. Ecological Risk Evaluation Framework for Federal Contaminated
Sites: Guidance for ERE Level 1 (Custodial Department Input Section). Version 2.2.
Hayashi, M. and Rosenberry, D. O. 2002. Effects of ground water exchange on the hydrology
and ecology of surface water. Ground Water 40(3): 309-316.
Health Canada. 2010. Federal Contaminated Site Risk Assessment in Canada, Part I:
Guidance on Human Health Preliminary Quantitative Risk Assessment (PQRA).
Health Canada. 2010. Federal Contaminated Site Risk Assessment in Canada, Part II: Health
Canada Toxicological Reference Values (TRVs).
Health Canada. 2010. Federal Contaminated Sites Risk Assessment in Canada Part V:
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080
76
Guidance on Human Health Detailed Quantitative Risk Assessment. Contaminated Sites
Division.
Health Canada. 2010. Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality. Federal-Provincial-
Territorial Committee on Drinking Water of the Federal-Provincial-Territorial Committee on
Health and the Environment.
OMEE (Ontario Ministry of Environment and Energy). 1997. Rationale for the Development and
Application of Generic Soil, Groundwater and Sediment Criteria for Use at Contaminated Sites
in Ontario. Standards Development Branch.
OMOE (Ontario Ministry of the Environment). 2010. Rationale for the Development of Soil and
Ground Water Standards for Use at Contaminated Site in Ontario.
US EPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency). 2008. Evaluating Ground-
Water/Surface-Water Transition Zones in Ecological Risk Assessments. Office of Solid Waste
and Emergency Response. EPA-540-R-06-072.
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080

77
www.ec.gc.ca
Additional information can be obtained at:
Environment Canada
Inquiry Centre
10 Wellington Street, 23rd Floor
Gatineau QC K1A 0H3
Telephone: 1-800-668-6767 (in Canada only) or 819-997-2800
Fax: 819-994-1412
TTY: 819-994-0736
Email: [email protected]c.ca
www.esdat.net
Esdat Environmental Database Management Software
+61 2 9232 8080
